Microbial curing-fiber reinforcement combined sandy soil modification method
A fiber-reinforced and microbial technology, applied in soil protection, construction, infrastructure engineering, etc., can solve problems such as matrix toughness and overall strength, and achieve the effects of improving planting problems, reducing adverse effects, and reducing emissions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] MICP-basalt fiber joint reinforcement of quartz sand
[0050] 1) Prepare sand for sample loading, take a certain amount of quartz sand, add 10% water by mass fraction and mix well, then disperse basalt fibers according to 0-1.2% by mass percentage and mix them into each sample, and stir until uniform. For sample loading, add the sand into a cylindrical mold with a height of 7.5cm and a diameter of 3.7cm in layers during the sand filling process, and carry out a compaction operation for each filling of sand with a thickness of 2.5cm. After the operation is completed, the entire sample Weigh to ensure that the weight error of each sample does not exceed 1%, otherwise sample preparation is performed again to ensure that the compactness of each sample is the same, until the sample is completed, and the sample is numbered.
[0051] 2) Bacterial activation, first configure the required ATCC 1376 NH 4 -YE microbial liquid medium, medium (1L) formula is: yeast extract 20g, amm...
Embodiment 2
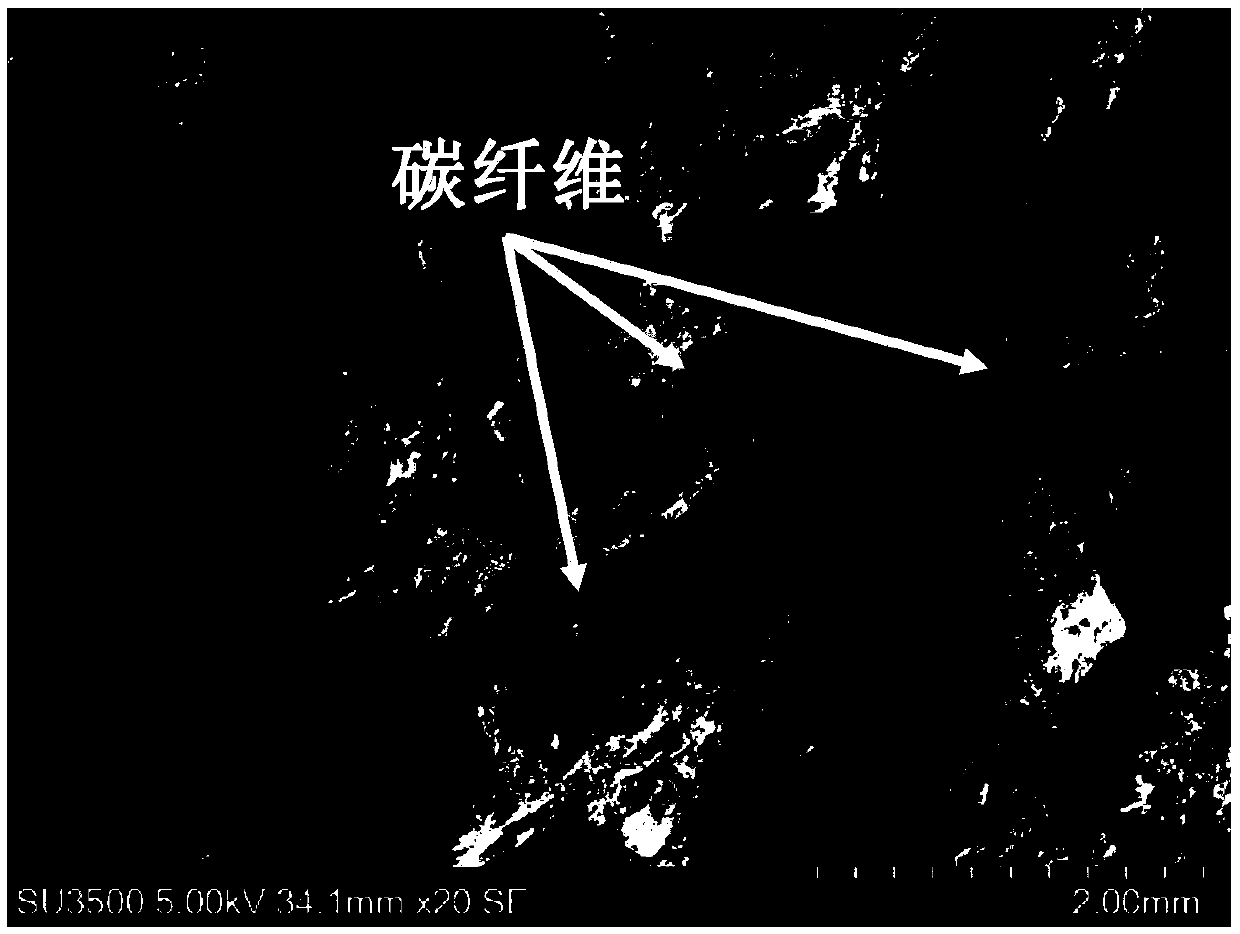
[0064] MICP-Carbon Fiber Jointly Reinforced Quartz Sand
[0065] In this embodiment, the steps are basically the same as in Embodiment 1, the difference is that:
[0066] In the sand preparation and sample loading step, the basalt fibers in Example 1 were replaced with carbon fibers and dispersed and mixed into each sample according to 0-0.8% by mass.
[0067] The carbon fiber density is 1.78g / cm 3 , diameter 0.01mm, tensile strength 3500 ~ 5000MPa, elastic modulus 240GPa, melting point 400 ℃, good acid and alkali resistance, good dispersion.
[0068] The unconfined compression test results of the sand samples after curing are shown in the table below:
[0069] Table 3 Unconfined compressive strength of sand samples with different carbon fiber content
[0070]
[0071] Table 4 Residual strength of sand samples with different carbon fiber content
[0072]
[0073] The test results show that the strength of the sand sample reinforced with carbon fiber is improved compare...
Embodiment 3
[0076] MICP-steel fiber joint reinforcement of quartz sand
[0077] In this embodiment, the steps are basically the same as in Embodiment 1, the difference is that:
[0078] In the sand preparation and sample loading step, the basalt fibers in Example 1 were replaced with steel fibers and dispersed and mixed into each sample according to 0-3.2% by mass.
[0079] The steel fiber density is 7.9g / cm 3 , diameter 0.2mm, tensile strength ≥ 2850MPa, excellent dispersion.
[0080] The unconfined compression test results of the sand samples after curing are shown in the table below:
[0081] Table 5 Unconfined compressive strength of sand samples with different steel fiber content
[0082]
[0083] Table 6 Residual strength of sand samples with different steel fiber content
[0084]
[0085] The test results show that the strength of the sand sample reinforced with steel fiber is improved compared with that of the plain soil after curing, and the strength of the sample incre...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com