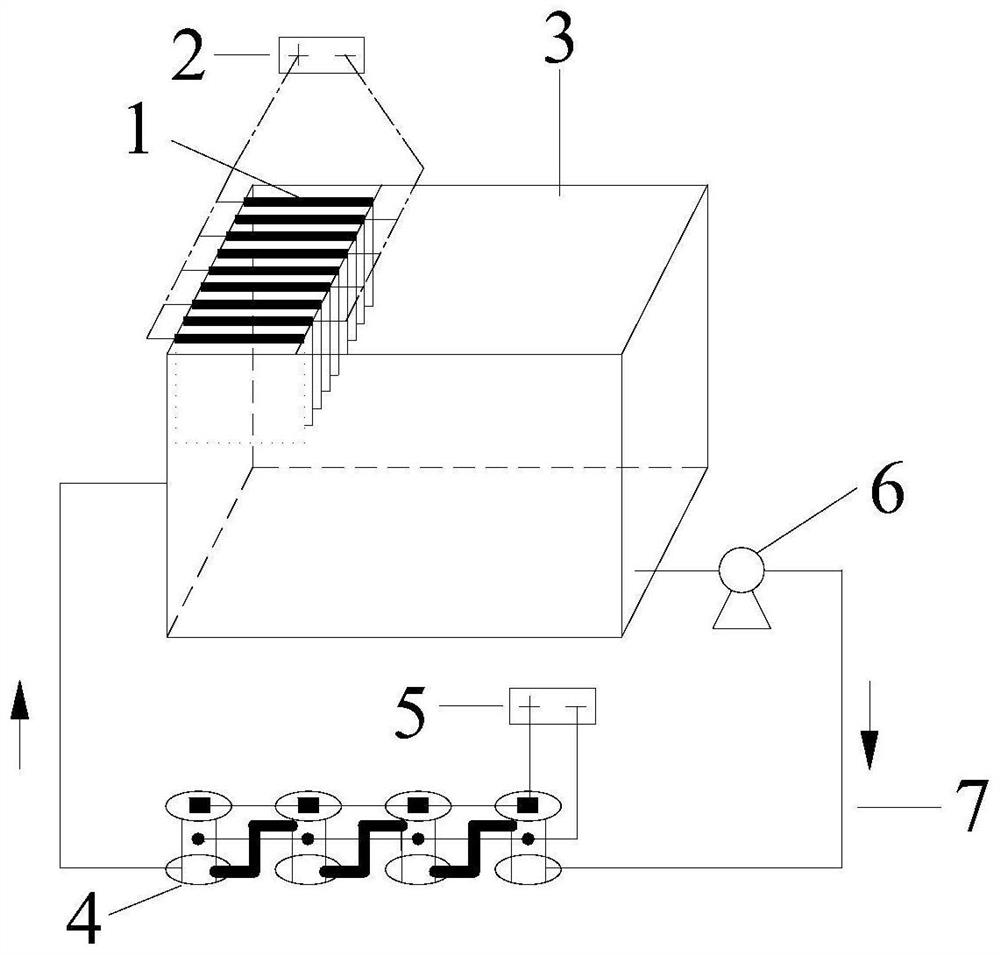
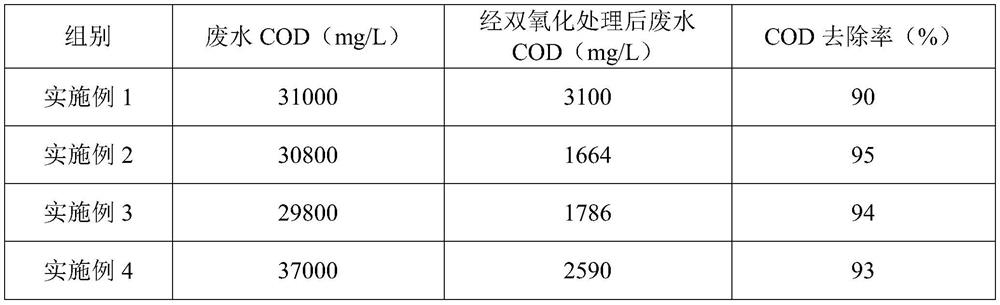
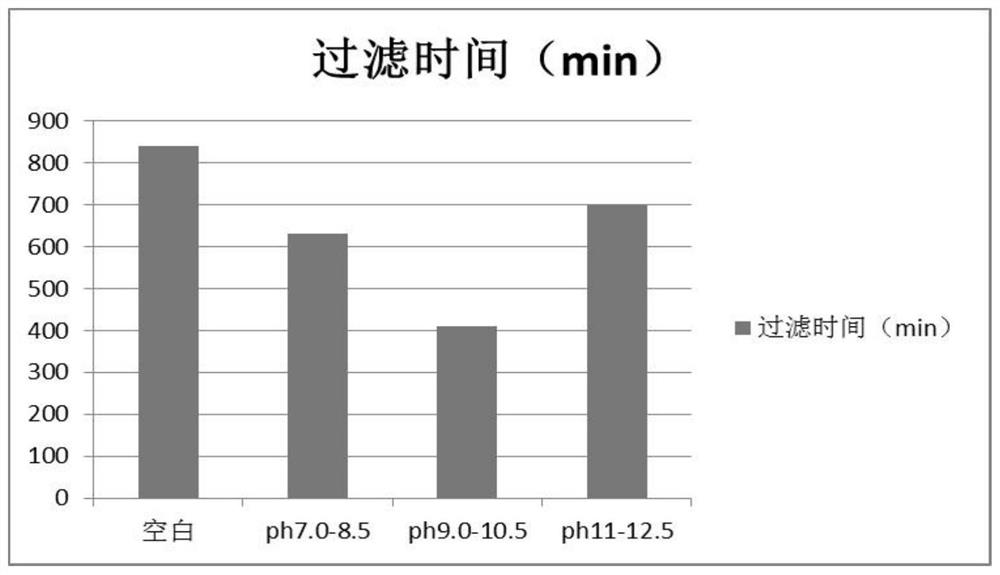
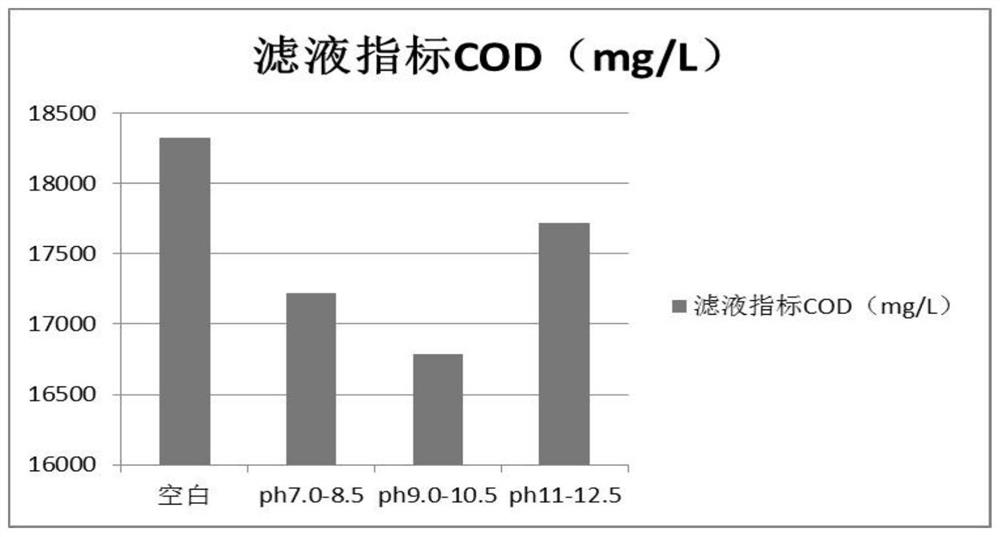
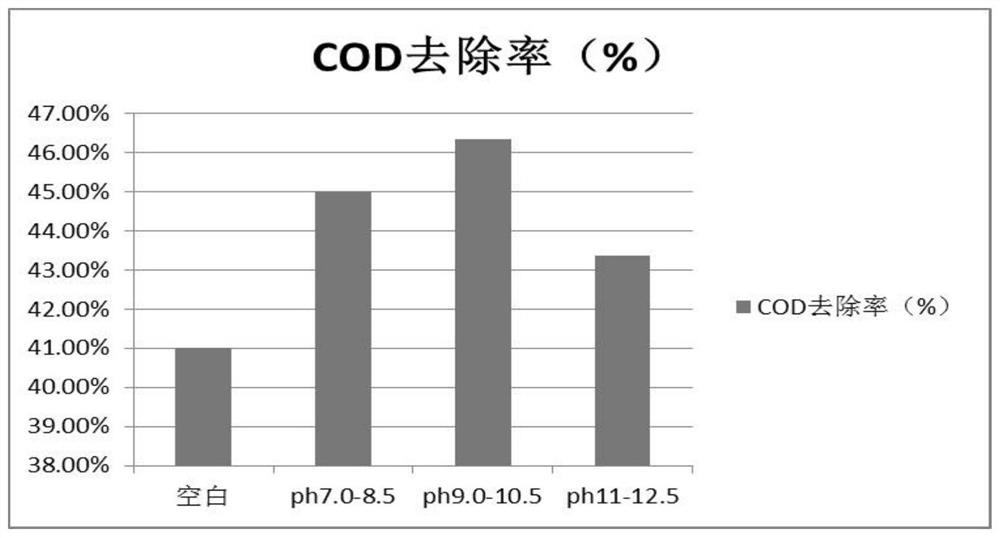
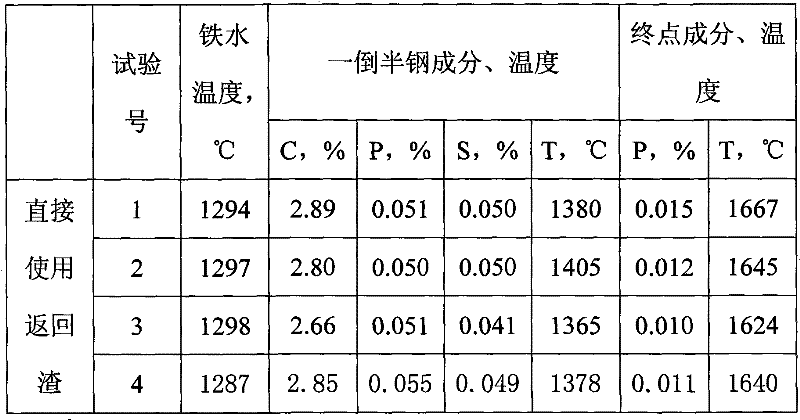
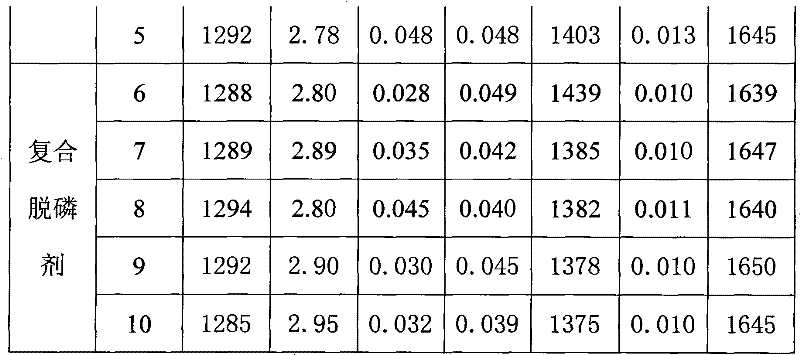
Patents
Literature
30results about How to "Low slag production" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
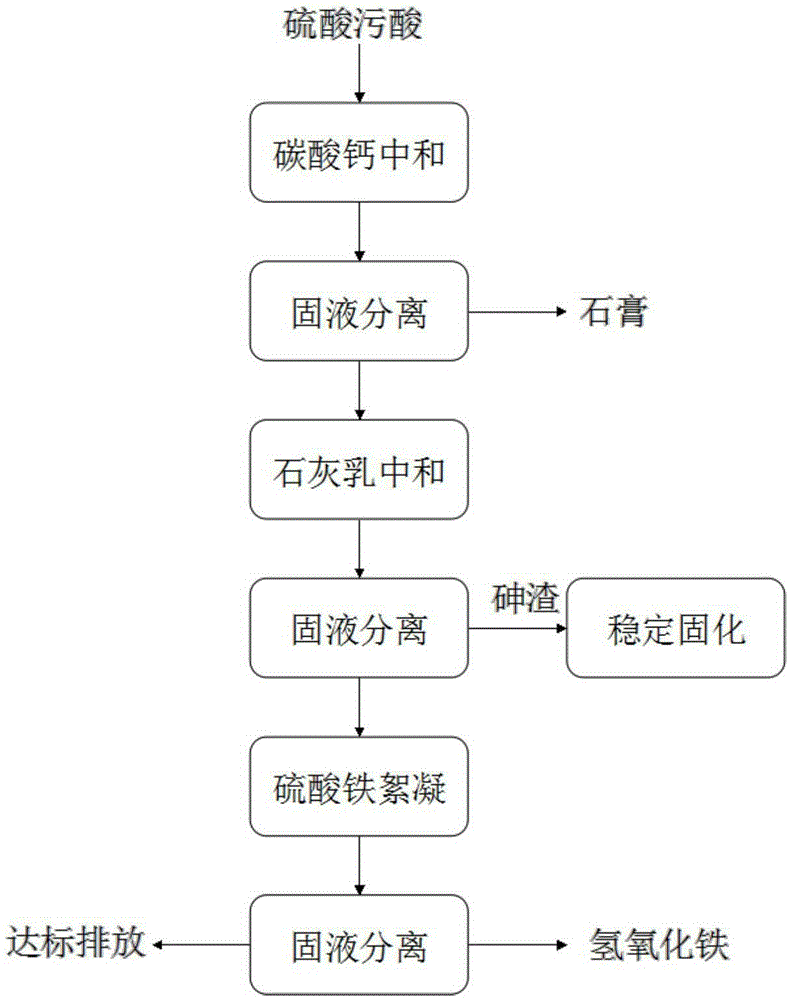
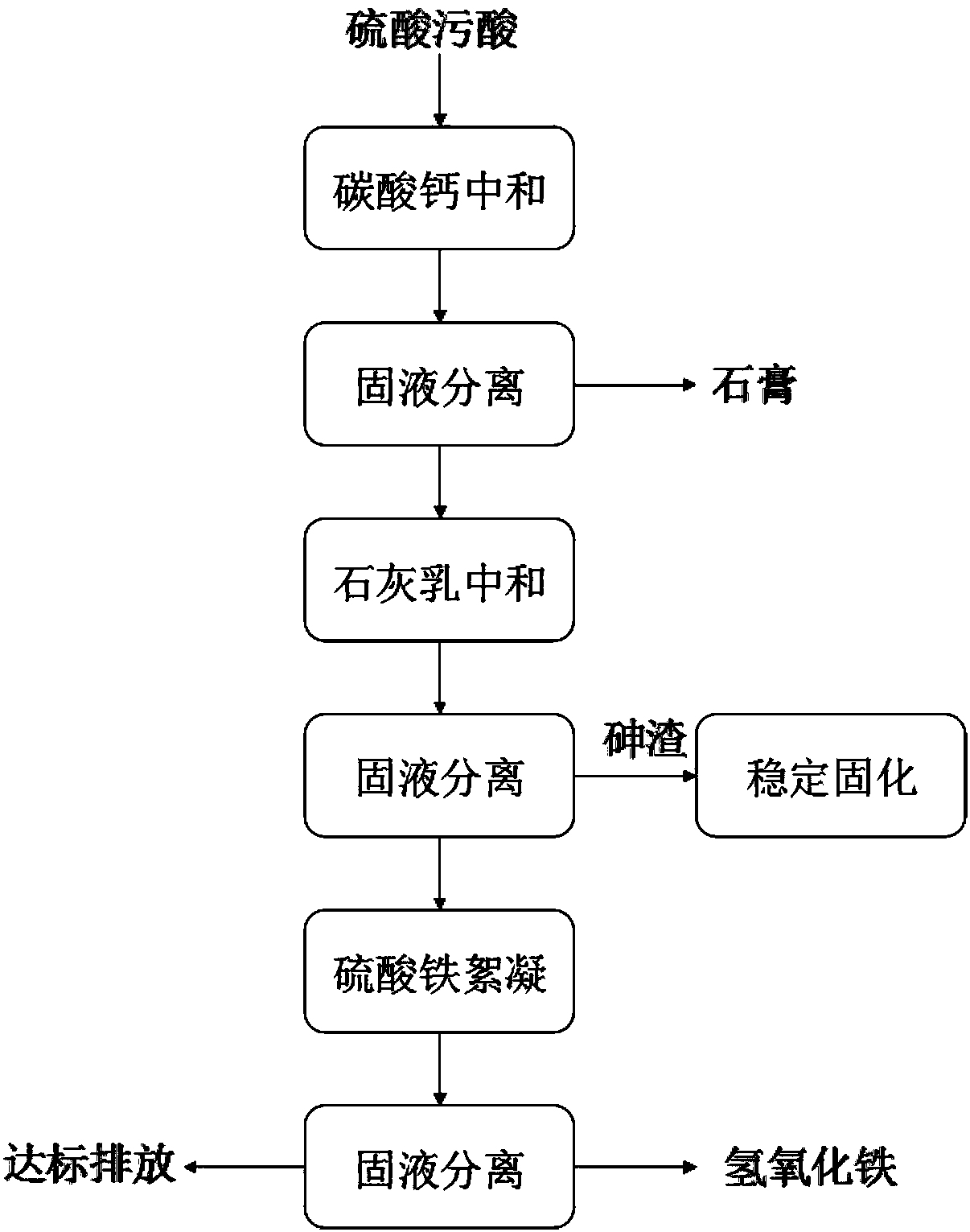
Method for removing arsenic from sulfate acidic wastewater
ActiveCN105417767AAdvantages of the treatment methodReduce arsenic levelsWater contaminantsCalcium/strontium/barium sulfatesHigh concentrationIron sulfate
The invention belongs to the technical field of industrial wastewater treatment, and particularly discloses a method for removing arsenic from sulfate acidic wastewater. The method comprises the following steps that 1, the sulfate acidic wastewater is neutralized through a calcium carbonate suspension of 5 wt%-8 wt%, and solid-liquid separation is conducted after neutralization is conducted; 2, neutralized filtrate is neutralized again through a lime milk suspension of 5 wt%-8 wt%, solid-liquid separation is conducted, and more than 98% of the arsenic is removed in the process; 3, ferric sulfate or polymeric ferric sulfate flocculent settling is conducted, and flocculent settling is conducted on the filtrate in the second step to remove the residual arsenic. The method for removing the arsenic from the sulfate acidic wastewater is low in treatment cost and simple in operation condition, and the treated wastewater can reach a corresponding national emission standard; meanwhile, high-concentration arsenic residues can be obtained, and resource recycling or stabilizing or curing of the arsenic is facilitated.
Owner:湖北金润德环保技术有限公司
Compound dephosphorization agent with converter slag as raw material and preparing method thereof
The invention discloses a molten iron pretreatment compound dephosphorization agent with converter slag as the raw material, and the compound dephosphorization agent contains the following raw materials by weight: 45 to 55 percent of converter slag, 3 to 5 percent of quartz sand, 22 to 34 percent of steel-rolling iron sheet, 3 to 6 percent of bauxite, 10 to 14 percent of soda and 0 to 5 percent of fluorite; the raw materials meeting the ingredient demands are evenly mixed according to the proportions after being crushed, and then the product with the diameter being 20 to 50mm is produced after ball-milling, screen separation, palletizing and drying. The compound dephosphorization agent realizes cyclic utilization of the converter slag which accounts for 45 to 55 percent, thus reducing the produced slag amount in the steel-making process and the environmental load; the converter slag contains plenty of CaO and FeO, which can reduce consumption of lime to a certain degree, thus increasing the metal yield rate and reducing the steel-making cost; the compound dephosphorization agent has low melting point, slag can be formed fast, the liquidity is good, thus shortening the treatment time, the dephosphorizing efficiency is high, and the dephosphorized final slag has low alkalinity and low melting point.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Method for preparing sodium chromate by mixing chromite and ferrochrome and device for method
The invention discloses a method for preparing sodium chromate by mixing chromite and ferrochrome and a device for the method. The method comprises the following steps: measuring and mixing chromite and ferrochrome with sodium carbonate, sodium nitrate and sodium peroxide; pelleting the mixture with extracted liquid sodium chromate in a pelletizer; drying in a drier; returning part of the clinker to a flame kiln after the material is dried and cooled, so that chromite and ferrochrome are decomposed and oxidized in the form of fused liquid phase in molten salts so as to obtain the clinker of sodium chromate; and continuously soaking, filtering and cleaning after the clinker is cooled so that a chromium chemical primary product of liquid sodium chromate is obtained, wherein the flame kiln comprises a U-shaped kiln body, a partition wall and a low-position molten salt suction port, wherein the partition wall and the low-position molten salt suction port are arranged in the U-shaped kiln body; one or more blowing oxygen lances and one or more charging holes are arranged at the top of the kiln body, and a smoke outlet is arranged on the upper side of the kiln; and one or more oxygen lances are arranged at the bottom of the kiln. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the oxidation rate is as high as 98%, the clinker extraction rate is as high as 99.97%, and the chromium yield is 97.96%.
Owner:HUBEI POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Method of treating industrial waste water by actived sludge-micro-electrolytic process
InactiveCN1429779ALow slag productionHigh removal rateWater/sewage treatmentSustainable biological treatmentActivated sludgeIndustrial waste water
A process for treating industrial waste water (including waste waters of acrylic fibre, dyeing-printing textile petrochemical trade, etc.) by the active sludge-microelectrolysis method features that the carbon steel is arranged in ordinary active sludge system and the microelectrolysis principle is used to treat industrial waste water. Its advantages are low generation of dregs and high removal rate of COD.
Owner:QILU PETRO CHEM - SINOPEC
Method for treating arsenic in waste smelting acid by using copper slag
InactiveCN109534476AIncrease management costsSusceptible to toxic leachingWater contaminantsWaste water treatment from metallurgical processSludgeImpurity
The invention discloses a method for treating arsenic in waste smelting acid by using copper slag, and belongs to the field of heavy metal pollution treatment and metallurgical solid waste utilization. The method includes firstly subjecting the copper slag to drying, ball milling and magnetic separation to obtain iron-rich copper slag and other impurities; subjecting the iron-rich copper slag to high-temperature pretreatment at 500-800 DEG C; subjecting the high-temperature iron-rich copper slag to water quenching through high-speed water blowing; then drying and grinding the copper slag afterwater quenching; adding H2O2 into waste acid and mixing to perform oxidation pretreatment at 60-80 DEG C; then adding the copper slag into the waste acid after oxidation pretreatment; performing an arsenic removing reaction at atmospheric pressure under stirring; and finally performing solid liquid separation. The method achieves arsenic removal with cheap copper slag, reduces sludge storage volume in the process of waste acid treatment when compared with a traditional arsenic removal process, and achieves an effect of treating waste with a waste material. The method has characteristics of simple process operation, a low production cost and a wide market prospect.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
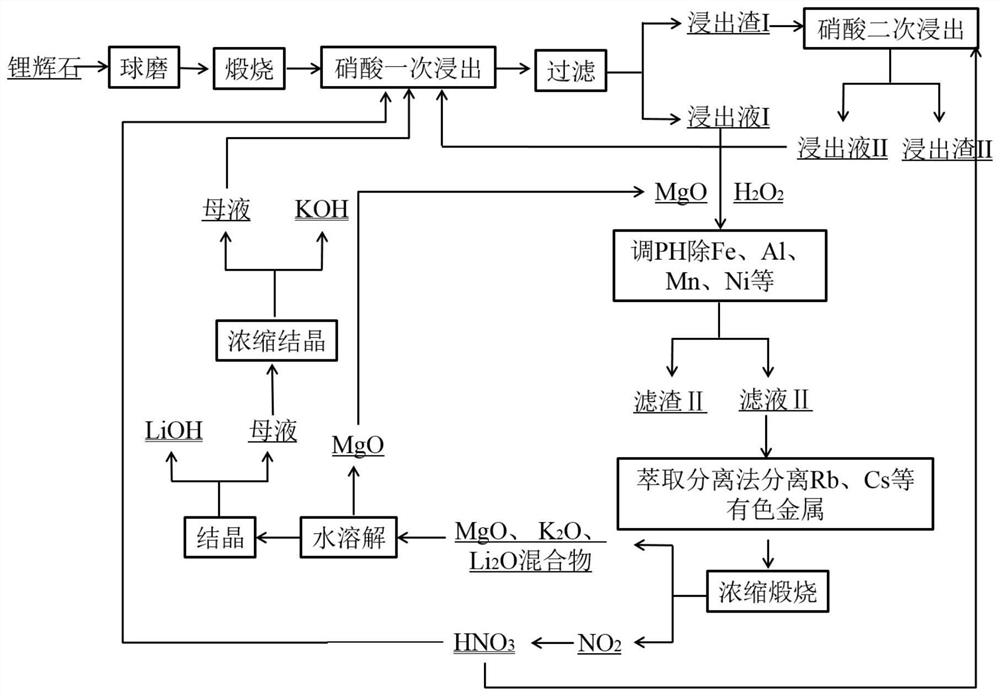
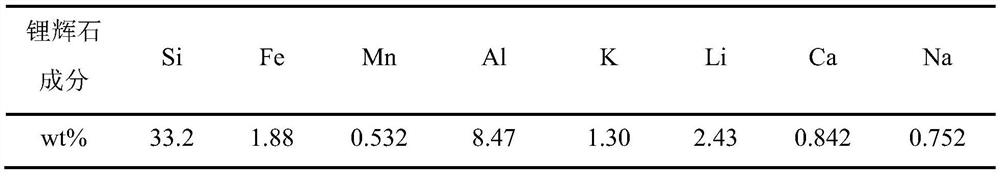
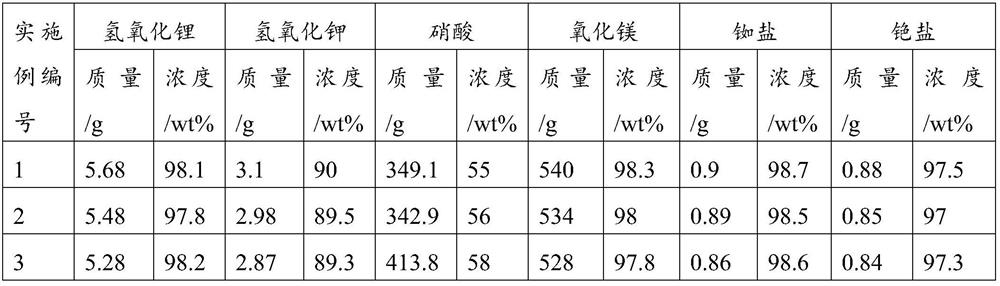
Method for extracting lithium through secondary reverse leaching of spodumene by nitric acid
ActiveCN114318008AReduce dosageLow costProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionLithium hydroxide
The invention discloses a method for extracting lithium from spodumene through secondary reverse leaching of nitric acid, which comprises the following steps: S1, ball-milling the spodumene, and calcining the ball-milled spodumene at 900-1300 DEG C for 1-5 hours; s2, pulping the calcined spodumene and water according to a liquid-solid mass ratio of (2.5-6): 1, then adding a proper amount of nitric acid into the slurry to carry out a primary leaching reaction for 1-6 hours, and filtering a solid-liquid mixture obtained after the reaction to obtain a leaching solution I and a leaching residue I; according to the method, the product value utilization of spodumene can be maximized, and lithium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, nitric acid, magnesium oxide, rubidium salt and cesium salt can be prepared. The method is suitable for the field of mineral raw material treatment.
Owner:四川顺应锂材料科技有限公司
Environmentally-protective slag reducing agent of phosphating solution
ActiveCN102965662ALess sedimentImprove corrosion resistanceMetallic material coating processesEthylene diamineRegenerative process
The invention discloses an environmentally-protective slag reducing agent of a phosphating solution. The agent contains ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid, hydroxy ethylidene diphosphonic acid, tartrate and phytic acid. The agent mainly uses a principle of a composite complexing agent, and can perform complexation for part heavy metal easy to produce slag in the phosphating solution, thereby obviously reducing the amount of slag during a regenerative process. The complexing agent also has an effect of improving corrosion resistance of metal phosphide films. When the phosphating solution is to be discarded or is discarded all ready, the agent is added in a proportion of 0.1 to 0.3 %, and sediment of the phosphating solution can be greatly reduced; and the quality of the newly transformed phosphating solution fully meet production demands.
Owner:DALIAN BETRUST ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH CO LTD
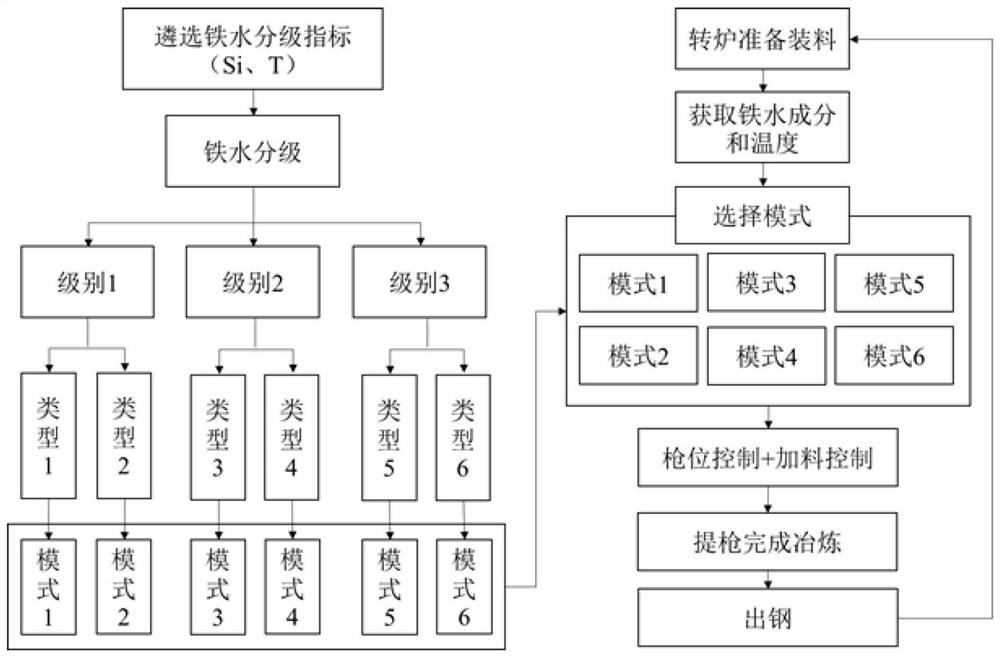
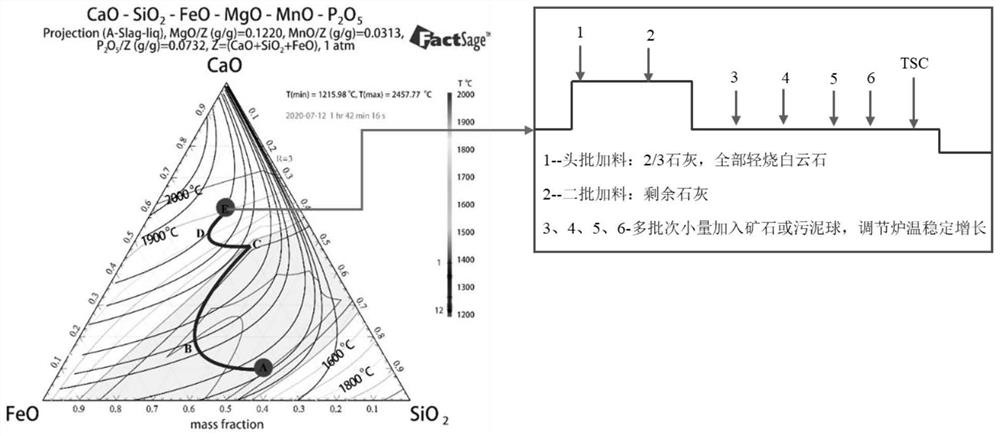
Converter multi-mode smelting method based on molten iron grading system
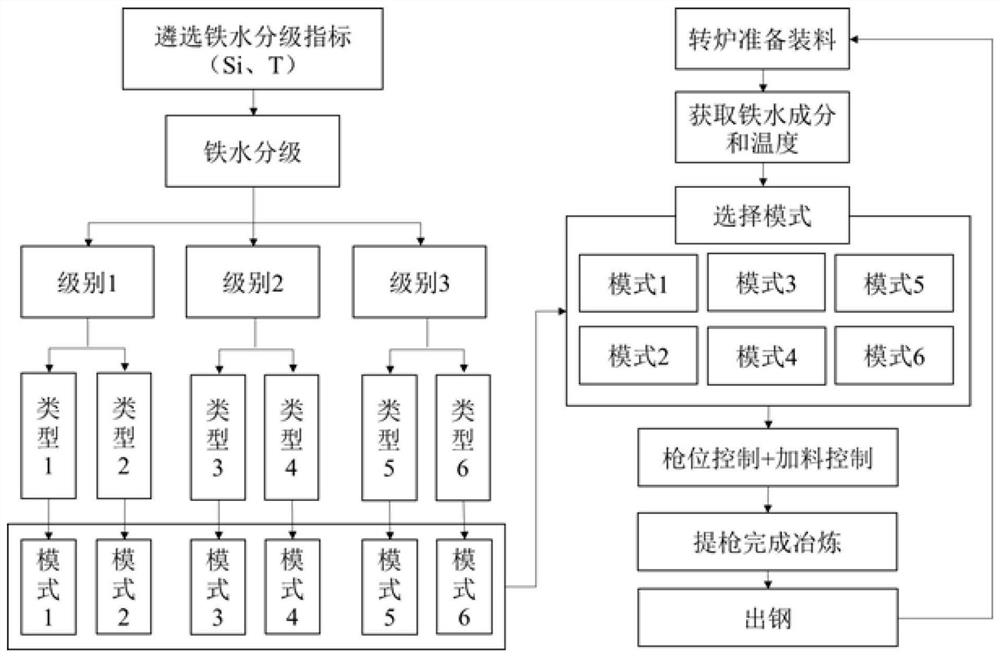
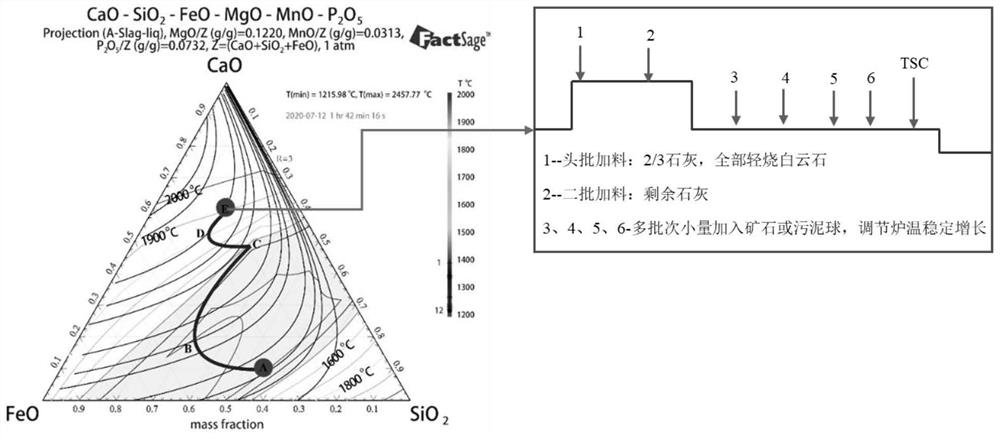
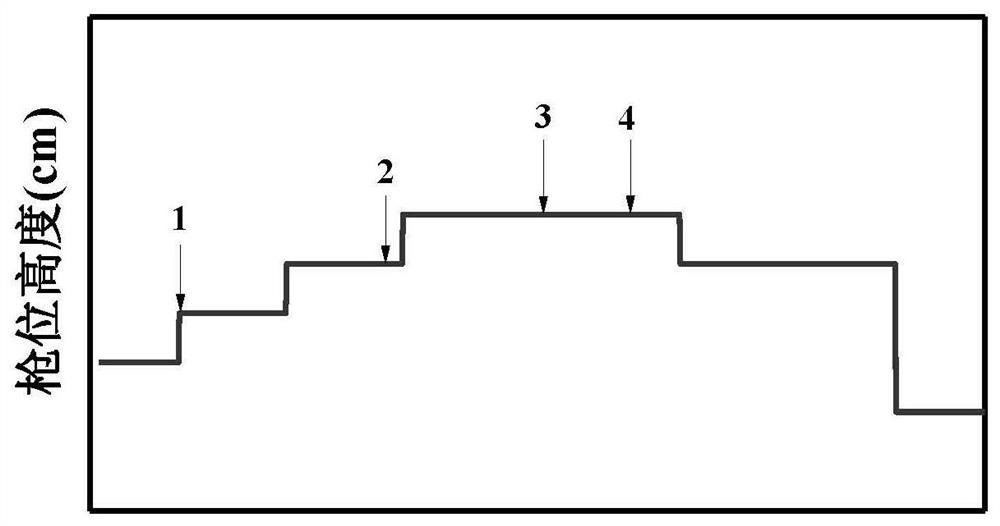
ActiveCN113981167AStable blowingReduce consumptionSteel manufacturing process aspectsIncreasing energy efficiencySlagMaterial consumption
The invention provides a converter multi-mode smelting method based on a molten iron grading system. The converter multi-mode smelting method comprises the following steps: firstly, selecting grading indexes of molten iron, formulating the molten iron grading system, designing blowing modes matched with different grades of molten iron according to the different grades of molten iron, firstly obtaining components and temperature of the molten iron before charging, and selecting the corresponding blowing mode to assist in completing smelting. According to the method, the molten iron with large component fluctuation is classified based on the 'differential' thought in mathematics, the molten iron falling into the same category can be regarded as stable, the same blowing mode is adopted, stable blowing of the converter can be achieved, blowing accidents caused by large fluctuation of the molten iron are avoided, the dephosphorization effect can be improved to a certain degree, and material consumption can be reduced, the slag production amount is reduced, the smelting period is shortened, and the good metallurgical effect is achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
A method for removing arsenic from sulfuric acid polluted acid wastewater
ActiveCN105417767BLow arsenic content in slagReduce arsenic levelsWater contaminantsCalcium/strontium/barium sulfatesHigh concentrationSulfate
The invention belongs to the technical field of industrial wastewater treatment, and particularly discloses a method for removing arsenic from sulfate acidic wastewater. The method comprises the following steps that 1, the sulfate acidic wastewater is neutralized through a calcium carbonate suspension of 5 wt%-8 wt%, and solid-liquid separation is conducted after neutralization is conducted; 2, neutralized filtrate is neutralized again through a lime milk suspension of 5 wt%-8 wt%, solid-liquid separation is conducted, and more than 98% of the arsenic is removed in the process; 3, ferric sulfate or polymeric ferric sulfate flocculent settling is conducted, and flocculent settling is conducted on the filtrate in the second step to remove the residual arsenic. The method for removing the arsenic from the sulfate acidic wastewater is low in treatment cost and simple in operation condition, and the treated wastewater can reach a corresponding national emission standard; meanwhile, high-concentration arsenic residues can be obtained, and resource recycling or stabilizing or curing of the arsenic is facilitated.
Owner:湖北金润德环保技术有限公司
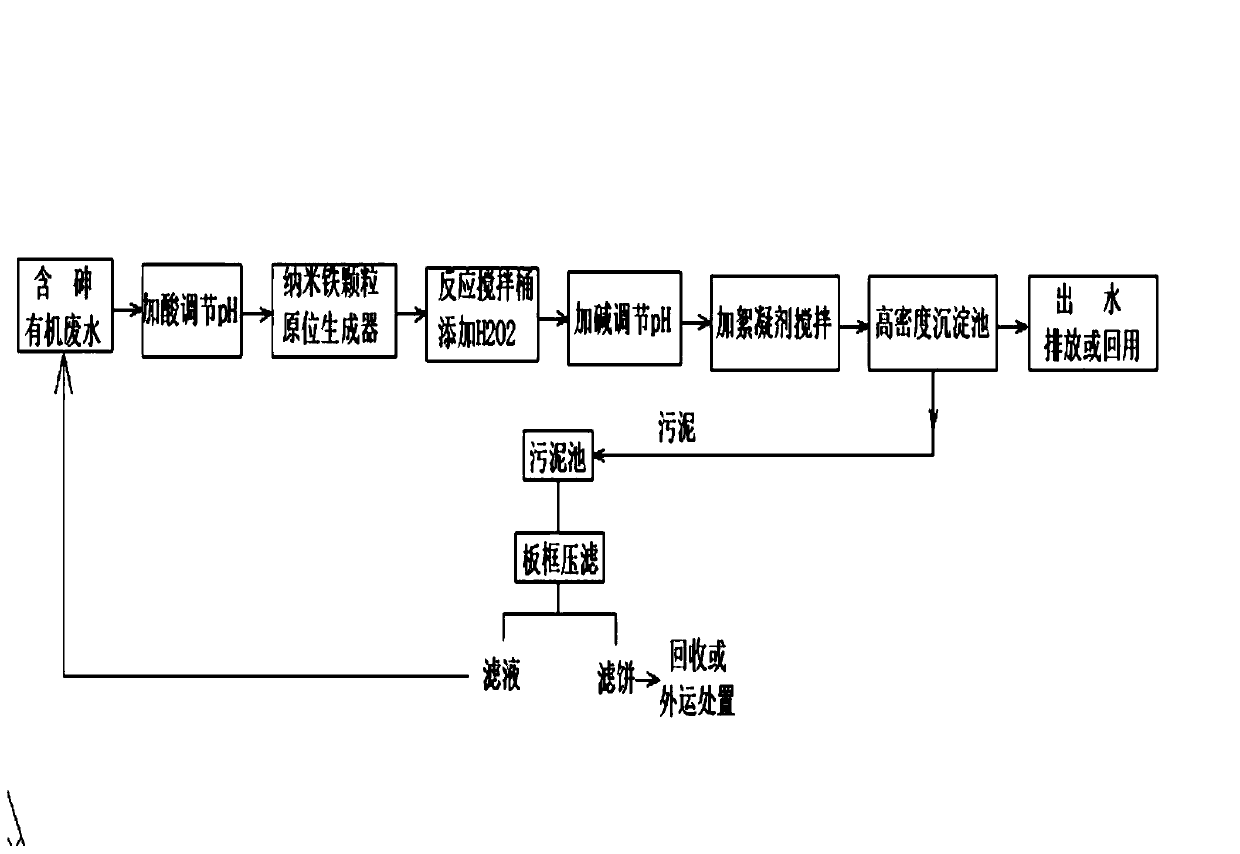
Treatment method of arsenic-containing organic wastewater
ActiveCN111470671AInfluent COD concentration requirement is lowSimple processWater treatment parameter controlWater treatment compoundsArsenite ionFenton oxidation
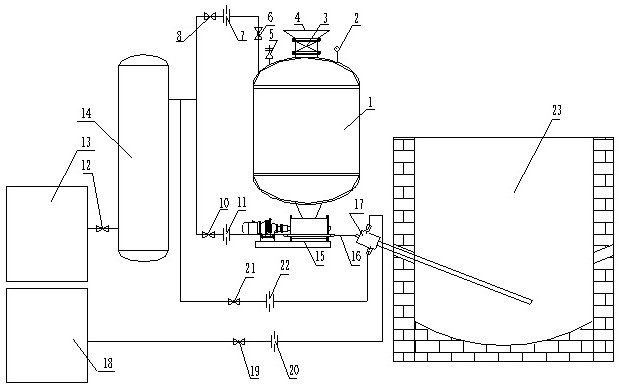
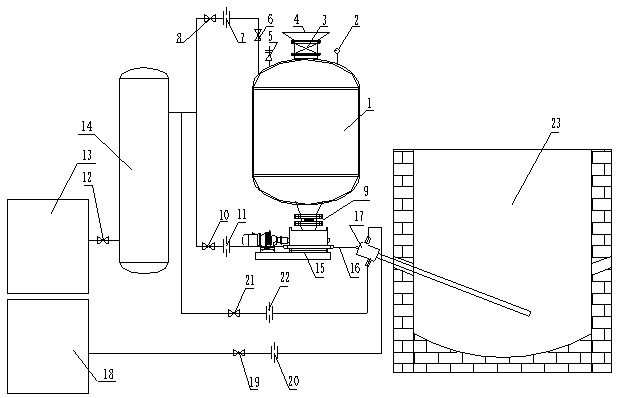
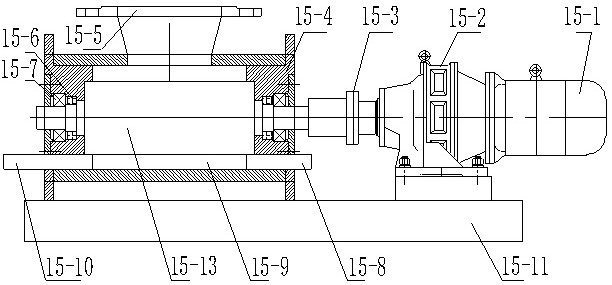
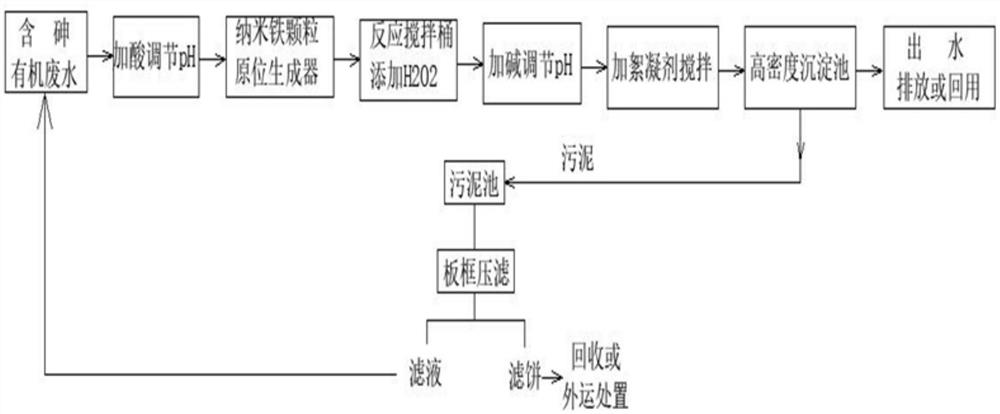
The invention relates to a treatment method of arsenic-containing organic wastewater, which comprises the following steps: (1) regulating the pH value of the arsenic-containing organic wastewater to 2-4, and enabling the pH-regulated wastewater to flow through a nano-iron particle generation device, so that the nano-iron particle generation device generates nano-iron particles in situ in the wastewater; (2) adding H2O2 into the wastewater added with the nano-iron particles to carry out nano-iron / heterogeneous Fenton oxidation reaction until the reaction is finished; and (3) adjusting the pH value of the reacted mixed solution to 8-9, and separating out the arsenic ion flocculent precipitate from the wastewater. The treatment method provided by the invention has good arsenic removal and CODremoval effects on arsenic-containing organic wastewater, and can meet increasingly strict arsenic discharge standards.
Owner:LASER RES INST OF SHANDONG ACAD OF SCI
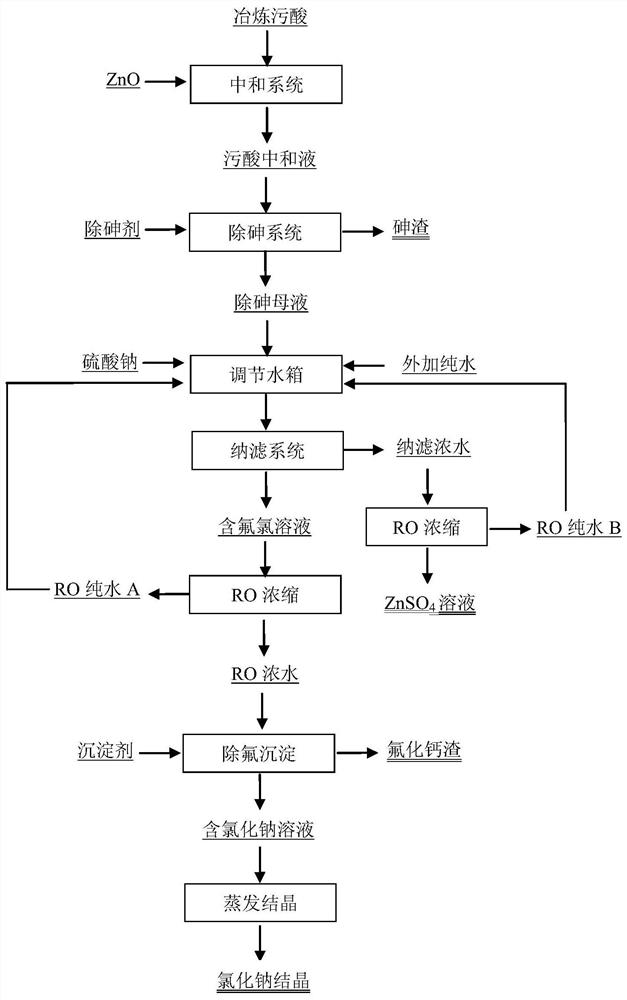
Treatment method of lead-zinc smelting waste acid
ActiveCN111661950AImprove the separation effect of nanofiltrationLow costZinc sulatesWaste water treatment from metallurgical processEngineeringSodium sulfate
The invention provides a treatment method of lead-zinc smelting waste acid. The method comprises the following steps: (1) adding ZnO into the smelting waste acid, and carrying out a neutralization reaction to obtain a neutralized waste acid solution; (2) adding an arsenic removal agent into the neutralized waste acid solution, carrying out an arsenic removal reaction, and filtering after the reaction is completed to obtain arsenic slag and an arsenic-removed mother liquor; (3) mixing the arsenic-removed mother liquor with sodium sulfate and pure water, and carrying out nanofiltration to obtainnanofiltered concentrated water and a fluorine-containing chlorine solution; (4) carrying out RO concentration on the fluorine-containing chlorine solution to obtain RO pure water and RO concentratedwater; and (5) adding a precipitant into the RO concentrated water, and carrying out a defluorination precipitation reaction and solid-liquid separation to obtain a sodium chloride-containing solution and calcium fluoride slag. The treatment method provided by the invention is simple and safe in operation management, can effectively reduce the operation energy consumption and the treatment cost,can recover sulfuric acid in the waste acid at the same time, and ensures that the water quality index of the waste acid reaches the standard and is discharged.
Owner:湖南中金岭南康盟环保科技有限公司
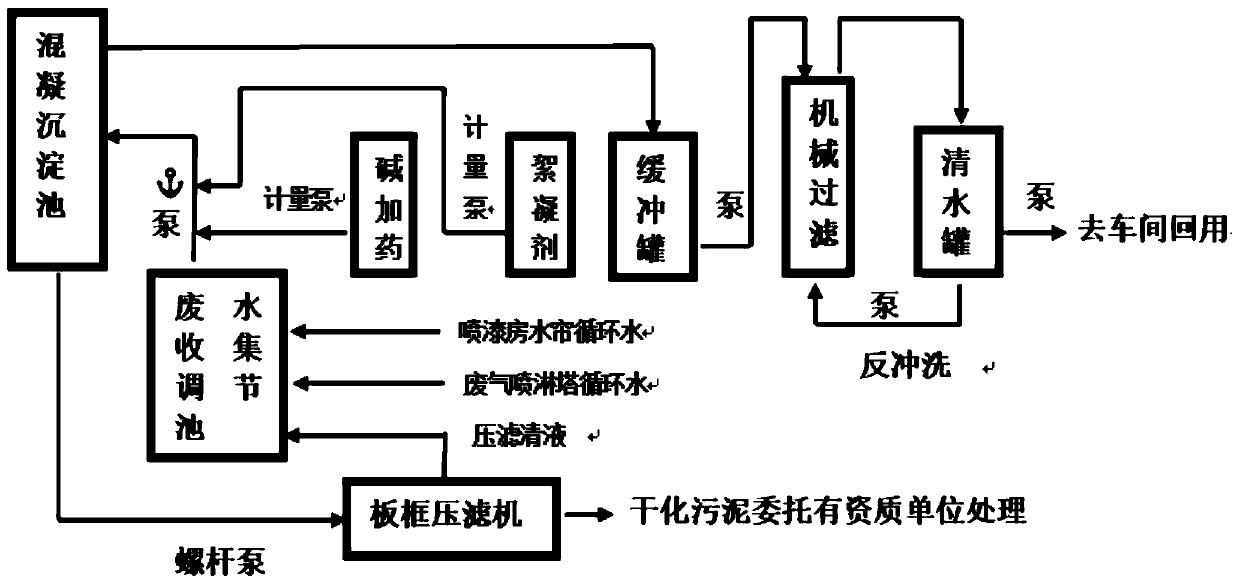
Convenient-integrated paint spray wastewater treatment and reuse system and method
PendingCN110746003ASimple processingReduce processing costsSludge treatmentPaint waste treatmentProcess engineeringWater use
The invention discloses a convenient-integrated paint spray wastewater treatment and reuse system and method. Sewage is sequentially treated by the following equipment: a wastewater collection and regulation tank for sewage storage and water quality stabilization, a neutralization and coagulation sedimentation device which is connected with a dosing device, a buffer tank for storing supernate treated by the neutralization and coagulation sedimentation device, and a mechanical filter, wherein precipitate is dewatered and dried by a plate and frame filter press, and the supernate is stored in aclear water tank after filtering. The system and method meet the reuse water standard in the production link of enterprises.
Owner:南通汇佰川工程技术有限公司
Method for producing electrolytic manganese metal by lixiviating sinter ore by adding ferrous sulphate in replacement of manganese carbonate ore
The invention discloses a method for producing electrolytic manganese metal by lixiviating sinter ore by adding ferrous sulphate in replacement of manganese carbonate ore. The method comprises the working procedures of lixiviation and oxidation, neutralization, filtration, purification, electrolyzation and the like, and is characterized in that the process of lixiviation and oxidation is implemented by injecting anolyte enough to lead the material to react into the lixiviation vessel, adding concentrated sulfuric acid, adding sinter ore and finally adding ferrous sulphate for lixiviation for 3-4 hours at 70-75 DEG C; adding ammonia water immediately when Fe2+ in the feed liquid is less than or equal to 0.001g / l so as to carry out neutralization, testing the pH value of the feed liquid several times during the process of neutralization, and stopping adding ammonia water when full-valent Fe up to standard is less than or equal to 0.001g / l and the pH value reaches 6.8-7.2. The invention can reduce production cost, and solve the difficulty in purchasing manganese carbonate ore. The sinter ore contains high grade manganese, therefore, ore input quantity is small, and correspondingly the slag quantity and fee liquid carried away by the slag are little. No carbon dioxide gas is exhausted during lixiviation with sinter ore as raw material, thus working environment is improved.
Owner:CITIC JINZHOU METAL
Method of treating industrial waste water by actived sludge-micro-electrolytic process
InactiveCN1180987CLow slag productionHigh removal rateWater/sewage treatmentSustainable biological treatmentActivated sludgeIndustrial waste water
A process for treating industrial waste water (including waste waters of acrylic fibre, dyeing-printing textile petrochemical trade, etc.) by the active sludge-microelectrolysis method features that the carbon steel is arranged in ordinary active sludge system and the microelectrolysis principle is used to treat industrial waste water. Its advantages are low generation of dregs and high removal rate of COD.
Owner:QILU PETRO CHEM - SINOPEC
A multi-mode smelting method based on molten iron classification system
ActiveCN113981167BStable blowingReduce consumptionSteel manufacturing process aspectsManufacturing convertersSlagMaterial consumption
The invention provides a converter multi-mode smelting method based on the molten iron classification system. First, the classification index of the molten iron is selected, the molten iron classification system is formulated, and the matching blowing mode is designed for the molten iron of different grades, and the molten iron is first obtained before charging. composition and temperature, and select the corresponding blowing mode to assist in the completion of smelting. The invention is based on the idea of "differentiation" in mathematics, and classifies molten irons with relatively large fluctuations in composition. The molten irons falling in the same category can be regarded as stable, and the same blowing mode can be used to realize the stable blowing of the converter. It avoids blowing accidents caused by large fluctuations of molten iron, not only can improve the dephosphorization effect to a certain extent, but also can reduce material consumption, reduce slag production, shorten smelting cycle, and have good metallurgical effects.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Reverse osmosis recycling device of electrophoresis phosphating wastewater
PendingCN109576764AReduce energy consumptionQuality improvementElectrophoretic coatingsElectrophoresisWastewater
The invention discloses a reverse osmosis recycling device of electrophoresis phosphating wastewater. The reverse osmosis recycling device of the electrophoresis phosphating wastewater comprises an assembly line area and a processing area, wherein the assembly line area includes a first soaking pool, a second soaking pool, a third soaking pool, a first phosphating water washing pool, a fourth soaking pool, a pure water prewash pool and a shack body workpiece outlet; the processing area includes a pure water washing and soaking pool, a second phosphating water washing pool, a phosphating pool,a meter adjusting pool and a degreasing washing pool; the first soaking pool, the second soaking pool, the third soaking pool and the fourth soaking pool are in through connection, and the first phosphating water washing pool is positioned between the third soaking pool and the fourth soaking pool; and the fourth soaking pool is arranged between the first phosphating water washing pool and the pure water prewash pool. According to the reverse osmosis recycling device of the electrophoresis phosphating wastewater, a cleaning tank communicates with a pipeline, and a circulating water pump is added to make clear water flow at a plurality of stations for multiple use, the water consumption is reduced, and the cleaning process of soaking, spraying, soaking and spraying is used, the extremely low water consumption is realized, and meanwhile, the cleaning effect of a workpiece is controlled, and the quality of electrophoretic coating of the workpiece and the stability of electrophoretic bathare guaranteed.
Owner:襄阳市志达海成科技实业有限公司
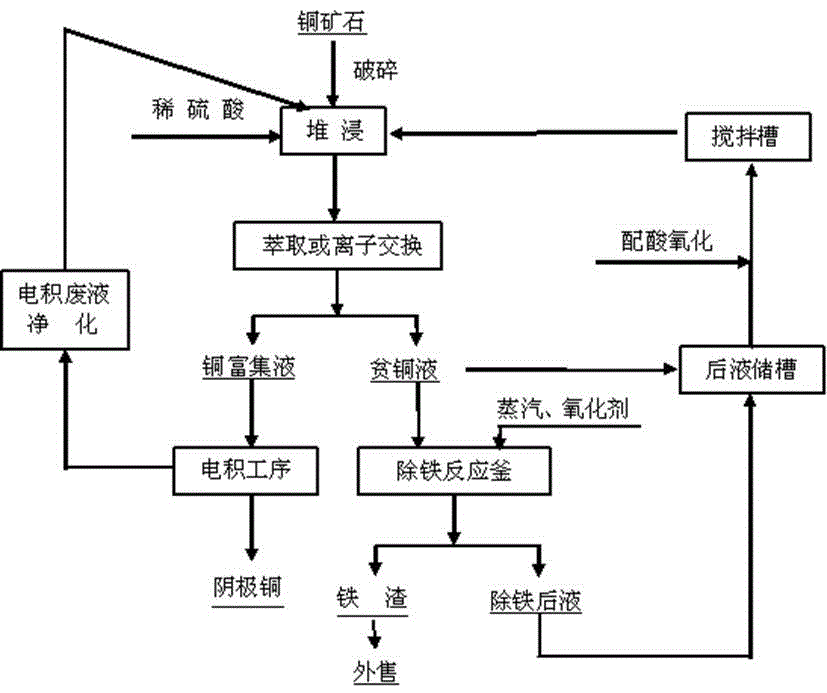
A method for extracting copper and removing iron from copper ore acid leaching solution
ActiveCN104232924BImprove the effect of iron removalSimple stepsRotary drum furnacesCrucible furnacesPregnant leach solutionSlag
The invention discloses a method for extracting copper and removing iron from acid leaching liquid of copper ore, which comprises crushing secondary copper oxide ore and secondary copper sulfide ore and mixing them for wet heap leaching; spraying and leaching with dilute sulfuric acid to obtain weak Acidic leaching solution; the leaching solution extracts copper through extraction or ion exchange to obtain copper-enriched solution and copper-poor solution; the copper-rich solution is electrolytically deposited to obtain cathode copper; the copper-depleted solution is continuously deironed at high temperature and high pressure under an oxidizing atmosphere, and the obtained pulp is passed through Hematite slag is obtained by filtration, and part of the copper-poor liquid is acidified and oxidized and sent to the storage yard for circular leaching. The present invention utilizes iron ions and copper sulfide ore to undergo oxidation-reduction in the heap leaching process, and the iron ions in the heap leaching solution mainly exist in the form of divalent iron ions, which eliminates the step of reducing divalent iron ions for the subsequent extraction of copper, and adopts high temperature The high-pressure method of iron removal has a small amount of slag production and low environmental protection pressure, and the iron slag can be reused; the sulfuric acid produced in the iron removal process does not need to be neutralized, and can be directly returned to the heap leaching for recycling, and the comprehensive utilization effect is good.
Owner:HENAN GONGXIN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION & TECH CO LTD
A kind of preparation method of ferro-vanadium alloy
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Environmentally-protective slag reducing agent of phosphating solution
ActiveCN102965662BLess sedimentImprove corrosion resistanceMetallic material coating processesEthylene diamineRegenerative process
The invention discloses an environmentally-protective slag reducing agent of a phosphating solution. The agent contains ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid, hydroxy ethylidene diphosphonic acid, tartrate and phytic acid. The agent mainly uses a principle of a composite complexing agent, and can perform complexation for part heavy metal easy to produce slag in the phosphating solution, thereby obviously reducing the amount of slag during a regenerative process. The complexing agent also has an effect of improving corrosion resistance of metal phosphide films. When the phosphating solution is to be discarded or is discarded all ready, the agent is added in a proportion of 0.1 to 0.3 %, and sediment of the phosphating solution can be greatly reduced; and the quality of the newly transformed phosphating solution fully meet production demands.
Owner:DALIAN BETRUST ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH CO LTD
Three-phase catalytic oxidation preparation technology of soluble chromate
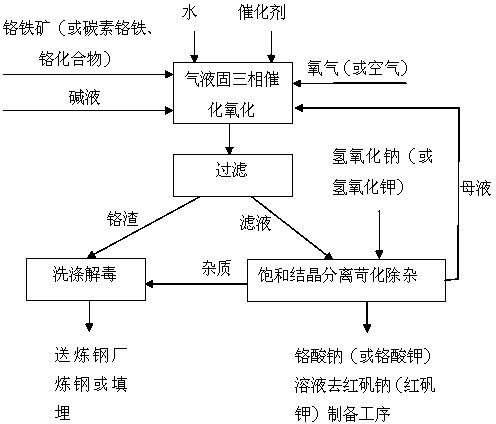
ActiveCN102320661BAvoid generatingReduce the difficulty of separation and recoveryChromates/bichromatesCatalytic oxidationOxygen
The invention relates to a preparation technology of chromate, specifically to a three-phase catalytic oxidation preparation technology of soluble chromate. The technology comprises the following steps of: heating alkali liquor with concentration of 20-60% to 50-300 DEG C, then, mixing chromite or carbon ferrochrome with the alkali liquor according to mass ratio of Cr2O3 : alkali liquor = 1 : 1.5-10 to form suspending liquid, and introducing the suspending liquid into a reactor; continuously inputting the air or the oxygen heated to 50-300 DEG C to the bottom of the reactor through a pipeline; setting a catalyst in the reactor according to the mass ratio of catalyst : Cr2O3 = 0.1-1.5 : 100, maintaining the temperature of the suspending liquid in the reactor at 50-300 DEG C, executing gas-liquid-solid three-phase bubbling reaction for 0.5-6 hours to generate soluble chromate raw products and chromium residues; removing impurities through filtering and crystallization to obtain the chromate. With the three-phase catalytic oxidation preparation technology of the soluble chromate, Cr2O3 conversion rate is high, reaction speed is fast, energy consumption is low, residue quantity is low, environment pollution is less, equipment investment is low and corrosion is low.
Owner:CHONGQING MINFENG CHEM
Method for preparing sodium chromate by mixing chromite and ferrochrome and device for method
The invention discloses a method for preparing sodium chromate by mixing chromite and ferrochrome and a device for the method. The method comprises the following steps: measuring and mixing chromite and ferrochrome with sodium carbonate, sodium nitrate and sodium peroxide; pelleting the mixture with extracted liquid sodium chromate in a pelletizer; drying in a drier; returning part of the clinker to a flame kiln after the material is dried and cooled, so that chromite and ferrochrome are decomposed and oxidized in the form of fused liquid phase in molten salts so as to obtain the clinker of sodium chromate; and continuously soaking, filtering and cleaning after the clinker is cooled so that a chromium chemical primary product of liquid sodium chromate is obtained, wherein the flame kiln comprises a U-shaped kiln body, a partition wall and a low-position molten salt suction port, wherein the partition wall and the low-position molten salt suction port are arranged in the U-shaped kiln body; one or more blowing oxygen lances and one or more charging holes are arranged at the top of the kiln body, and a smoke outlet is arranged on the upper side of the kiln; and one or more oxygen lances are arranged at the bottom of the kiln. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the oxidation rate is as high as 98%, the clinker extraction rate is as high as 99.97%, and the chromium yield is 97.96%.
Owner:HUBEI POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Method for producing electrolytic manganese metal by lixiviating sinter ore by adding ferrous sulphate in replacement of manganese carbonate ore
The invention discloses a method for producing electrolytic manganese metal by lixiviating sinter ore by adding ferrous sulphate in replacement of manganese carbonate ore. The method comprises the working procedures of lixiviation and oxidation, neutralization, filtration, purification, electrolyzation and the like, and is characterized in that the process of lixiviation and oxidation is implemented by injecting anolyte enough to lead the material to react into the lixiviation vessel, adding concentrated sulfuric acid, adding sinter ore and finally adding ferrous sulphate for lixiviation for 3-4 hours at 70-75 DEG C; adding ammonia water immediately when Fe2+ in the feed liquid is less than or equal to 0.001g / l so as to carry out neutralization, testing the pH value of the feed liquid several times during the process of neutralization, and stopping adding ammonia water when full-valent Fe up to standard is less than or equal to 0.001g / l and the pH value reaches 6.8-7.2. The invention can reduce production cost, and solve the difficulty in purchasing manganese carbonate ore. The sinter ore contains high grade manganese, therefore, ore input quantity is small, and correspondingly the slag quantity and fee liquid carried away by the slag are little. No carbon dioxide gas is exhausted during lixiviation with sinter ore as raw material, thus working environment is improved.
Owner:CITIC JINZHOU METAL
A coating control method and its application
The invention discloses a plating control method. In the process that strip steel is separated from the solution surface of a plating solution, plating solution brought out of the solution surface by the strip steel is subjected to ultrasonic vibrating treatment through ultrasonic waves at first, and then jetting treatment is conducted through an air knife device. A curved surface of the plating solution brought out of the solution surface by the strip steel is formed between the strip steel and the solution surface, and the ultrasonic wave acts on plating solution within the range of the curved surface. The viscosity of nonferrous liquid metal is lowered through an ultrasonic device, and the splatter effect of liquid metal adhered to the strip steel surface is produced through the vibration produced by the ultrasonic wave in the liquid metal, so that a part of liquid metal is automatically stripped from the strip steel surface and the weight of nonferrous liquid metal brought out by the strip steel in operation is lowered. The accurate control over the thickness of plating can be achieved through the air knife scraping device with low gas pressure and flow. The slag production amount is greatly reduced; the pollution of noise and dust is also reduced; the design and manufacturing cost of an air knife is reduced; the problem of plating of thin plating in high speed condition is solved.
Owner:CISDI ENG CO LTD
Oxygen blowing and coal injection secondary lead smelting furnace and oxygen blowing and coal injection method
PendingCN113188146AIncrease burn rateIncrease furnace temperatureFuel supply regulationFurnace componentsLead smeltingNon-ferrous extractive metallurgy
The invention discloses an oxygen blowing and coal injection secondary lead smelting furnace and an oxygen blowing and coal injection method, and belongs to the technical field of non-ferrous metal smelting. A discharge hole in the bottom of a coal injection tank is connected with a coal injection machine; the inlet end of the coal injection machine is connected with the gas outlet port of a gas storage tank, the outlet end of the coal injection machine is connected with a pulverized coal inlet of a coal injection oxygen lance through a coal injection pipe, and the coal injection oxygen lance is inserted into a smelting furnace body; a gas outlet port of the gas storage tank is communicated with the coal injection tank, and a gas inlet port of the gas storage tank is connected with an air compressor through an air storage pressurizing valve; an upper sealing top of the coal injection tank is also connected with a coal feeding valve, a pressure gauge and a gas inlet valve, and the upper inlet end of the coal feeding valve is connected with a coal hopper; an oxygen station is connected with an oxygen inlet of the coal injection oxygen lance; and the gas outlet port of the gas storage tank is connected with a compressed air inlet of the coal injection oxygen lance. The oxygen blowing and coal injection secondary lead smelting furnace has the advantages of simple structure and low manufacturing cost; combustion is more complete, and the smelting efficiency is improved; and the pulverized coal goes deep into molten liquid slag to accelerate the decomposition of lead sulfate, so that the consumption of scrap iron or iron ore is greatly reduced, and the slag yield is reduced.
Owner:JIANGSU NEW CHUNXING RESOURCE RECYCLING CO LTD
Method for treating high-concentration organic hybrid wastewater by using micro-electrolytic filler
InactiveCN106430805AHigh removal rateLow slag productionWater treatment compoundsTreatment involving filtrationHigh concentrationWastewater
The invention discloses a method for treating high-concentration organic hybrid wastewater by using a micro-electrolytic filler. The method comprises the following steps: filtering the high-concentration organic hybrid wastewater to remove insoluble solid impurities, carrying out air floatation to remove oil, adjusting the pH value by using an acid or an alkali, allowing the obtained wastewater to go through a micro-electrolytic filled column, adding hydrogen peroxide into outlet water, carrying out a reaction for a certain time, neutralizing obtained water, filtering the neutralized water, and carrying out biochemical treatment on the obtained outlet water to realize standard-reaching discharge. The method has the advantages of high practicality, simple technology, high COD removal rate and low cost, and is a good treatment method of the high-concentration organic hybrid wastewater.
Owner:四川欣欣环保科技有限公司
A kind of treatment method of organic waste water containing arsenic
ActiveCN111470671BInfluent COD concentration requirement is lowSimple processWater treatment parameter controlWater treatment compoundsArsenite ionFenton oxidation
The invention relates to a method for treating arsenic-containing organic wastewater, comprising the following steps: (1) adjusting the pH of the arsenic-containing organic wastewater to 2 to 4, allowing the pH-adjusted wastewater to flow through a nano-iron particle generating device to make the nano-iron particles The iron particle generation device generates nano-iron particles in situ in wastewater; (2), adding H to the wastewater added with nano-iron particles 2 o 2 Carrying out the nano-iron / heterogeneous Fenton oxidation reaction until the reaction is completed; (3), adjusting the pH of the mixed liquid after the reaction to 8-9, and arsenic ion flocculation and precipitation are separated from the waste water. The treatment method of the invention has good effect on removing arsenic and COD from the arsenic-containing organic wastewater, and can meet increasingly stringent arsenic discharge standards.
Owner:LASER RES INST OF SHANDONG ACAD OF SCI
Deironing method for reducing accumulated iron ions in electrodeposition solution
InactiveCN111304693AImprove removal efficiencyHigh in ironElectrolysis componentsPhotography auxillary processesSodium chlorateSlag
The invention discloses a deironing method for reducing accumulated iron ions in an electrodeposition solution. The method comprises the steps of adding the electrodeposition solution obtained by an electrodeposition process into a first deironing reaction tank, oxidizing divalent iron ions in the electrodeposition solution into trivalent iron ions by using a sodium chlorate solution to obtain a first mixed feed liquid, then continuously performing a low-temperature deironing reaction on the first mixed feed liquid, controlling the pH value of the low-temperature deironing reaction to enable the trivalent iron ions in the first mixed feed liquid to generate goethite, obtaining a second mixed feed liquid, and carrying out filter pressing treatment to obtain an electrodeposition solution after deironing. Therefore, the method has the advantages that the temperature requirement is low, the iron content of iron slag is high, the method is suitable for continuous production, the entrainmenteffect on valuable metal cobalt in the deironing process is weak, the removal efficiency of the divalent iron is improved by the deironing process, the energy consumption in the deironing process isreduced, the slag yield is less, and the operation stability is further enhanced by the continuous process.
Owner:GEM JIANGSU COBALT IND CO LTD
A method for recovering waste salt in saline wastewater in the production of tebuconazole
ActiveCN112125460BHigh removal rateLow slag productionWater treatment parameter controlWater treatment compoundsCatalytic oxidationEnvironmental engineering
The invention discloses a method for recovering waste salt from salt-containing wastewater in the production of tebuconazole. It is specifically implemented according to the following steps: adjusting the pH of the salt-containing wastewater to 3-4; passing the wastewater into electro-Fenton catalytic oxidation and electrochemical processes. The reaction is carried out for 24 hours in the oxidation-coupled double oxidation reactor; after the reaction is completed, the pH of the wastewater is adjusted back to 7-8; the double oxidation effluent is crystallized by multi-effect evaporation to obtain high-purity potassium sulfate solid salt; the potassium content of the potassium sulfate solid salt reaches Requirements for qualified potassium sulfate products for agricultural use (GB20406-2006). The present invention uses tebuconazole synthetic wastewater as raw material, turning waste into treasure, which is beneficial to environmental protection and comprehensive utilization. The process cost of the present invention is low, the recovered potassium sulfate is of high quality, has good crystal size, and the recovery rate can reach 90%. Above, the potassium content of the product can reach more than 45% (in K 2 O meter).
Owner:南京华工创新环境研究院有限公司 +1
A kind of gentamicin fermentation waste liquid solid-liquid separation treatment method
ActiveCN112546731BReduce filter specific resistanceSpeed up filteringTreatment involving filtrationMultistage water/sewage treatmentBiotechnologyFiltration
The invention discloses a solid-liquid separation treatment method for gentamicin fermentation waste liquid. After conditioning and modifying the gentamicin fermentation waste liquid, the filtration specific resistance of the fermentation waste liquid is reduced, and then filtered through a plate and frame. It can effectively intercept suspended solids (SS), increase the filtration speed of fermentation waste liquid, and prevent suspended solids in fermentation waste liquid from entering the water treatment biochemical system and causing serious impact on the biochemical system. The key technology of conditioning modification is to add lovastatin fermented bacteria residue, which belongs to the waste of fermented raw materials, and has the characteristics of large particle size, light weight after drying, and water swelling. The water content of the fungus residue obtained after filtration in the invention can reach below 70%, which reduces the amount of residue produced and is beneficial to the subsequent drying and incineration of the fungus residue. At the same time, the filtered filtrate is clarified, free of SS, and COD can be reduced by 50%, which is beneficial to the subsequent entry into the biochemical treatment system.
Owner:福安药业集团烟台只楚药业有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com