Method for producing flat free contacting surface for semiconductor nanostructures
A technology of nanostructures and nanostructures, which is applied in the field of flattened nanostructures, and can solve problems such as inability to realize applications
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
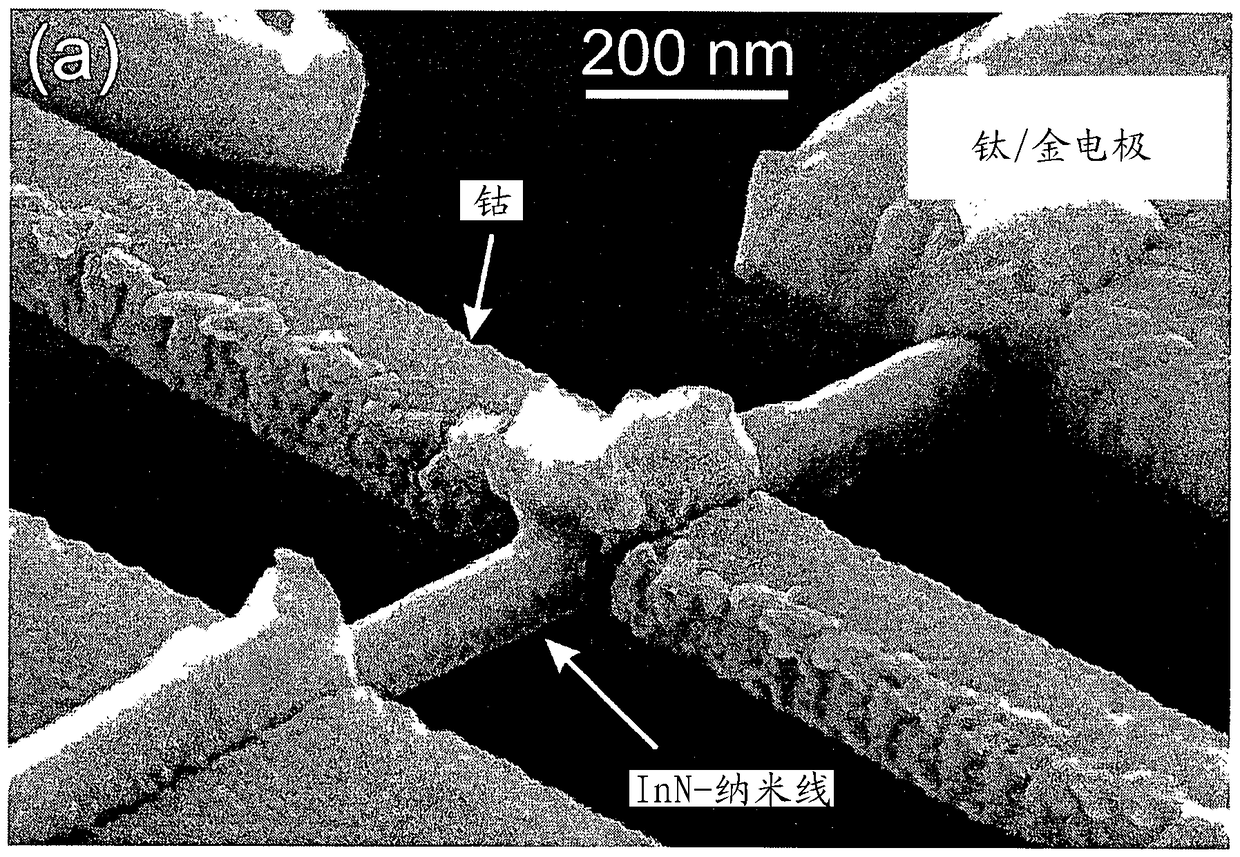
[0078] An unfavorable result that often occurs in conventionally evaporated nanowires with thin metal layers is identified in Fig. 1(a) with interruptions in the electrical contacts due to shadowing effects. In particular, ferromagnetic contacts, for example composed of cobalt, have a significant disturbance of the homogeneity of the magnetization, which is mandatory for several components of spintronics and is shown in Fig. 1(b) .
[0079] In Fig. 1(b), the calculated local magnetization is shown in cross-section along the cobalt contact surrounding this circular Nanowire cross-sections are laid. Here, the stated external magnetic field is applied along the main axis of the cobalt strip, ie perpendicular to the nanowire and parallel to the substrate.
[0080] Arrows inside cobalt contacts: local orientation of magnetic moments;
[0081] Highlighted in grey: localized magnetization points mostly to the right
[0082] Bright area: localized magnetization points mostly to th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com