A kind of recycling method of metal indium in waste liquid crystal screen
A recycling method and liquid crystal screen technology, applied in the field of circular economy, can solve problems such as complex sources of liquid crystal materials, difficulty in peeling off polarizers, difficulty in controlling non-indium metal ions, etc., achieving significant economy, easy industrial production, and avoiding the interference of impurity metals Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
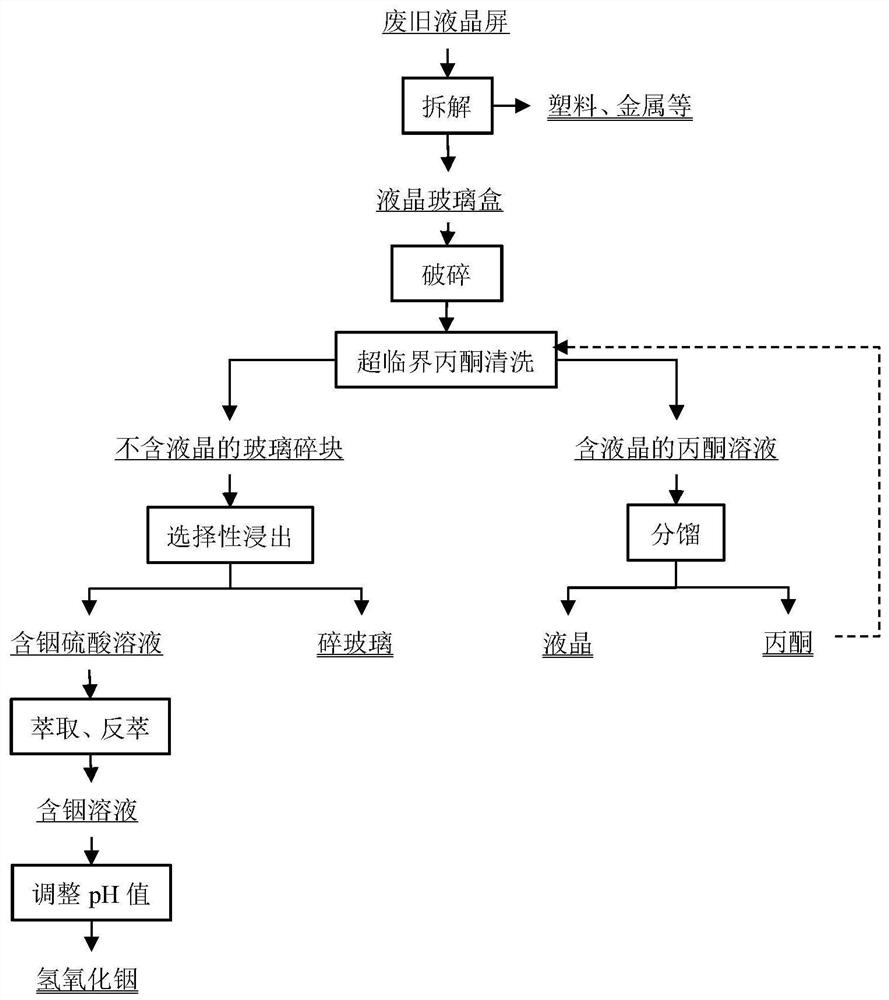
[0025] Disassemble waste LCD screens, separate out LCD glass boxes, and recycle plastic and metal materials. The liquid crystal glass cell was broken into small pieces of 10 cm using a shear shredder. The crushed material is mixed with acetone and then added to the supercritical reactor. The liquid-solid ratio of acetone to material is 30:1. Heat the reactor to 400°C, the reaction pressure is 8MPa, and keep it warm for 30min. After heat preservation, the reactor was cooled to room temperature and the materials were taken out. After filtration, an acetone solution containing liquid crystals and glass fragments without liquid crystals were obtained. The acetone solution containing liquid crystals is fractionally distilled to obtain liquid crystals and acetone, and the acetone can be reused. Use 2.0mol / L hydrochloric acid solution to carry out acid leaching on the glass fragments not containing liquid crystal, the liquid-solid ratio of hydrochloric acid to material is 8:1, the...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Disassemble waste LCD screens, separate out LCD glass boxes, and recycle plastic and metal materials. The liquid crystal glass cell was broken into small pieces of 1 cm using a shear shredder. The crushed material is mixed with acetone and then added to the supercritical reactor. The liquid-solid ratio of acetone to material is 10:1. Heat the reactor to 260°C, the reaction pressure is 4MPa, and keep it warm for 120min. After heat preservation, the reactor was cooled to room temperature and the materials were taken out. After filtration, an acetone solution containing liquid crystals and glass fragments without liquid crystals were obtained. The acetone solution containing liquid crystals is fractionally distilled to obtain liquid crystals and acetone, and the acetone can be reused. Use 8.0mol / L hydrochloric acid solution to carry out acid leaching on the glass fragments not containing liquid crystal, the liquid-solid ratio of hydrochloric acid to material is 15:1, th...
Embodiment 3
[0029] Disassemble waste LCD screens, separate out LCD glass boxes, and recycle plastic and metal materials. Use a shear shredder to break the liquid crystal glass cell into small pieces of 5 cm. Mix the crushed material with acetone and add it to the supercritical reactor. The liquid-solid ratio of acetone to material is 20:1. Heat the reactor to 300°C, the reaction pressure is 6MPa, and keep the temperature for 90min. After heat preservation, the reactor was cooled to room temperature and the materials were taken out. After filtration, an acetone solution containing liquid crystals and glass fragments without liquid crystals were obtained. The acetone solution containing liquid crystals is fractionally distilled to obtain liquid crystals and acetone, and the acetone can be reused. Use 5.0mol / L hydrochloric acid solution to carry out acid leaching on the glass fragments not containing liquid crystal. The liquid-solid ratio of hydrochloric acid to material is 10:1, the acid...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com