A kind of lysate and method for extracting meat nucleic acid
A technology for lysing liquid and meat, applied in the field of lysing liquid for extracting nucleic acid from meat, can solve the problems of long operation time, high cost, human harm, etc., and achieve the effects of no toxic side effects, low source cost, and guaranteed release.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] In order to determine the optimal concentration of the four components (sodium chloride, sodium dodecylsulfonate, ethylphenyl polyethylene glycol, polyvinylpyrrolidone) in the lysate, it was decided to use L 9 (3 4 ) to formulate the experimental scheme, and use the range analysis method to obtain the optimal concentration of the four components in the lysate. See Table 1 for their factor levels.
[0045] Table 1
[0046]
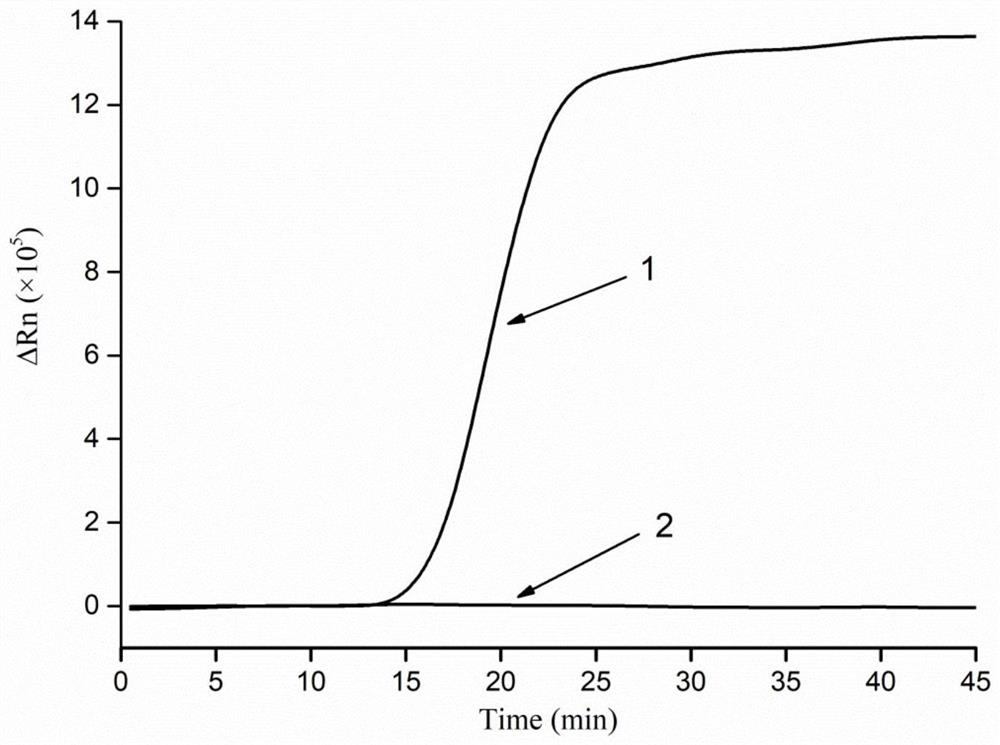
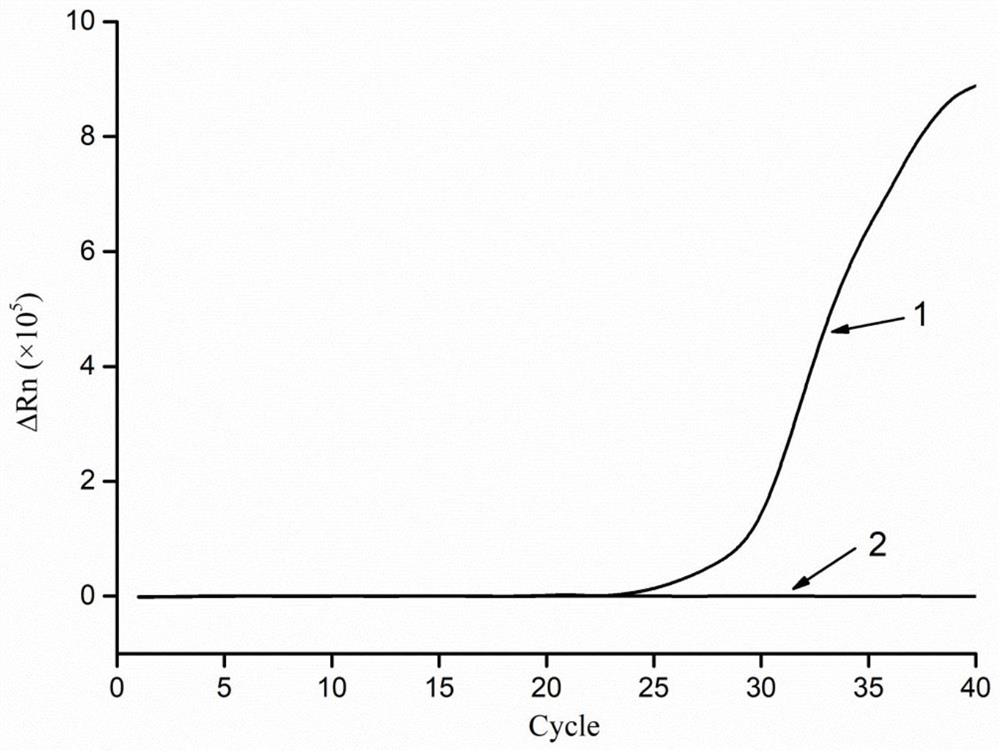
[0047] In the experiment, pork was used as a sample to conduct an orthogonal experiment. The mass volume ratio of pork and lysate was fixed at 2:3g / ml. The sample and lysate were mixed and allowed to stand for 1 min, then fixed at 8000 rpm and centrifuged for 1 min. Finally, 50-fold dilutions were uniformly performed with TE buffer to obtain nucleic acid extracts. C according to the real-time fluorescent PCR reaction t Value (the initial number of cycles that can detect the fluorescent signal in the PCR reaction) to determine the nucleic acid ...
Embodiment 2
[0060] After determining the optimal concentration of the four components in the lysate, it is also necessary to determine the mass-to-volume ratio of the sample to the lysate (unit: g / ml), the resting time after mixing the sample and the lysate, and the ability to separate nucleic acids from impurities Three factors such as the optimal rotational speed of the tester (the dilution factor of the nucleic acid extract is finally determined). In order to reduce the number of trials as much as possible, it is still decided to use L 9 (3 4 ) to formulate the experimental program, and use the range analysis method to obtain the best conditions of these three factors. See Table 3 for their factor levels. The letters A, B, and C in the table represent the mass-volume ratio of the sample to the lysate, the resting time, and the centrifugation speed, respectively.
[0061] table 3
[0062]
[0063] In the experiment, pork was used as a sample to carry out an orthogonal experiment,...
Embodiment 3
[0070] First, mix 100 mg of fresh pork with 150 μL of lysate (0.6M sodium chloride, 0.6 g / ml sodium dodecyl sulfate, 0.1 g / ml ethyl phenyl polyethylene glycol, 0.05 g / ml polyvinylpyrrolidone) and mix well, and let stand at room temperature for 2 minutes; then, centrifuge at 10,000 rpm for 1 minute, absorb the supernatant to obtain nucleic acid extract, and use PCR to determine the nucleic acid extraction effect.
[0071] Pork PCR amplification system, amplification program and amplification sequence are the same as in Example 1.
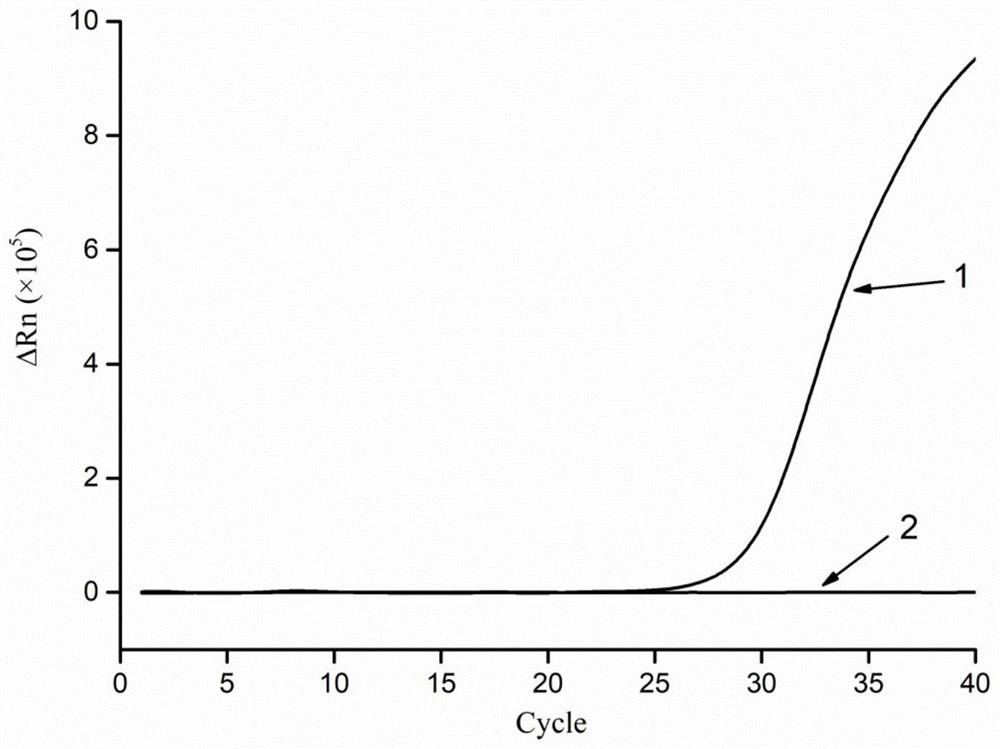
[0072] Dilute the nucleic acid extract 20 times with TE buffer solution as a PCR reaction template for amplification to obtain a fluorescence amplification curve figure 1 .
[0073] The results show: figure 1 The positive samples produced amplification curves, and the negative samples did not produce amplification, indicating that the nucleic acid extraction method can effectively extract the nucleic acid in pork, and can be detected by PCR reactio...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com