Method for effectively removing magnesium ions in zinc sulfate solution of electrolytic zinc
A technology of zinc zinc sulfate, magnesium ion, applied in the direction of zinc sulfate, improvement of process efficiency, magnesium halide, etc., can solve the problems of difficulty in solid-liquid separation, increased loss of zinc and fluorine, easy clogging of filter cloth and filter screen, etc. The effect of simple magnesium process, reducing zinc content and improving fluorine utilization rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] In the zinc sulfate liquid of present embodiment 1, Mg 27.71 g / L, Zn 146.22 g / L, F11.6mg / L.
[0039] A method for effectively removing magnesium ions in an electrolytic zinc-zinc sulfate solution is characterized in that it comprises the following steps:
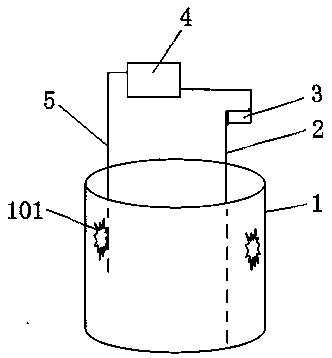
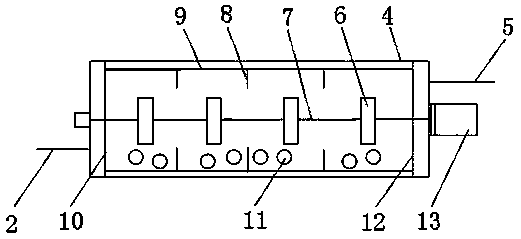
[0040] A) Magnesium fluoride precipitation, the magnesium precipitation fluoride is completed in the device with the patent number 201710215324.0 previously applied by the applicant, such as figure 1 , figure 2 As shown, the structure of the device includes: a cylinder 4 communicated with the reaction tank 1, the inner wall of the reaction tank 1 is provided with an ultrasonic shock plate 101 connected to the ultrasonic generator, the cylinder 4 is provided with a cavity, and the cylinder 4 is provided with The inlet and outlet connected to the cavity are connected to the reaction tank 1 through the feed pipe 2, the pump 3, and the discharge pipe 5 respectively. The cylinder 4 is provided with a stirring shaft 7 wit...
Embodiment 2
[0052] In the zinc sulfate liquid of present embodiment 2, Mg 21.89 g / L, Zn 148.41 g / L, F12.54mg / L.
[0053] A method for effectively removing magnesium ions in an electrolytic zinc-zinc sulfate solution is characterized in that it comprises the following steps:
[0054] A) magnesium fluoride precipitation, the magnesium precipitation fluoride is completed in the device with the patent number 201710215324.0 previously applied by the applicant, and the device is as in Example 1;
[0055] Utilize this device to carry out magnesium fluoride precipitation specifically as follows:
[0056] A1) In the zinc sulfate liquid in the reaction tank 1, add hydrofluoric acid according to the mass ratio of Mg: HF = 24: 38, and add alkaline zinc-containing materials at the same time until the pH of the zinc sulfate liquid is 5.2, so that the alkaline containing The zinc in the zinc material and the magnesium ion in the zinc sulfate solution undergo a displacement reaction to generate a magnes...
Embodiment 3
[0066] In the zinc sulfate liquid of present embodiment 3, Mg 29.43 g / L, Zn 152.70 g / L, F16.06mg / L.
[0067] A method for effectively removing magnesium ions in an electrolytic zinc-zinc sulfate solution is characterized in that it comprises the following steps:
[0068] A) Magnesium fluoride precipitation, the magnesium precipitation fluoride is completed in the device with the patent number 201710215324.0 previously applied by the applicant, and the structure of the device is as in Example 1;
[0069] Utilize this device to carry out magnesium fluoride precipitation specifically as follows:
[0070] A1) In the zinc sulfate liquid in the reaction tank 1, according to the mass ratio of Mg: HF = 24: 36, add hydrofluoric acid, and add alkaline zinc-containing materials at the same time until the pH of the zinc sulfate liquid is 4, so that the alkaline containing The zinc in the zinc material and the magnesium ion in the zinc sulfate solution undergo a displacement reaction to gen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com