Superhydrophobic multifunctional membrane and preparation method and application thereof in oil-water separation
A multi-functional, super-hydrophobic technology, applied in the direction of semi-permeable membrane separation, liquid separation, separation methods, etc., can solve the problems of limited application, no hydrophobic and lipophilic properties, and inability to selectively separate oil-water mixtures, so as to avoid uneven distribution , good reusability, beneficial to separation efficiency and cycle efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] The preparation of the non-woven fabric modified by perfluorodecyl trichlorosilane, the specific steps are as follows:
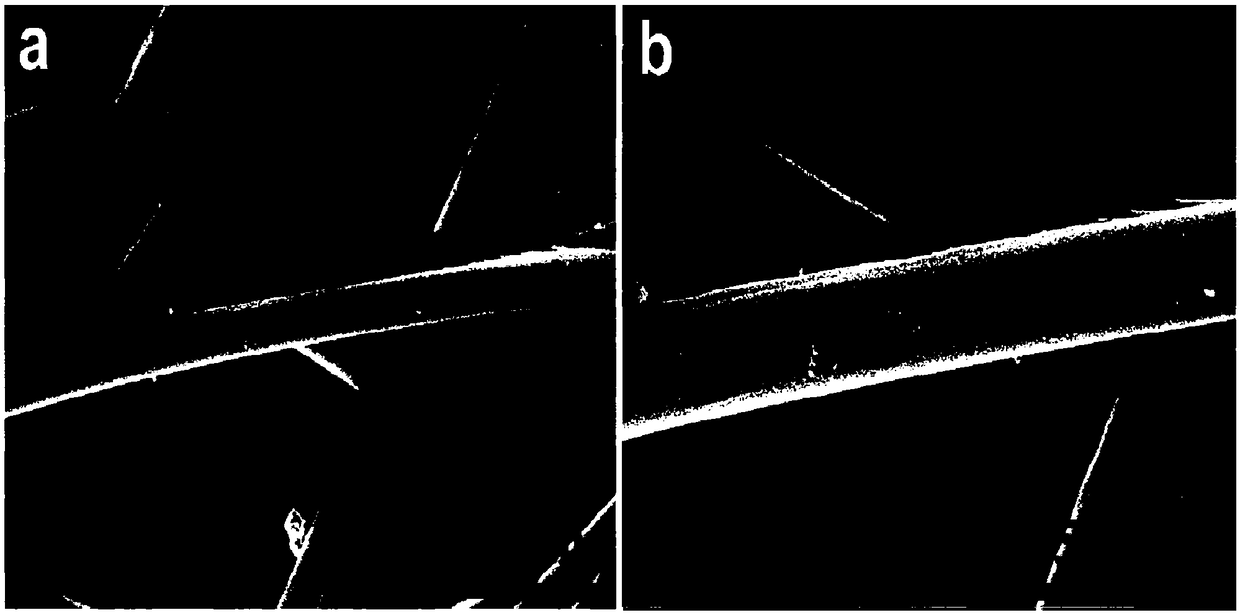
[0038] Wash the polypropylene non-woven fabric with ethanol and acetone to remove surface impurities, then put the cleaned non-woven fabric into 10% hydrochloric acid to acidify it, and then place the non-woven fabric material horizontally on a perfluorinated In the crystallization dish of decyltrichlorosilane (POTS), POTS vapor diffuses and reacts on the bottom surface of the non-woven fabric film through the silanization reaction between POTS and the hydroxyl groups on the non-woven fabric, and reacts at room temperature for 2 hours to form a hydrophobic one side;
[0039] figure 1 It is the SEM picture of the above-mentioned perfluorodecyltrichlorosilane modified non-woven fabric, a and b are different ratios.
Embodiment 2
[0041] The preparation of superhydrophobic multifunctional membrane, the specific steps are as follows:
[0042] In Example 1, the hydrophilic side of the non-woven fabric modified with perfluorodecyltrichlorosilane was modified with methacryloxypropyltrimethoxysilane (TMSPMA): the fabric sample was immersed in the mixture of TMSPMA, acetic acid and THF (respectively 2.0 mL, 0.06 mL and 18.0 mL), the mixture was stirred and heated at 70°C for 4 hours, then the fabric was desolventized and air-dried; then the fabric was heated at 100°C for 40 hours to form a sol-gel layer, followed by To graft poly N,N-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate (PDMAEMA), that is, to graft PDMAEMA, the TMSPMA-modified fabric was immersed in a mixture consisting of 2.64 g DMAEMA and 15.0 mL THF by bubbling the solution with nitrogen Deoxidize for 10 minutes, inject 0.066g of AIBN 5.0mLTHF into the deoxygenated solution, then heat at 65°C for 24 hours with stirring to polymerize DMAEMA, take out the non-wov...
Embodiment 3
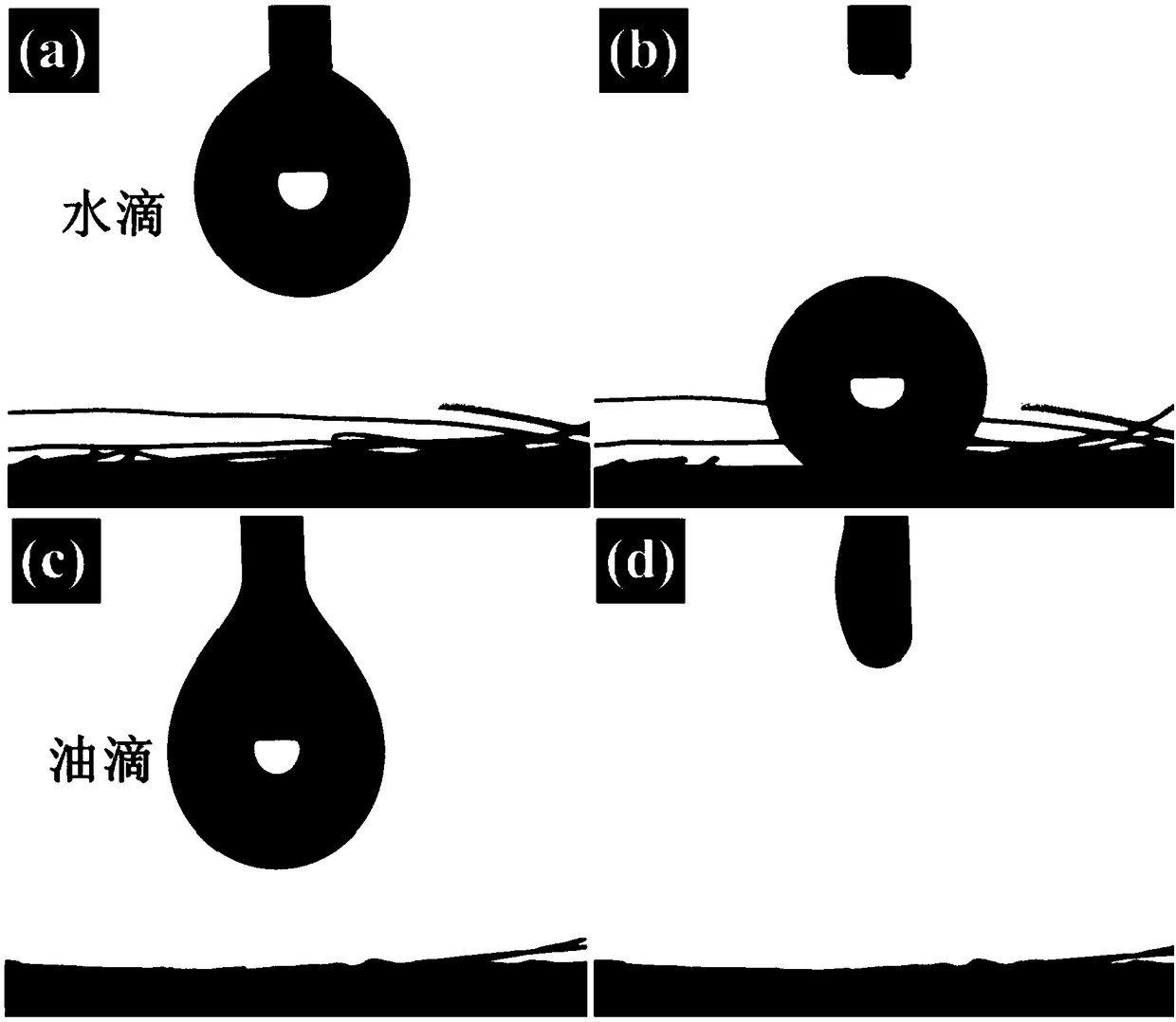
[0044] Example 3 The wettability behavior of the modified stainless steel mesh
[0045] attached image 3 The wettability behavior of POTS and PRMAEMA modified non-woven fabrics (superhydrophobic multifunctional membrane) to water and oil, a, b are the contact angles of water in air, c, d are the wettability of oil droplets in air Behavior; Through comparison, it can be seen that the water droplets on the modified POTS side form a spherical water droplet on the surface, indicating that it has good hydrophobic properties, while the modified PDMAEMA side shows good affinity for water and oil.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com