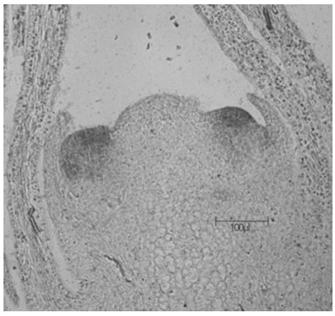
In-situ hybridization method for dianthus chinensis
A Chinese carnation and in situ hybridization technology, applied in the field of molecular biology of horticultural plants, can solve the problems of low signal sensitivity, gene expression detection, unclear coloring, etc., achieve low hybridization background, clear coloring, improve flexibility and reliability operational effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0071] 1. Fixation and embedding of Chinese Dianthus organs and tissues
[0072] Step A1: Fixation of Chinese Dianthus Buds
[0073] Take 0.3-0.5cm long Chinese Dianthus flower buds, place them in 10ml centrifuge tubes, fix them with EAF fixative respectively, label them (indicating date, time, sample) for 30min, open the lid, and vacuum at 0.08MPa for 30min.
[0074] Refer to Table 1 to prepare gradients to prepare ethanol (alcohol) solutions.
[0075] Table 1 Configuration of gradient concentration ethanol solution
[0076]
Absolute ethanol
Ultra-pure water
30% ethanol solution
30ml
Dilute to 100ml
50% ethanol solution
50ml
Dilute to 100ml
75% ethanol solution
75ml
Dilute to 100ml
85% ethanol solution
85ml
Dilute to 100ml
95% ethanol solution
95ml
Dilute to 100ml
100% ethanol
100ml
Dilute to 100ml
[0077] Step A2: Dehydration of Chinese Dianthus Buds
[0078] From th...
Embodiment 2
[0116] Step C1: Deparaffinization and rehydration of samples:
[0117] According to the method described in the above-mentioned Example 1, the embedded Dianthus flower bud sample was obtained using a German Lycra RM2265 microtome, and the wax block was sliced, with a thickness of 9 μm, and a drop of DEPC water was dropped on the adhesive slide, and the slice was placed on it. Spread the slices on a heating plate at 37°C and dry them, and bake the stretched slices in an oven at 37°C for more than 12 hours. Take out the slides, wash them twice with xylene, 10 minutes each time, then rehydrate with 100%, 95%, 70%, 50%, 30% ethanol aqueous solution, each treatment for 2 minutes, wash twice with DEPC, each time 2min.
[0118] Step C2: Protein Digestion of Samples
[0119] Specifically, this embodiment is to move the slide with the sample into 1×PBS buffer, let it stand for 2min, then incubate the slide in 0.2M HCl for 15min, then put it in DEPC water for 3min, and rinse Excess H...
Embodiment 3
[0131] Step C1: Deparaffinization and rehydration of samples
[0132] According to the method described in the above-mentioned Example 1, the embedded Dianthus flower buds were obtained. Use a Leica RM2265 microtome to slice the wax block with a thickness of 10 μm. Drop a drop of DEPC water on the adhesive slide, place the slice on it, and incubate at 37°C. Spread the slices on a hot plate and dry them, and bake the stretched slices in an oven at 37°C for more than 12 hours. Take out the slides and wash them twice with xylene for 10 minutes each time, then rehydrate with ethanol solutions with gradient concentrations of 100%, 95%, 70%, 50% and 30% for 1 minute each time, and wash with DEPC water Twice, 2 minutes each time.
[0133] Step C2: Protein Digestion of Samples
[0134] Specifically, this embodiment is to move the slide with the sample into 1×PBS buffer, let it stand for 2min, then incubate the slide in 0.2M HCl for 15min, then put it in DEPC water for 3min, and rins...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com