Process of recycling platinum-rhenium aluminum from platinum-rhenium waste catalyst of alumina carrier
A waste catalyst and catalyst technology, applied in the field of extracting platinum, rhenium and aluminum, can solve the problems of low recovery rate, complex process, large amount of waste water, etc., and achieve the effects of short process, simple operation and high recovery rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0044] Example 1: The aluminum carrier is leached as follows:
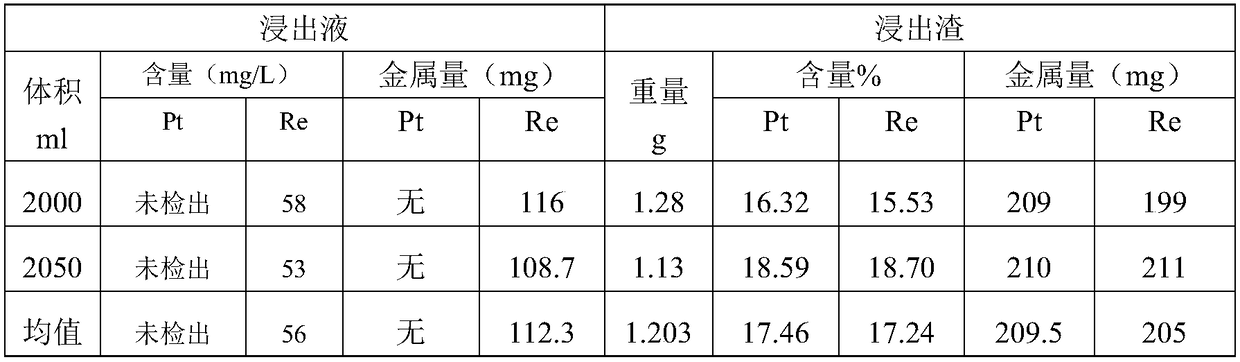
[0045] After the roasting, the catalyst 100g containing 0.21mass% of platinum and 0.32mass% rhenium of the aluminum support was added with 1760ml of water, 240ml of concentrated sulfuric acid, and the temperature was raised and maintained at 100°C for 2 hours, then 10ml of ammonium sulfide (10% content solution) was added, and kept at 30 minutes, add 10ml flocculant (containing 1% polyacrylamide) and keep for 10 minutes, stop stirring and add water to make up the total volume of 2000ml, and filter after standing for 24 hours.
[0046] The results are as follows: (100g of input material weight, 210mg of platinum metal input, and 320mg of rhenium metal input)
[0047]
[0048] Conclusion: It can be seen from the above data that 1. All platinum enters the slag and is enriched. 2. Part of the rhenium enters the leaching solution. The rest all enter the slag for enrichment.
example 2
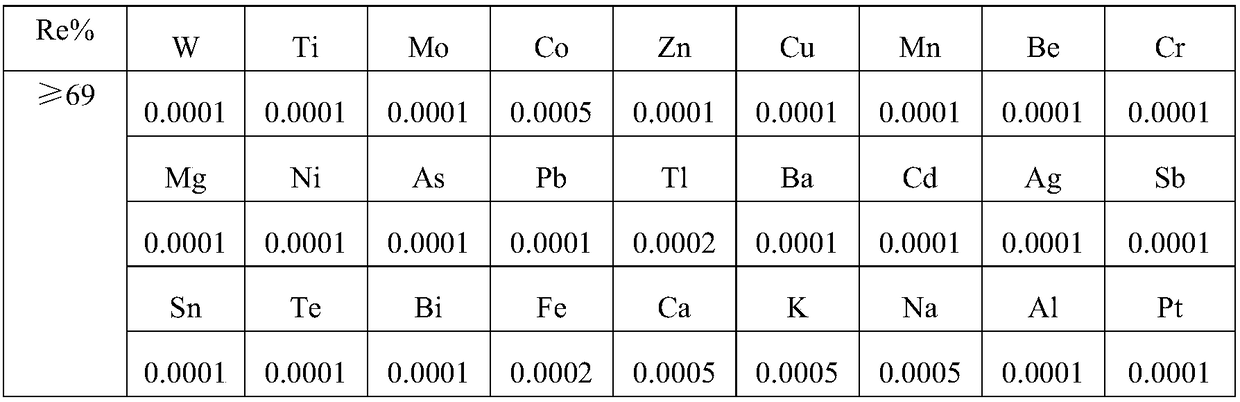
[0049] Example 2: R410 anion exchange resin adsorbs and desorbs rhenium-containing platinum-rhenium spent catalysts on rhenium-aluminum carriers and is leached with sulfuric acid. The main components of a batch of leachate are as follows:
[0050] Platinum content
Aciditymol / L
Rhenium content (mg / L)
Aluminum content (g / L)
SO 4 2-(g / L)
not detected
0.77
61
26
216
[0051] The above solution is adsorbed rhenium by R410 resin, the solution flow rate is 1 times the resin volume per hour, the resin column is a plexiglass column filled with 100ml resin, the two columns are connected in series, when the volume of the inflow solution is 160L The content of rhenium is equivalent, and the rhenium in the first column is saturated, and the calculation shows that the rhenium co-adsorbed in the first column is 0.061×160=9.76g. That is, the saturated adsorption capacity of rhenium adsorbed by R410 resin is 9.76g / 100ml resin.
[0052] After ...
example 3
[0056] Example 3: Recovery and refining of rhenium and platinum
[0057] Refining of rhenium:
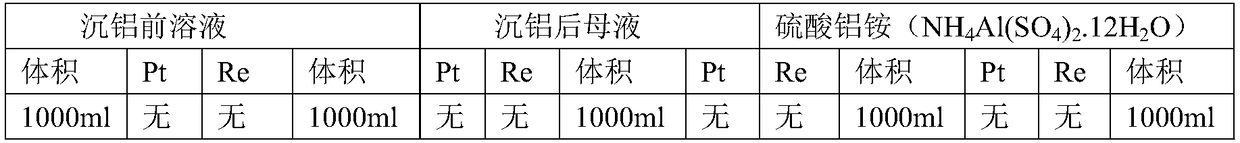
[0058] 1. the first 300ml analysis solution that obtains among the example 2 is concentrated to solution containing rhenium 80g / L after adjusting PH7 with ammoniacal liquor, then removes the ammonium perrhenate that freezing crystallization becomes crude product. ② Add lime to the leaching slag in Example 1 at 700°C for 3 hours at a ratio of 1:1, and then add water for leaching at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:3. The leaching solution is a rhenium-containing solution containing about 20-30g / L rhenium. The leaching slag is water leaching platinum-containing slag. ③The leaching solution directly enters the 001×7 cation exchange column for refining, and the crude product ammonium perrhenate is dissolved in water (concentration 60g / L) and then enters the 001×7 cation resin to remove cations such as calcium and ammonium, and after flowing out, the perrhenic acid solution is Neutralize w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com