3D bioprinting nano cellulose hydrogel ink
A nanocellulose, bioprinting technology, applied in inks, drug delivery, applications, etc., can solve the problem of adsorption and encapsulation of cells, inefficiency in transporting nutrients and excretion of metabolites, mechanical properties of hydrogel inks, and biocompatibility. In order to achieve the effect of good cell adhesion, low price and good biodegradability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
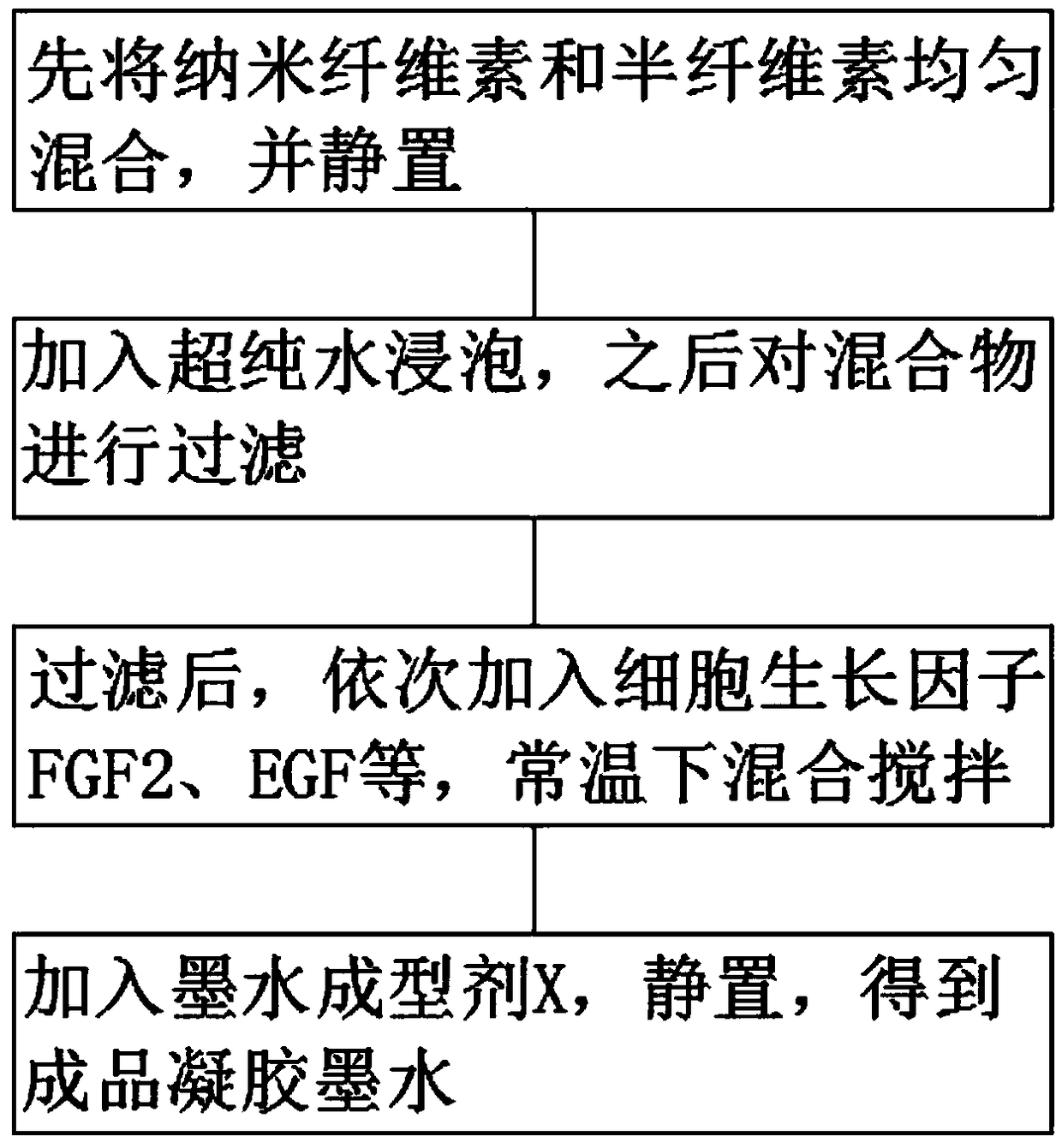
[0025] A 3D bioprinting nanocellulose hydrogel ink is made from the following components in parts by weight: 1100 parts of nanocellulose, 900 parts of hemicellulose, 1250 parts of ultrapure water, 380 parts of cell growth factor FGF2, and 175 parts of EGF , 225 copies of VEGF, 315 copies of collagen, 165 copies of fibrinogen, 60 copies of hyaluronic acid, and 700 copies of ink forming agent.
[0026] The preparation method of 3D bioprinting nanocellulose hydrogel ink includes the following steps:
[0027] (1) First, uniformly mix nanocellulose and hemicellulose, and let stand to obtain a mixture, stir with a glass rod, control the temperature at 60 °C, and let stand for 5 hours;
[0028] (2), adding ultrapure water to the mixture obtained in step (1) and soaking, then filtering the mixture, soaking for 1.5h, and controlling the temperature at 23°C;
[0029] (3) After filtering the mixture, add cell growth factors FGF2, EGF, VEGF, collagen, fibrinogen and hyaluronic acid in se...
Embodiment 2
[0032] A 3D bioprinting nanocellulose hydrogel ink is made from the following components in parts by weight: 1100 parts of nanocellulose, 900 parts of hemicellulose, 1250 parts of ultrapure water, 380 parts of cell growth factor FGF2, and 175 parts of EGF , 225 copies of VEGF, 315 copies of collagen, 165 copies of fibrinogen, 60 copies of hyaluronic acid, and 700 copies of ink forming agent.
[0033] The preparation method of 3D bioprinting nanocellulose hydrogel ink includes the following steps:
[0034] (1) First, uniformly mix nanocellulose and hemicellulose, and let stand to obtain a mixture, stir with a glass rod, control the temperature at 65 °C, and let stand for 5 hours;
[0035] (2), adding ultrapure water to the mixture obtained in step (1) and soaking, then filtering the mixture, soaking for 1.5h, and controlling the temperature at 23°C;
[0036] (3) After filtering the mixture, add cell growth factors FGF2, EGF, VEGF, collagen, fibrinogen and hyaluronic acid in tu...
Embodiment 3
[0039] A 3D bioprinting nanocellulose hydrogel ink is made of the following components by weight: 1100 parts of nanocellulose, 900 parts of hemicellulose, 1250 parts of ultrapure water, 380 parts of cell growth factor FGF2, and 175 parts of EGF , 225 copies of VEGF, 315 copies of collagen, 165 copies of fibrinogen, 60 copies of hyaluronic acid, and 700 copies of ink forming agent.
[0040] The preparation method of 3D bioprinting nanocellulose hydrogel ink includes the following steps:
[0041] (1) First, uniformly mix nanocellulose and hemicellulose, and let stand to obtain a mixture, stir with a glass rod, control the temperature at 70 ° C, and let stand for 5 hours;
[0042] (2), adding ultrapure water to the mixture obtained in step (1) and soaking, then filtering the mixture, soaking for 1.5h, and controlling the temperature at 23°C;
[0043] (3) After filtering the mixture, add cell growth factors FGF2, EGF, VEGF, collagen, fibrinogen and hyaluronic acid in turn, mix at...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com