Primer group and kit for detecting polymorphic sites of aspirin-resistant related genes, and application thereof
An aspirin and polymorphic site technology is applied in the field of primer sets and kits for detecting aspirin resistance-related gene polymorphic sites, which can solve the problems of easy contamination, time-consuming, complicated operation, etc., achieve easy results and avoid calculation , The signal is clear, accurate and stable
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0102] Embodiment 1 primer / probe sequence selection
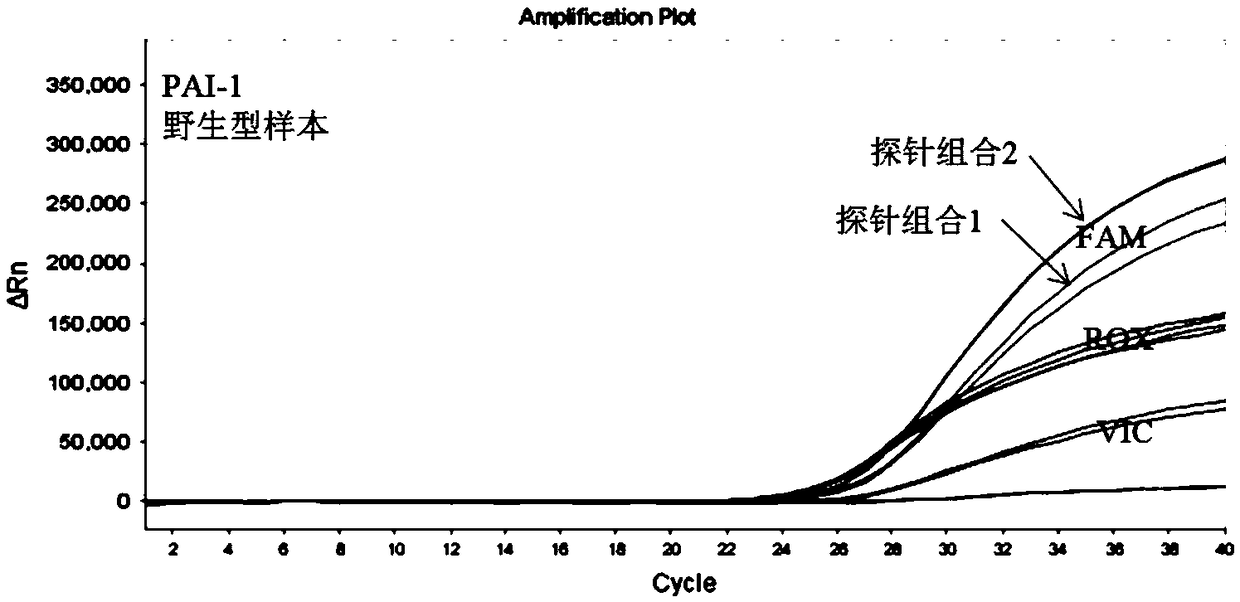
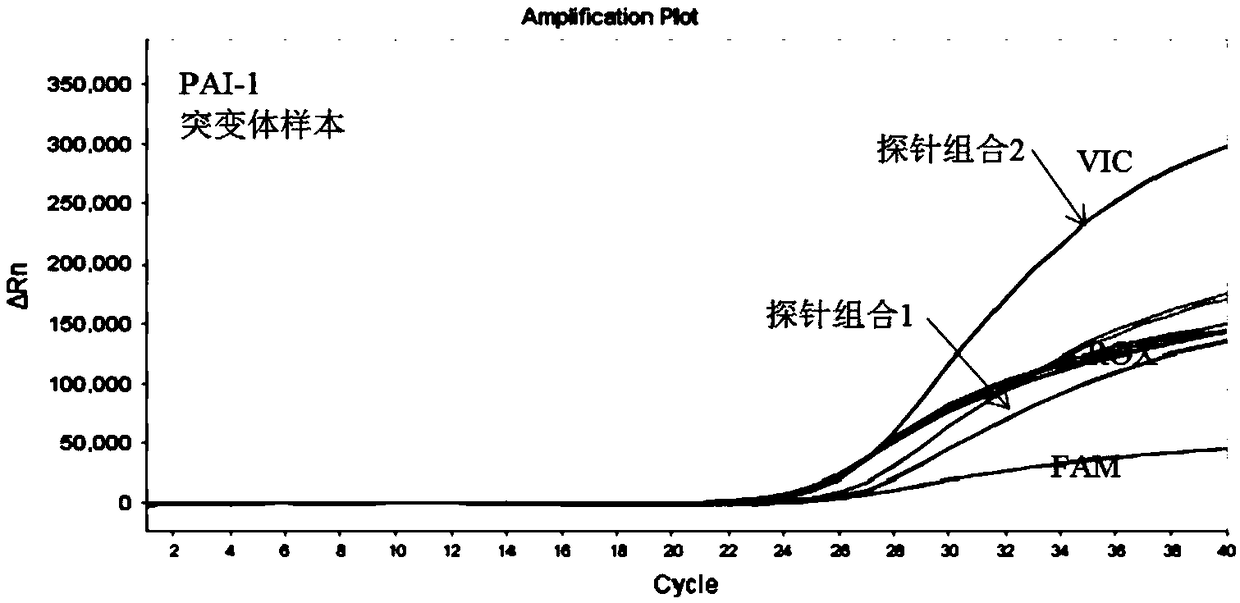
[0103] According to the sequence characteristics of SNP, 3 sets of primers and 5 sets of probes were designed, and PCR systems were prepared respectively. Use the above system to detect wild-type and mutant genomic DNA samples, and compare the differences in amplification performance between different primer-probe combinations. The results are as follows: figure 1 with figure 2 as shown, figure 1 It is the result graph of wild-type samples amplified by different probe sequences of PAI-1 gene, figure 2 It is the result graph of amplifying mutant samples with different probe sequences of PAI-1 gene. After a large number of screening experiments, the best primer-probe combination (probe combination 2), that is, the combination of SEQ ID NO.25 / SEQ ID NO.26 primer pair and SEQ ID NO.27 / SEQ ID NO.28 probe pair was obtained The composed PCR system has the best performance among all the combinations, showing good specificit...
Embodiment 2
[0104] Embodiment 2 different dosages of probes are selected
[0105] The probe uses FAM fluorescence and VIC fluorescence to monitor the amplification of the target sequence in real time. Probe concentration directly affects the value of the amplified fluorescence signal. When the probe concentration is low, the fluorescence signal value is low. When the probe concentration is high, the fluorescence signal is high, and the non-specific signal is also high.
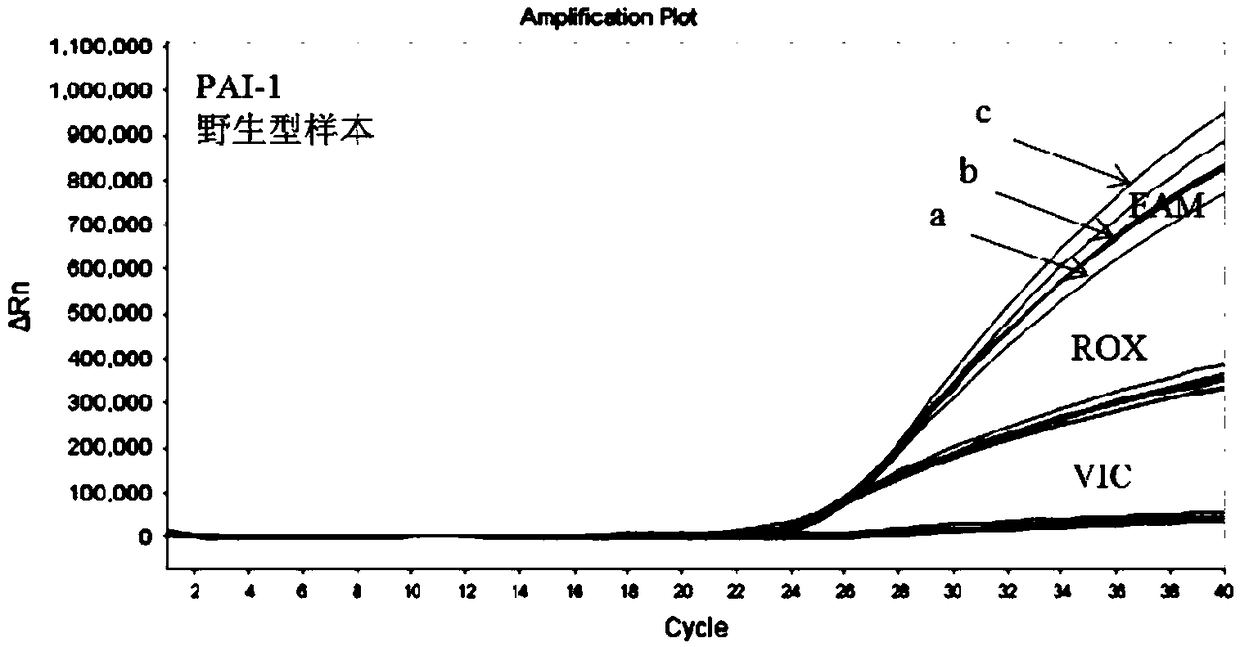
[0106] On the basis of the optimal primer-probe combination screened above, the system performance was further optimized by adjusting the probe concentration. Set 3 probe concentrations (a: 0.1 μM, b: 0.2 μM, c: 0.3 μM)
[0107] Prepare the PCR reaction system separately. Use the above system to detect wild-type and mutant genomic DNA samples, and compare the difference in amplification performance under different probe concentrations. Test results such as image 3 with Figure 4 As shown, among them, image 3 The r...
Embodiment 3
[0109] Example 3 PCR buffer component optimization
[0110] Usually, repeated sequences (especially >3 G repeats) near the SNP site will reduce the ability of the probe to recognize the target SNP site. Due to the presence of repetitive sequences, the target detection gene PAI-1 (4G>5G) has poor specificity and cannot tolerate high concentration (eg 300ng / μL) genomic samples. The specificity could not be improved by adding conventional dimethyl sulfoxide, so a new sulfur-containing organic compound, tetramethylene sulfoxide, was added to the PCR buffer instead. The performance of tetramethylene sulfoxide in improving PCR specificity is stronger than that of dimethylene sulfoxide, but it is particularly critical to accurately select its optimal concentration. If the amount of tetramethylene sulfoxide is too large, it will easily inhibit PCR, and if the amount is too small, the effect of improving system specificity is limited. Therefore, the optimal concentration of this comp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com