Method for treating arsenic in non-ferrous smelting waste acid by using iron-rich copper slag
A technology of copper slag and dirty acid, which is applied in the field of heavy metal pollution control and metallurgical solid waste utilization, can solve the problems of toxic elements polluting the environment, difficult to recycle and apply, difficult to stockpile, etc., to achieve simple operation process, good arsenic removal effect, The effect of low economic cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Example 1: The method for treating non-ferrous smelting sewage acid with the iron-rich copper slag is as follows:
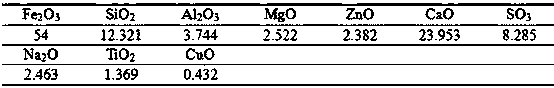
[0023] 1. Press H 2 O 2 The molar ratio with arsenic is 1:1, and the H 2 O 2 Mixed with non-ferrous smelting acid, and oxidizing pretreatment at a temperature of 60°C for 3h; among them, the non-ferrous smelting acid is from a copper smelting plant in the southwestern region after washing the smelting flue gas and containing a large amount of arsenic and other impurities. , The main components are shown in Table 1; the copper slag is dried and ground, and the particle size is controlled below 0.070 mm (the composition of the copper slag is shown in Table 2);
[0024] Table 1
[0025] ;
[0026] Table 2
[0027]
[0028] 2. Mix the oxidized pretreated acid and iron-rich copper slag in a ratio of 5:1 liquid-solid ratio mL:g, and stir for 24h under normal pressure for arsenic removal reaction at a stirring speed of 180r / min; solid-liquid separation , Obtain arsenic-...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Example 2: The method for treating non-ferrous smelting sewage acid with the iron-rich copper slag is as follows:
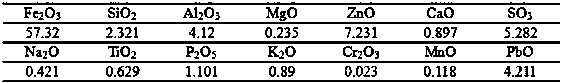
[0031] 1. Press H 2 O 2 The molar ratio with arsenic is 1.2:1, and the H 2 O 2 It is mixed with non-ferrous smelting waste acid, and oxidized and pretreated at a temperature of 70°C for 2.5 hours; among them, the non-ferrous smelting waste acid is from a copper smelting plant in the southwestern region after washing the smelting flue gas with a large amount of arsenic and other impurities. Acid, the main components are shown in Table 1; the copper slag is dried and ground, and the particle size is controlled below 0.057 mm (the composition of the copper slag is shown in Table 2);
[0032] Table 1
[0033]
[0034] Table 2
[0035]
[0036] 2. Mix the dirty acid pretreated by oxidation and the iron-rich copper slag in a ratio of 6:1 liquid-solid ratio mL:g, and stir for 12h under normal pressure for arsenic removal at a stirring speed of 200r / min; solid-liquid sepa...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Example 3: The method for treating non-ferrous smelting sewage acid with the iron-rich copper slag is as follows:
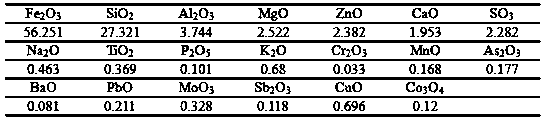
[0039] 1. Press H 2 O 2 The molar ratio with arsenic is 1.1:1, the H 2 O 2 Mixed with non-ferrous smelting acid, oxidized and pretreated at a temperature of 80℃ for 2h; among them, the non-ferrous smelting acid is from a copper smelter's sulfuric acid workshop in southwestern China, which contains a large amount of arsenic and other impurities after washing the smelting flue gas. , The main components are shown in Table 1;
[0040] The copper slag is dried and ground, and the particle size is controlled below 0.045 mm (the composition of the copper slag is shown in Table 2);
[0041] Table 1
[0042]
[0043] Table 2
[0044]
[0045] 2. Mix the oxidized pretreated dirty acid and iron-rich copper slag at a liquid-solid ratio mL:g of 5.5:1, and stir for 18h under normal pressure for arsenic removal at a stirring speed of 180r / min; solid-liquid separation , Get arse...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com