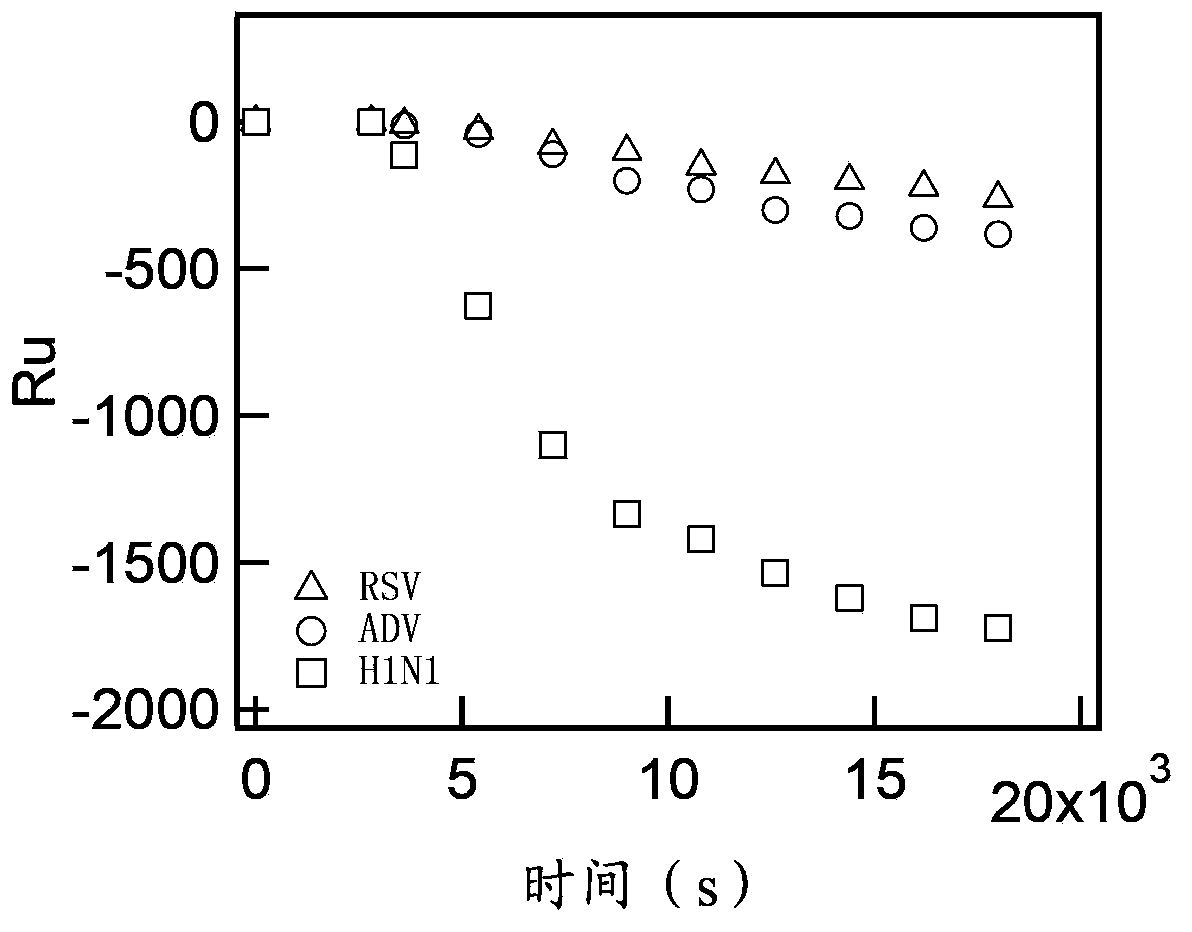
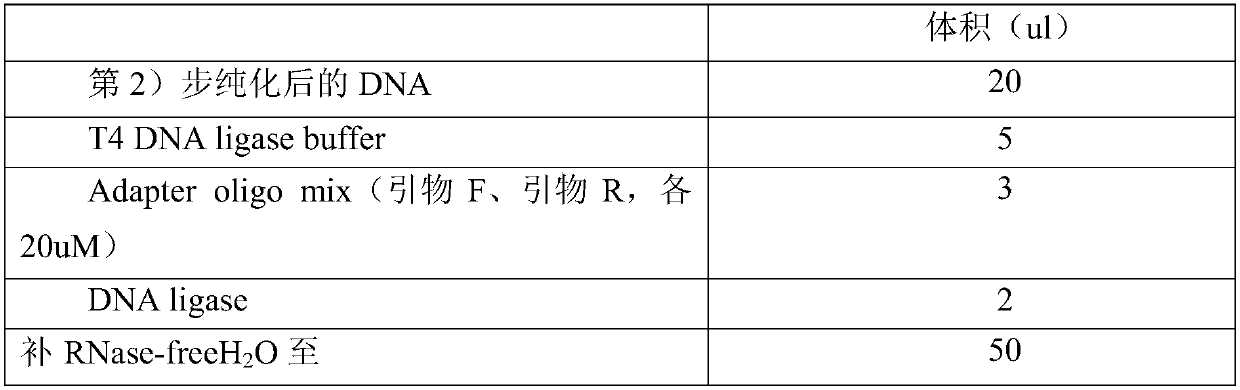
Patents
Literature
56 results about "RNA Probes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
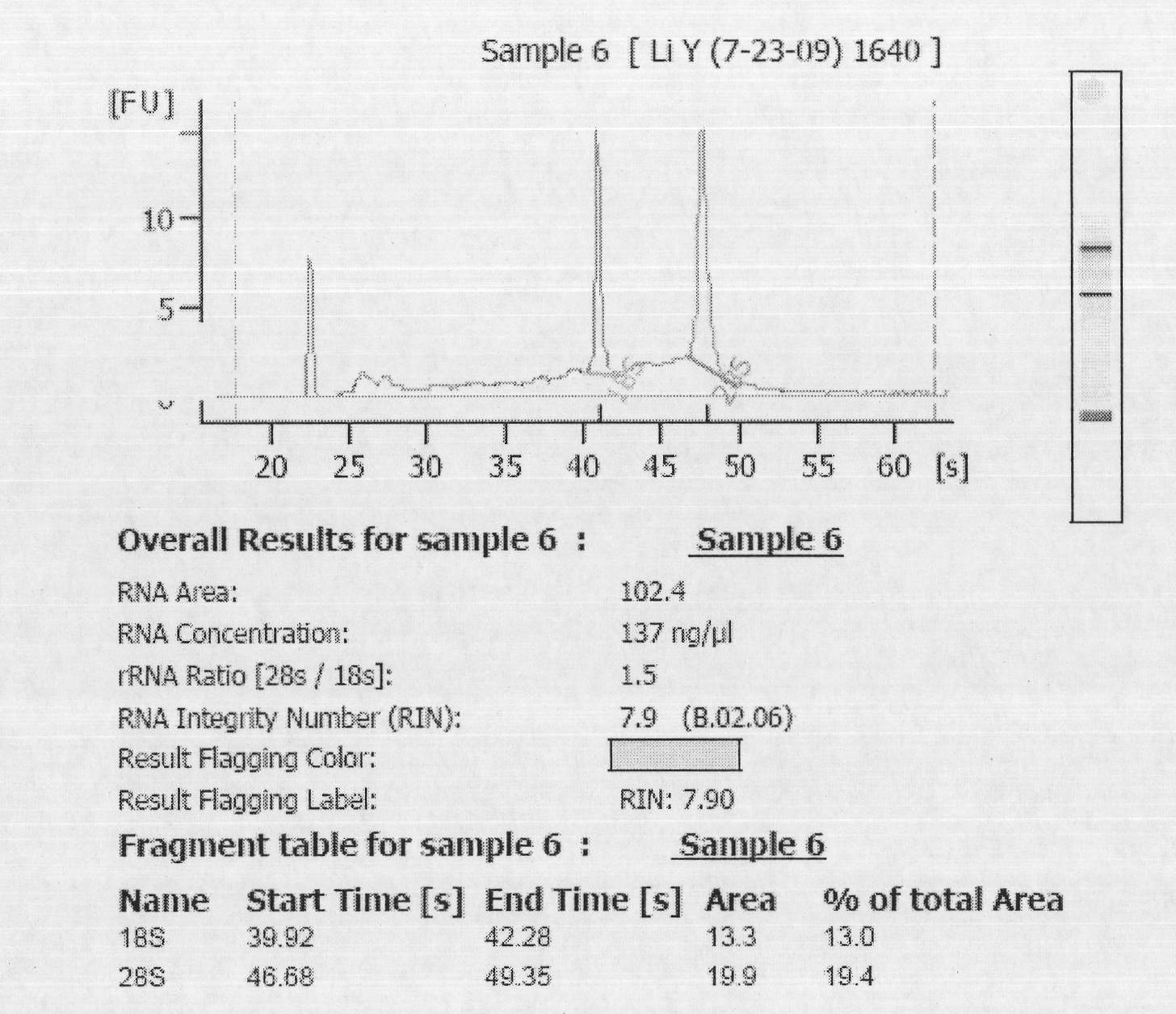
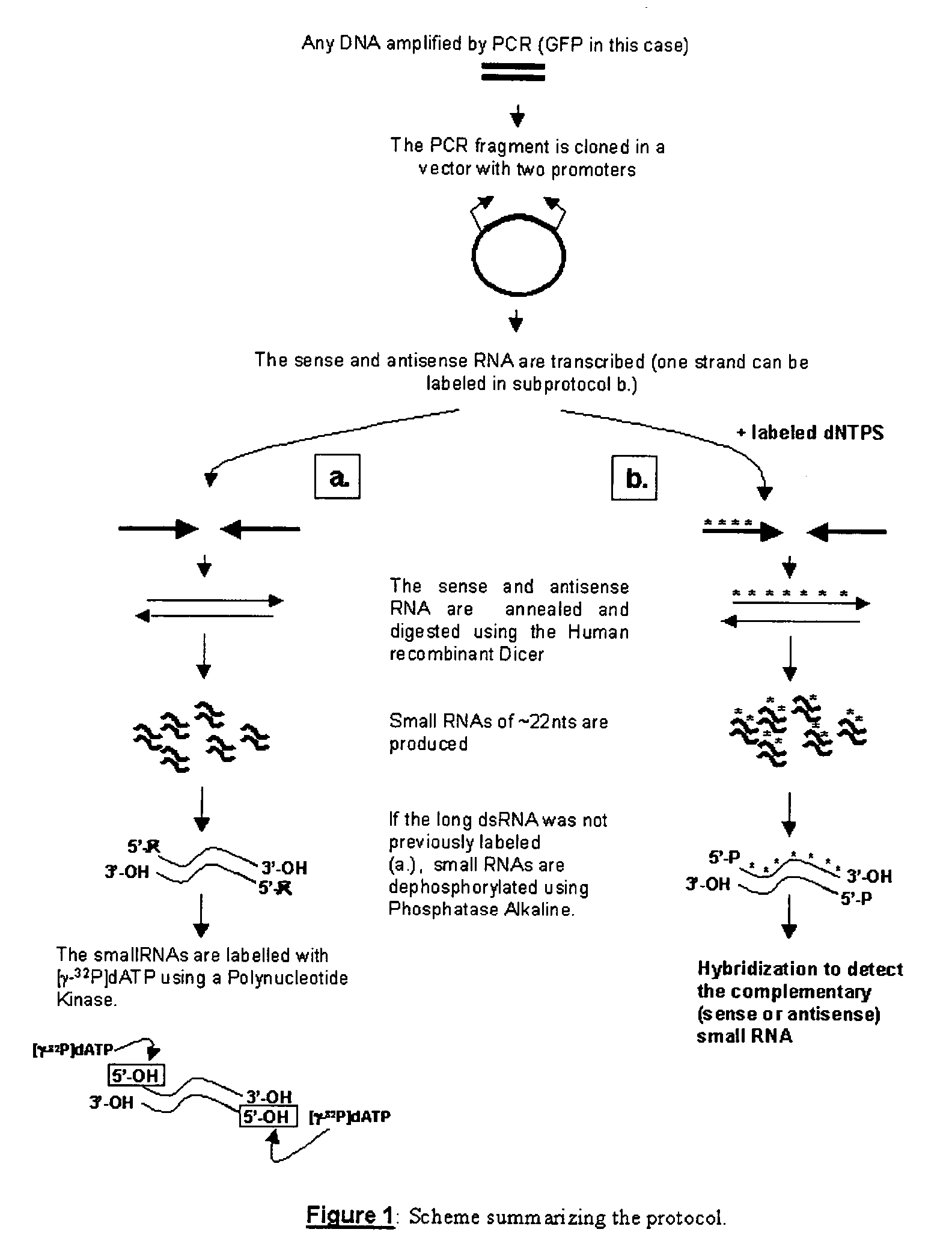
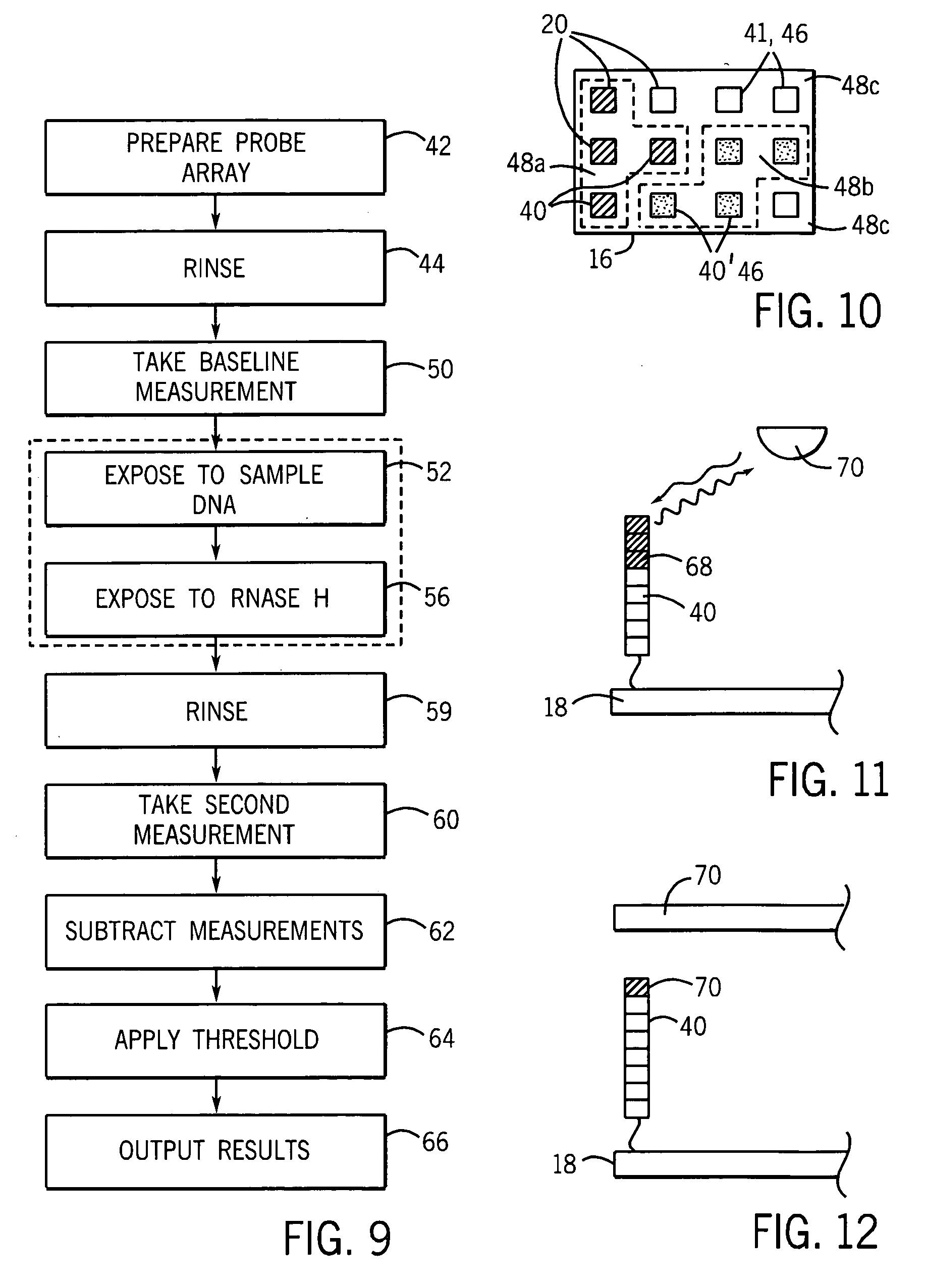
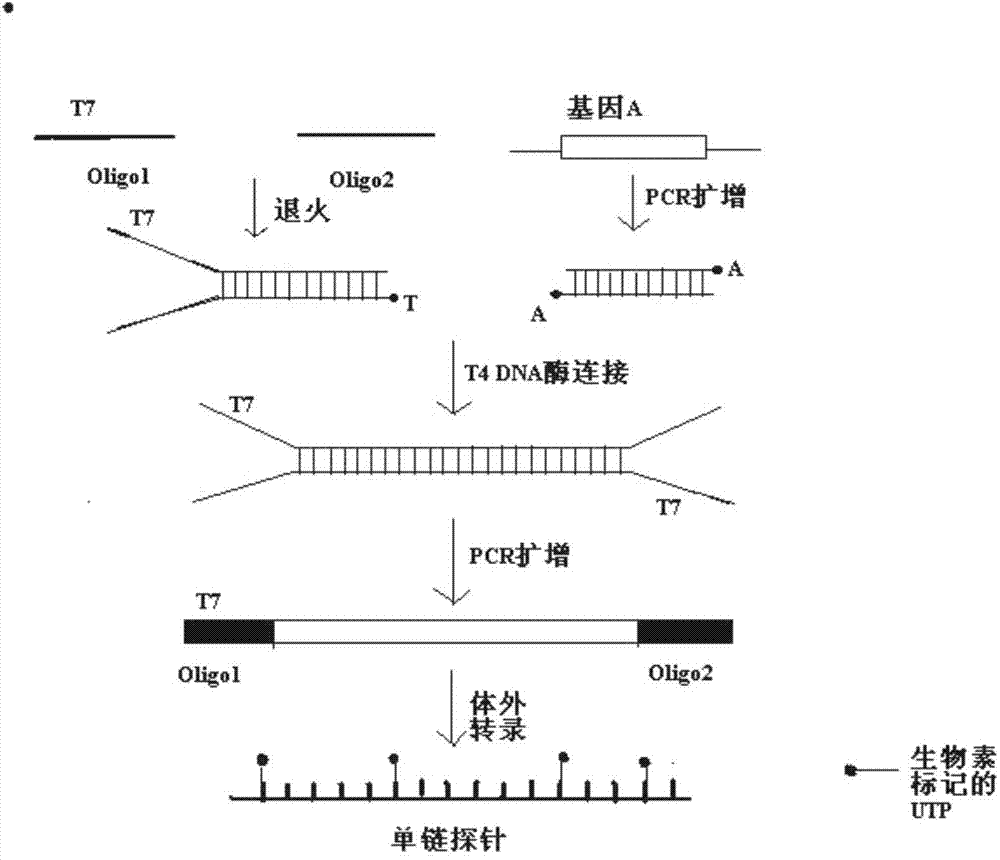
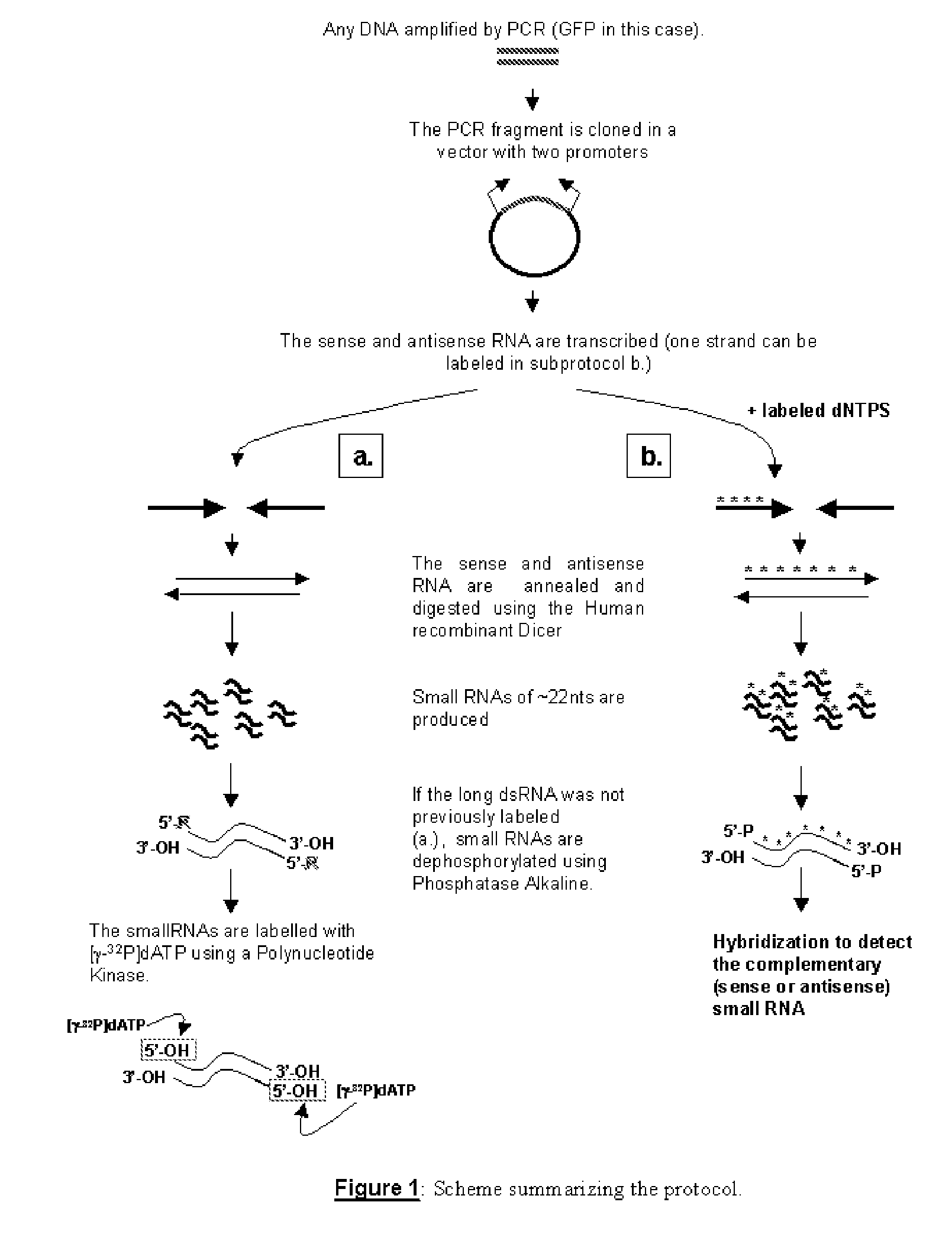
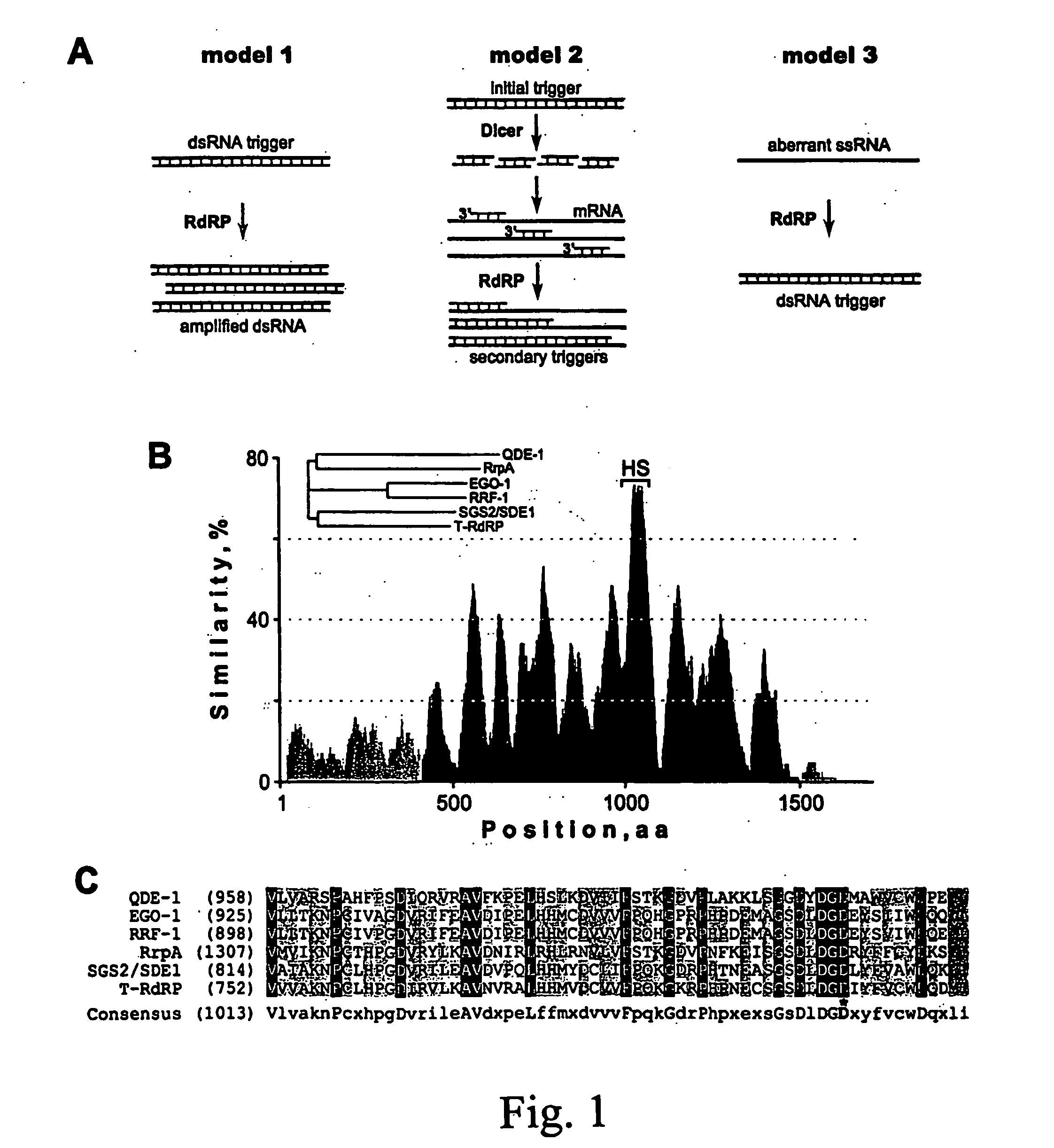
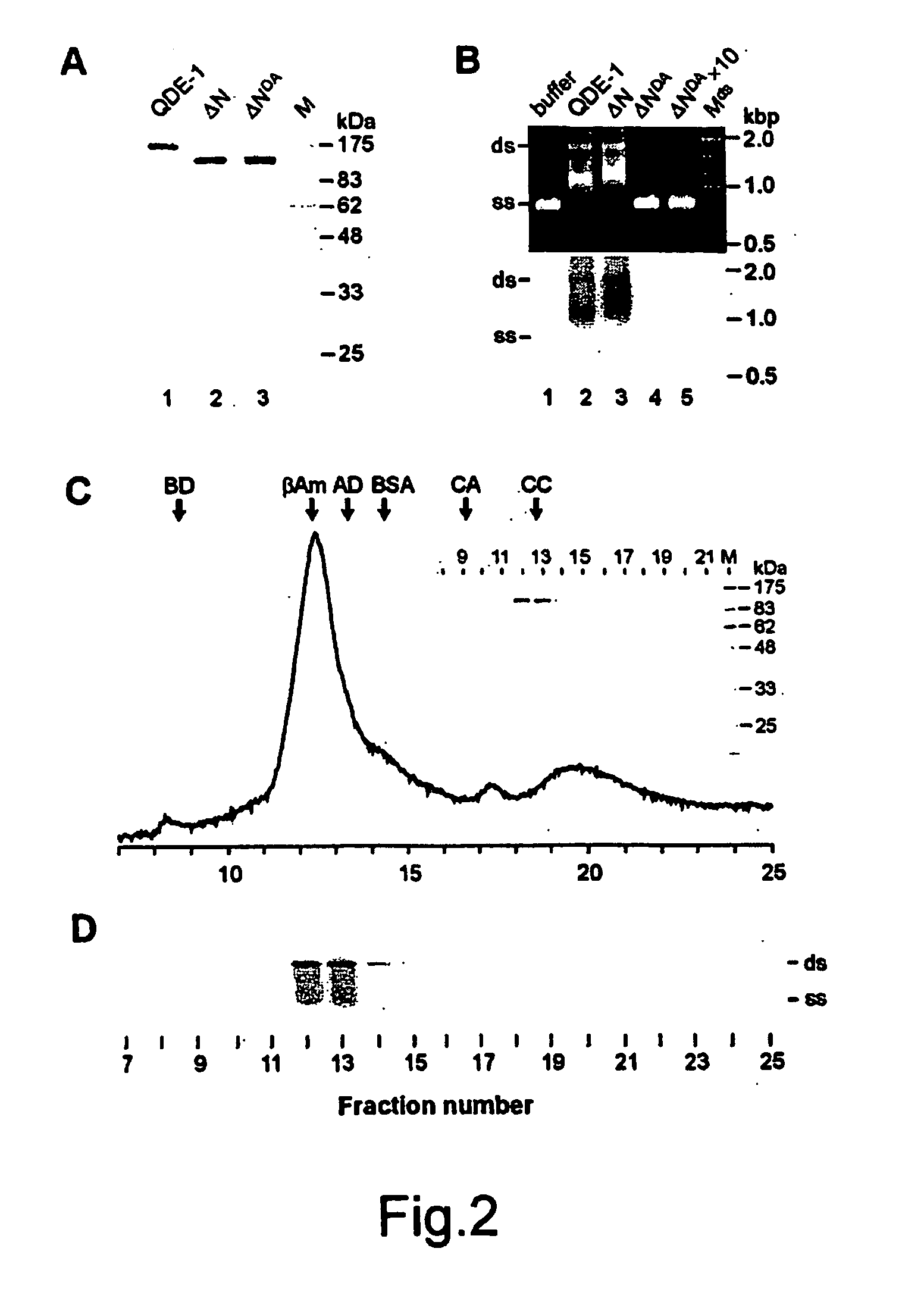
RNA probes are usually prepared by in vitro transcription (see Fig. 1 above). The RNA probe is transcribed from a linear DNA template using highly specific bacteriophage DNA-dependant RNA polymerases from the Salmonella bacteriophage SP6, and the E. coli. bacteriophages T3 and T7 (RNA polymerase T7, T3 or SP6).
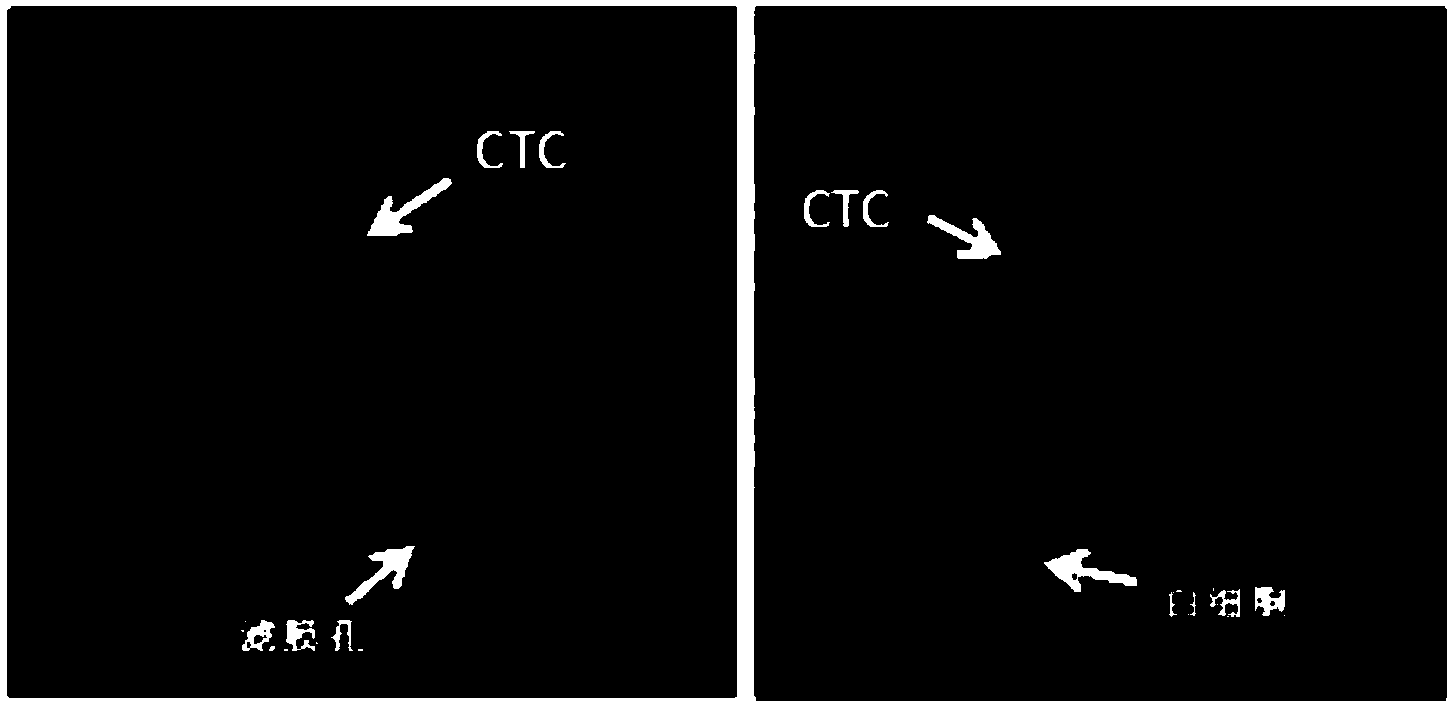
Circulating tumor cell identification kit and circulating tumor cell identification method
ActiveCN104031993AComprehensive detectionAvoid false negativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHybridization probeFluorescence
The invention discloses a circulating tumor cell identification kit and a circulating tumor cell identification method. The circulating tumor cell identification kit comprises a detection probe for detecting mRNA of an epithelial cell marking gene and / or mRNA of a mesenchymal cell marking gene, wherein the epithelial cell marking gene is selected from one or more of CDH2, VIMENTIN, FN1 and AKT2. Multiple RNA probes are adopted in the identification method, specific genes of a plurality of circulating tumor cells (CTCs) can be marked at the same time and are divided into genes I (epithelial genes), genes II (epithelial-mesenchymal genes) and genes III (mesenchymal genes), and false positive results caused by lack of part of the specific genes of the CTCs in a process that the CTCs enter peripheral blood for circulation are reduced; the method can be finished within eight hours, and a single copied mRNA hybridization probe is combined with a corresponding fluorescent probe by virtue of a signal amplification system, so that the detection sensitivity of in-situ RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) hybridization is remarkably improved.
Owner:SUREXAM BIO TECH
Solid phase technique for selectively isolating nucleic acids
InactiveUS20060003357A1High purityIncrease ionic strengthMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid reductionPurification methodsMagnetic bead
A method of isolating target nucleic acid molecules from a solution comprising a mixture of different size nucleic acid molecules, in the presence or absence of other biomolecules, by selectively facilitating the adsorption of a particular species of nucleic acid molecule to the functional group-coated surface of magnetically responsive paramagnetic microparticles is disclosed. Separation is accomplished by manipulating the ionic strength and polyalkylene glycol concentration of the solution to selectively precipitate, and reversibly adsorb, the target species of nucleic acid molecule, characterized by a particular molecular size, to paramagnetic microparticles, the surfaces of which act as a bioaffinity adsorbent for the nucleic acids. The target nucleic acid is isolated from the starting mixture based on molecular size and through the removal of magnetic beads to which the target nucleic acid molecules have been adsorbed. The disclosed method provides a simple, robust and readily automatable means of nucleic acid isolation and purification which produces high quality nucleic acid molecules suitable for: capillary electrophoresis, nucleotide sequencing, reverse transcription cloning the transfection, transduction or microinjection of mammalian cells, gene therapy protocols, the in vitro synthesis of RNA probes, cDNA library construction and PCR amplification.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
Methods and reagents for the isolation of nucleic acids
InactiveUS20060024701A1Simple procedureImprove automationMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid reductionMicroinjectionsSolid phases
The invention includes reagents and methods for the isolation of nucleic acids. The reagents described herein contain a nucleic acid precipitating agent and a solid phase carrier. The reagents can optionally be formulated to cause the lysis of a cell. These reagents can be used to isolate a target nucleic acid molecule from a cell or a solution containing a mixture of different size nucleic acid molecules. The disclosed reagents and methods provides a simple, robust and readily automatable means of nucleic acid isolation and purification which produces high quality nucleic acid molecules suitable for: capillary electrophoresis, nucleotide sequencing, reverse transcription cloning the transfection, transduction or microinjection of mammalian cells, gene therapy protocols, the in vitro synthesis of RNA probes, cDNA library construction and PCR amplification.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
Method for screening new internal reference molecules suitable for cervical tissue micro RNA real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR research
InactiveCN101818202AAvoid YieldAvoid quality problemsMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceCervical tissueFluorescence
The invention discloses a method for screening new internal reference molecules suitable for cervical tissue micro RNA real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR research. The method comprises the following technical steps: screening human Micro RNA probes by using a Micro RNA chip, and selecting Micro RNAs with constant normal tissue expression and high expression abundance of cervical cancer and cervix as candidate internal references; selecting a normal cervical epithelial tissue and a cancerous cervical tissue as clinical cervical tissue specimens respectively, and verifying the specimens by using fluorescence quantitative PCR; and analyzing data by using two special internal reference analysis software comprising geNorm software and Norm Finder so as to discover the internal reference molecules suitable for cervical tissue Micro RNA research. The internal reference molecules screened and verified by using the method of the invention can avoid possible differences of different cervical tissue specimens on the yield, quality and reverse transcription efficiency of the RNA, well correct and standardize the data for real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR detection, and improve the accuracy and the reliability of the search.
Owner:ATTACHED OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY OSPITAL MEDICALCOLLEGE ZHEJIANG UNIV
Composition for detecting nucleic acid and method for detecting nucleic acid using same
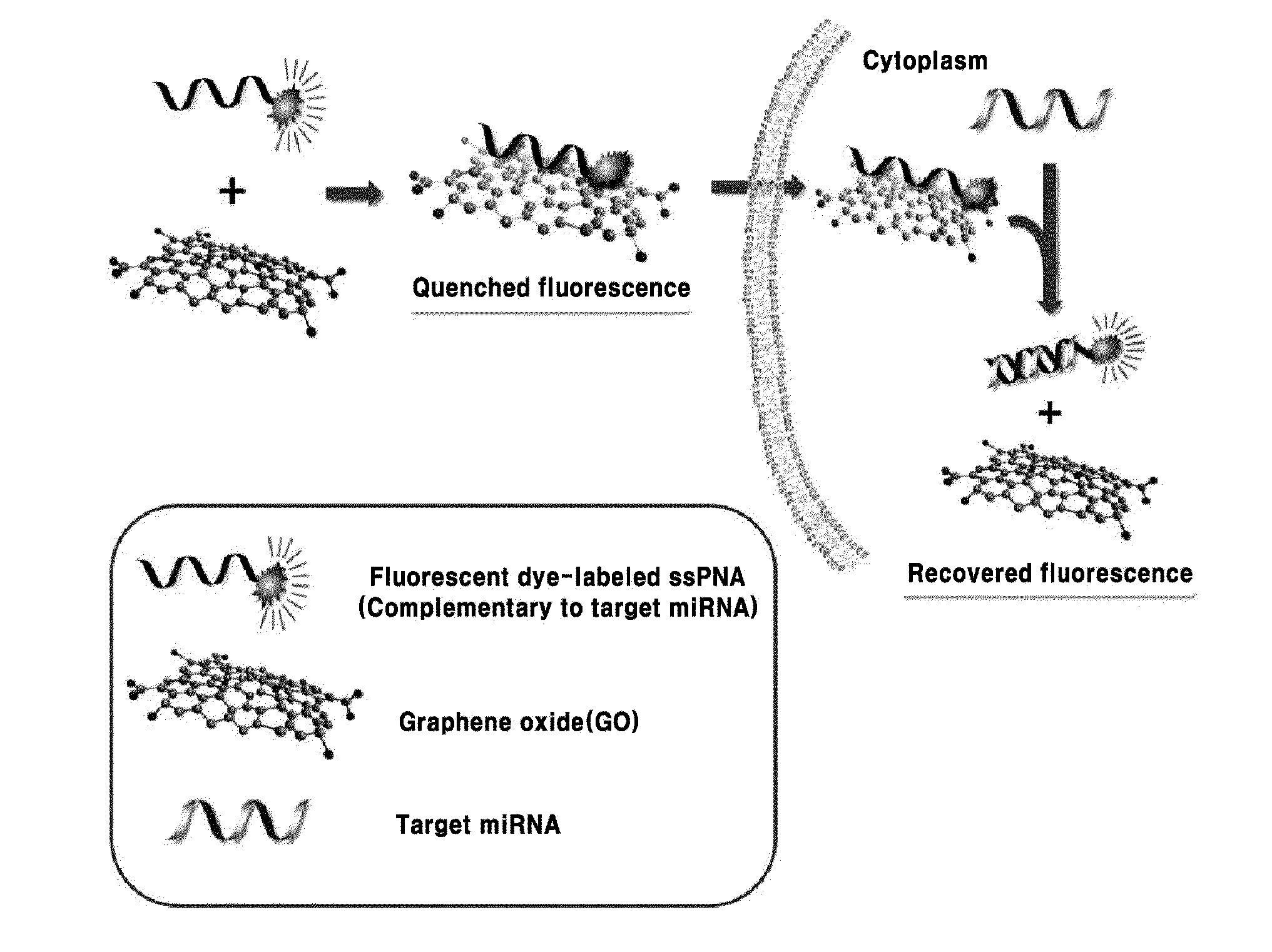
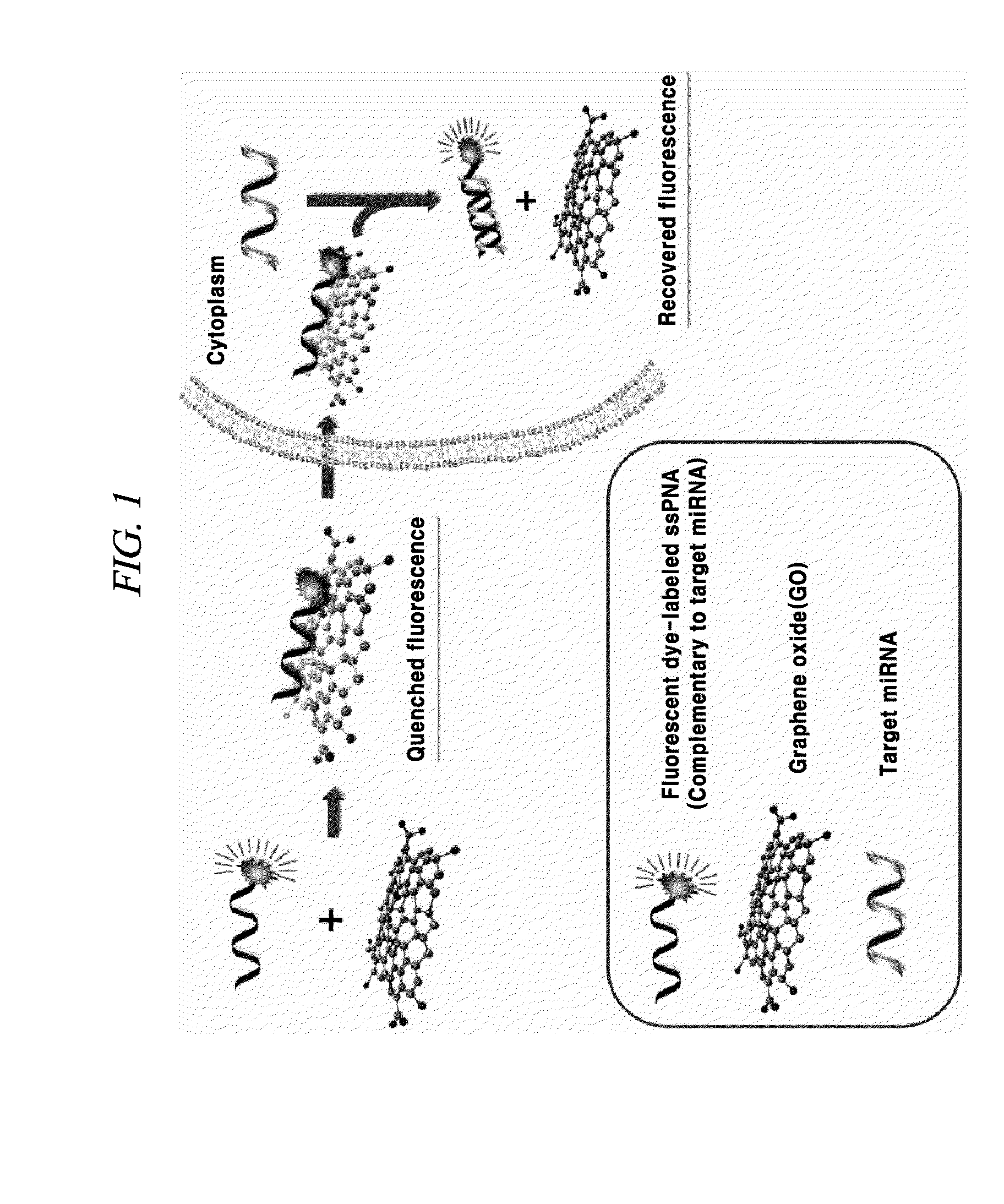
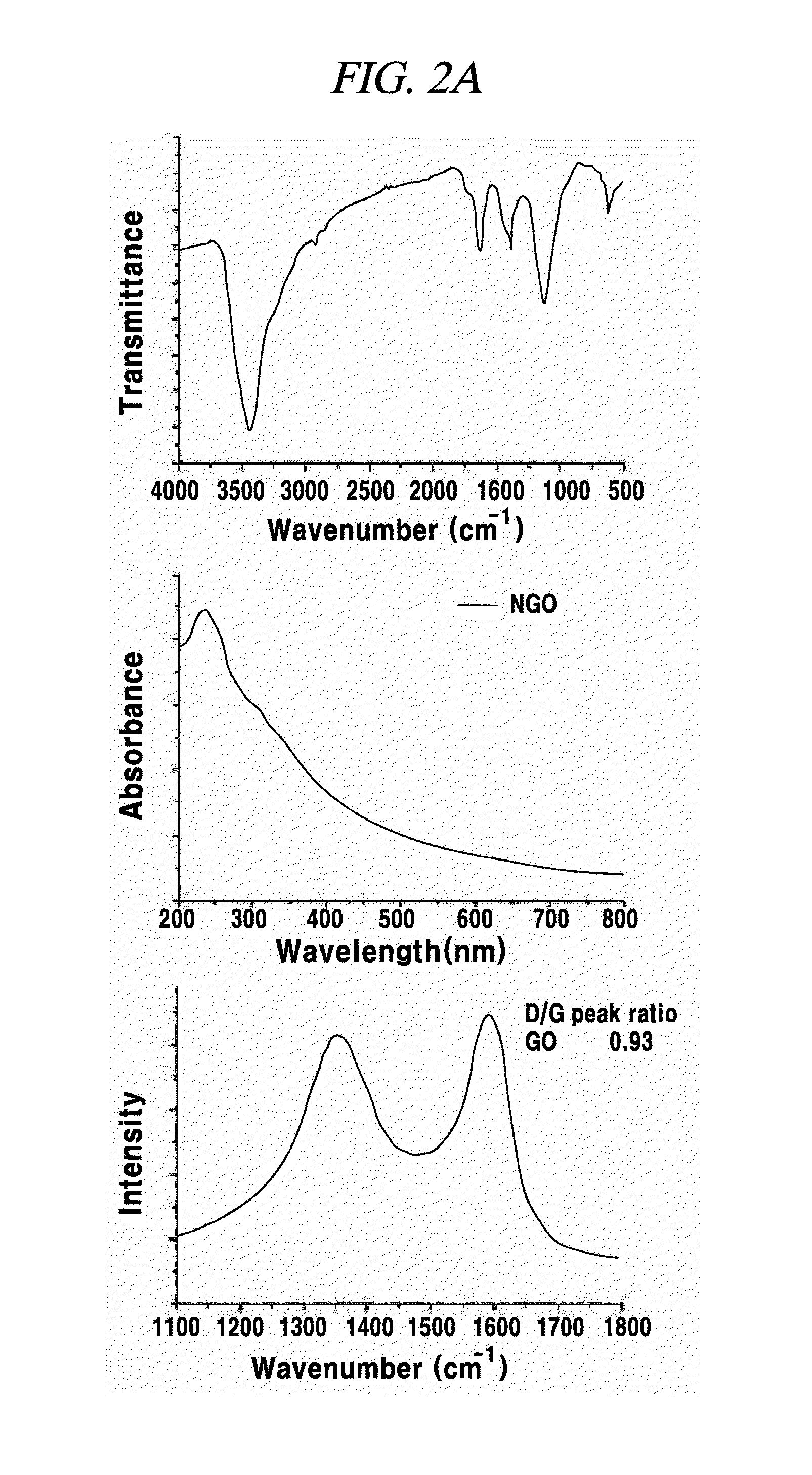
ActiveUS20150080251A1Stable storageLow pricePeptide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceGraphene
The present invention relates a composition, including an RNA probe which contains a fluorescence material absorbed in graphene oxide, for detecting a nucleic acid, and to a method for detecting a nucleic acid using the composition. By means of the composition and the method, the presence and expression pattern of a target nucleic acid in a sample or a cell can be observed in real time, and a plurality of target nucleic acids can be detected in multitude.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
RNA probe capable of detecting multiple neonatal hereditary diseases and gene screening kit
InactiveCN104673925AAchieve early diagnosisAchieve therapeutic effectMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationExonBiology
The invention provides a RNA probe capable of simultaneously detecting multiple neonatal hereditary diseases and a qualitative detection method in vitro of multiple neonatal genetic metabolic diseases, and the detection method provided by the invention is used for reducing the detection cost. Specifically, the invention discloses a RNA probe capable of simultaneously detecting multiple neonatal hereditary diseases, and the design method of the RNA probe comprises the following steps: 1) obtaining exon regions of genes corresponding to the neonatal genetic metabolic diseases; 2) regulating an oligonucleotide design principle. 1760 oligonucleotide sequences of the RNA probe provided by the invention are specifically as shown in table 1. The invention further provides a kit containing the RNA probe, and the kit can be used for simultaneously detecting multiple neonatal hereditary diseases.
Owner:绍兴锐创生物科技有限公司
Bastard halibut embryonic-period primordial germ cell tracking and positioning method
InactiveCN104878102AEasy to operateSlow down the speed of color developmentMicrobiological testing/measurementYolkPlant Germ Cells
The invention relates to a positioning and marking method for embryonic-period primordial germ cells (PGCs), in particular to a bastard halibut embryonic-period primordial germ cell tracking and positioning method. The bastard halibut embryonic-period primordial germ cell tracking and positioning method includes the steps of fixing collected various periods of embryo samples of the bastard halibuts by a 4% PFA solution; using a PBS (phosphate buffer saline) solution with 50% of deionized formamide to preserve the embryo samples at the temperature of -20 DEG C, and subjecting the fixed and preserved embryo samples to oolemma removing, gradient methanol dewatering and rewatering; after rewatering, washing the various periods of embryo samples with PBS buffering liquid without RNA ( ribonucleic acid) enzyme, pre-hybridizing at the temperature of 62-65 DEG C for 2-4 hours; after hybridization, adding a hybridization solution with bastard halibut RNA probes into the various periods of embryo samples subjected to pre-hybridization for hybridizing overnight at the temperature of 62-65 DEG C; after hybridization, subjecting the various periods of embryo samples to washing, antibody incubation and rewashing, keeping away from light, and developing colors to achieve marking for tracking and positioning of the embryonic-period primordial germ cells of the bastard halibuts. The bastard halibut embryonic-period primordial germ cell tracking and positioning method has the advantages that the problems that yolks and oolemma of the samples hybridized in situ conventionally are difficult to strip and a background color is too deep after color developing detection are solved, and operation steps are simplified.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
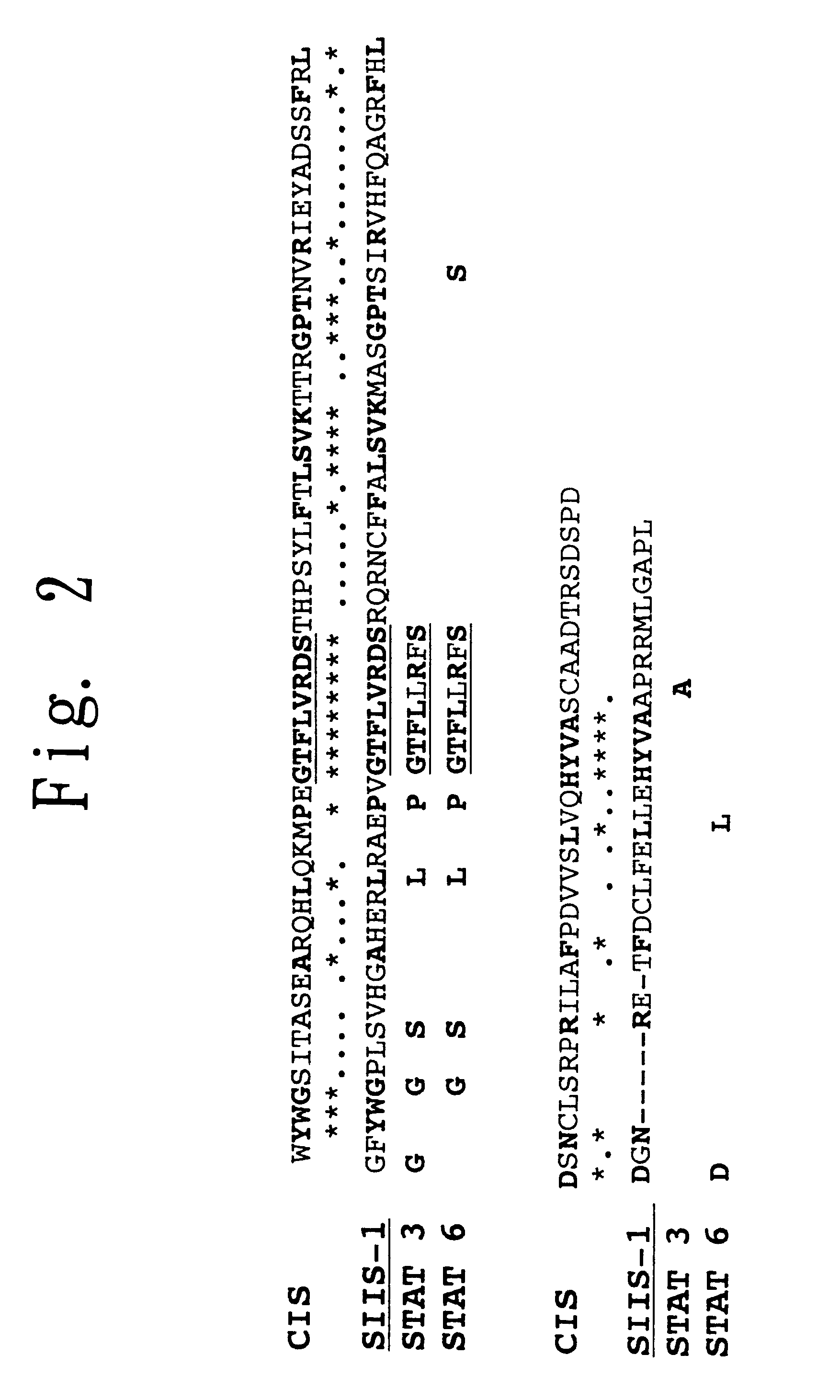
STAT function-regulatory protein
Disclosed is a protein having the ability to inhibit the function of a STAT in a mammalian JAK / STAT signal transduction pathway, which is induced by STAT3 or STAT6, which has the ability to inhibit tyrosine phosphorylation of gp130 or STAT3 and which comprises an SH2 domain; and also disclosed is a DNA coding for the same. Further disclosed is a method for screening a substance having the capability to regulate cytokine activity, in which the protein of the present invention is used. Still further disclosed are an antisense DNA and an antisense RNA capable of inhibiting the biosynthesis of the above-mentioned protein; a monoclonal antibody capable of binding to the above-mentioned protein; and a DNA probe and an RNA probe capable of hybridizing to the above-mentioned DNA. Still further disclosed are a replicable recombinant DNA molecule comprising a replicable expression vector and, operably inserted therein, the DNA of the present invention; a cell of a microorganism or cell culture, transformed with the replicable recombinant DNA molecule; and a method for screening a substance having the capability to regulate cytokine activity in which the transformant is used.
Owner:NAT INST OF BIOMEDICAL INNOVATION HEALTH & NUTRITION
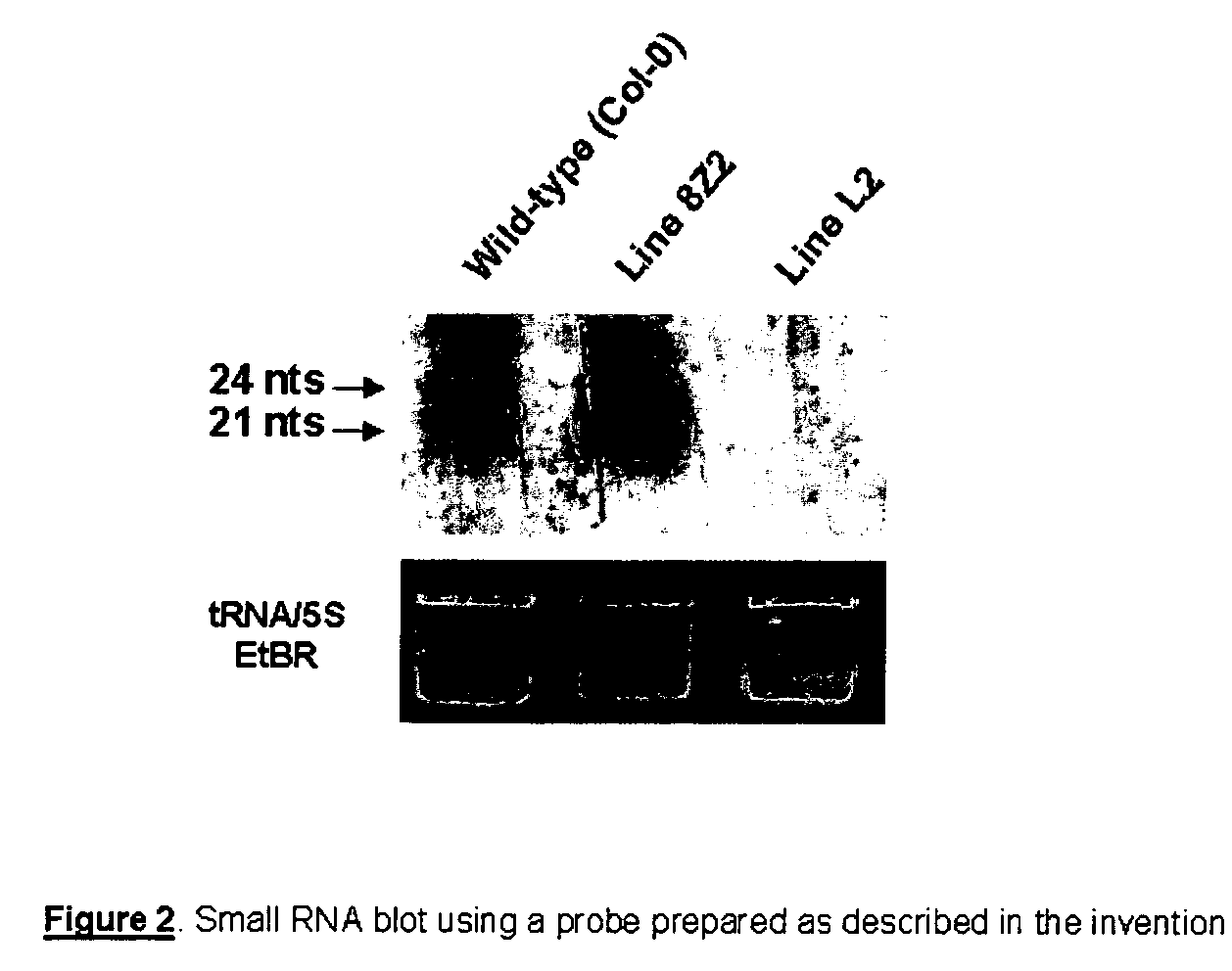
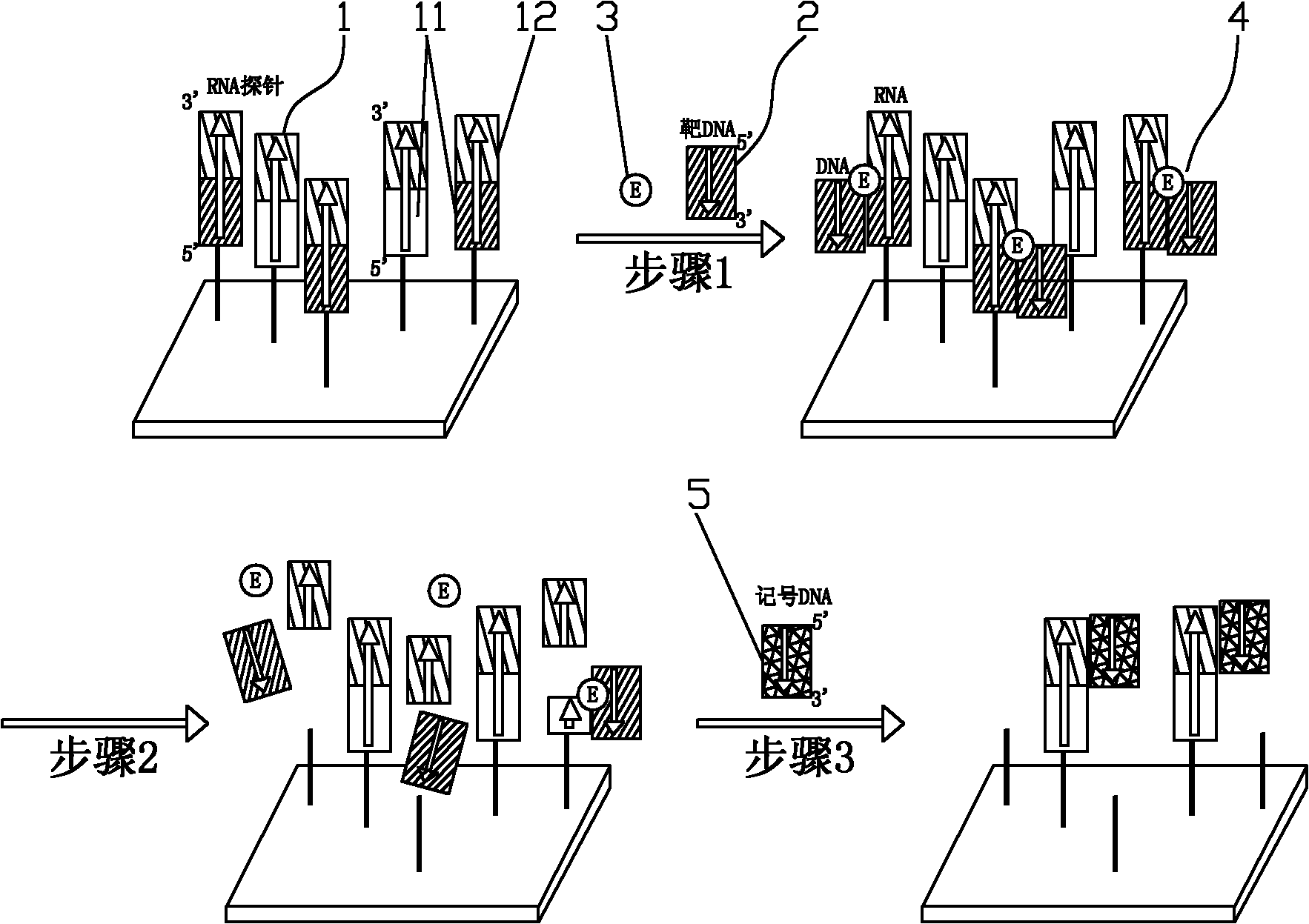
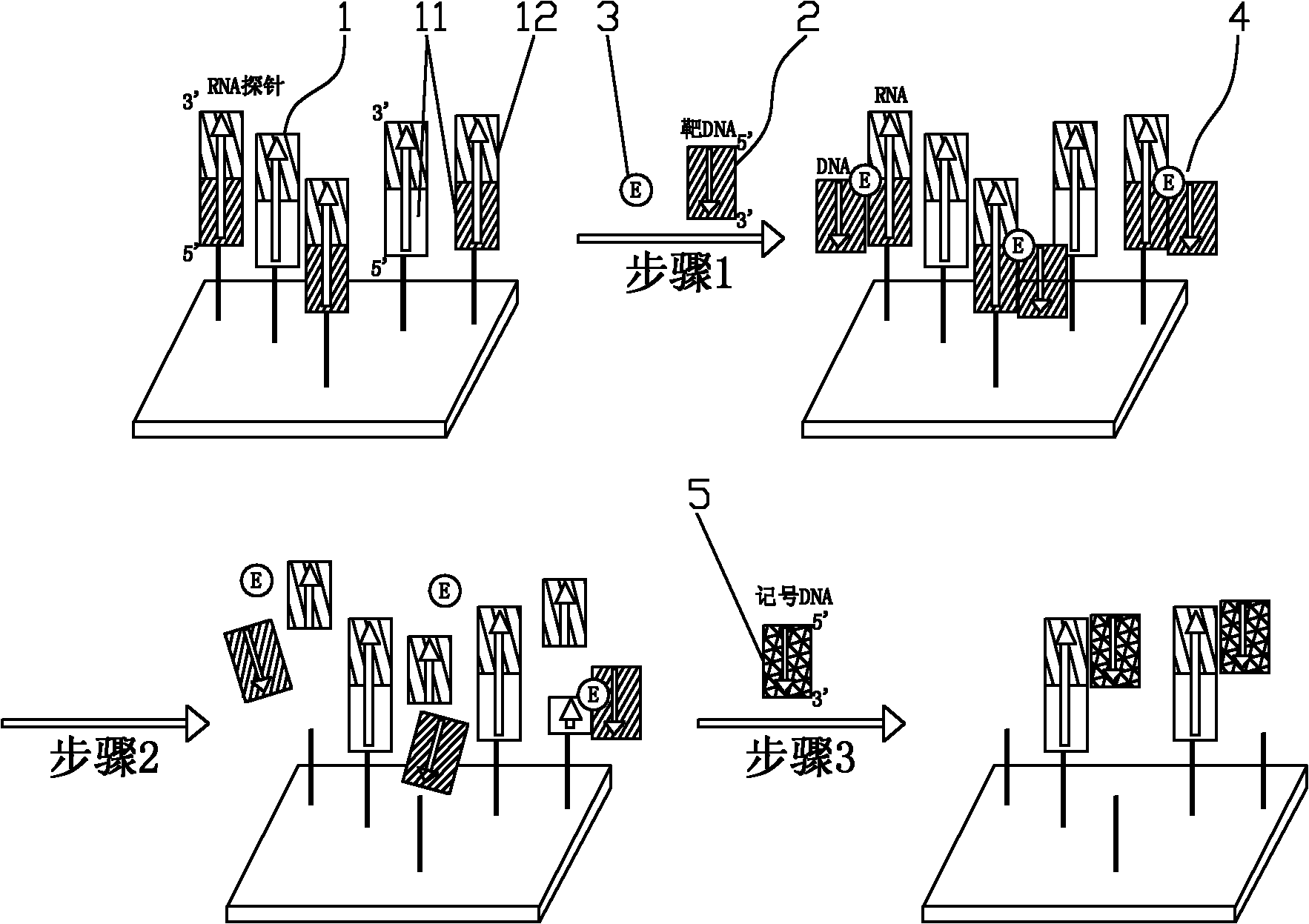
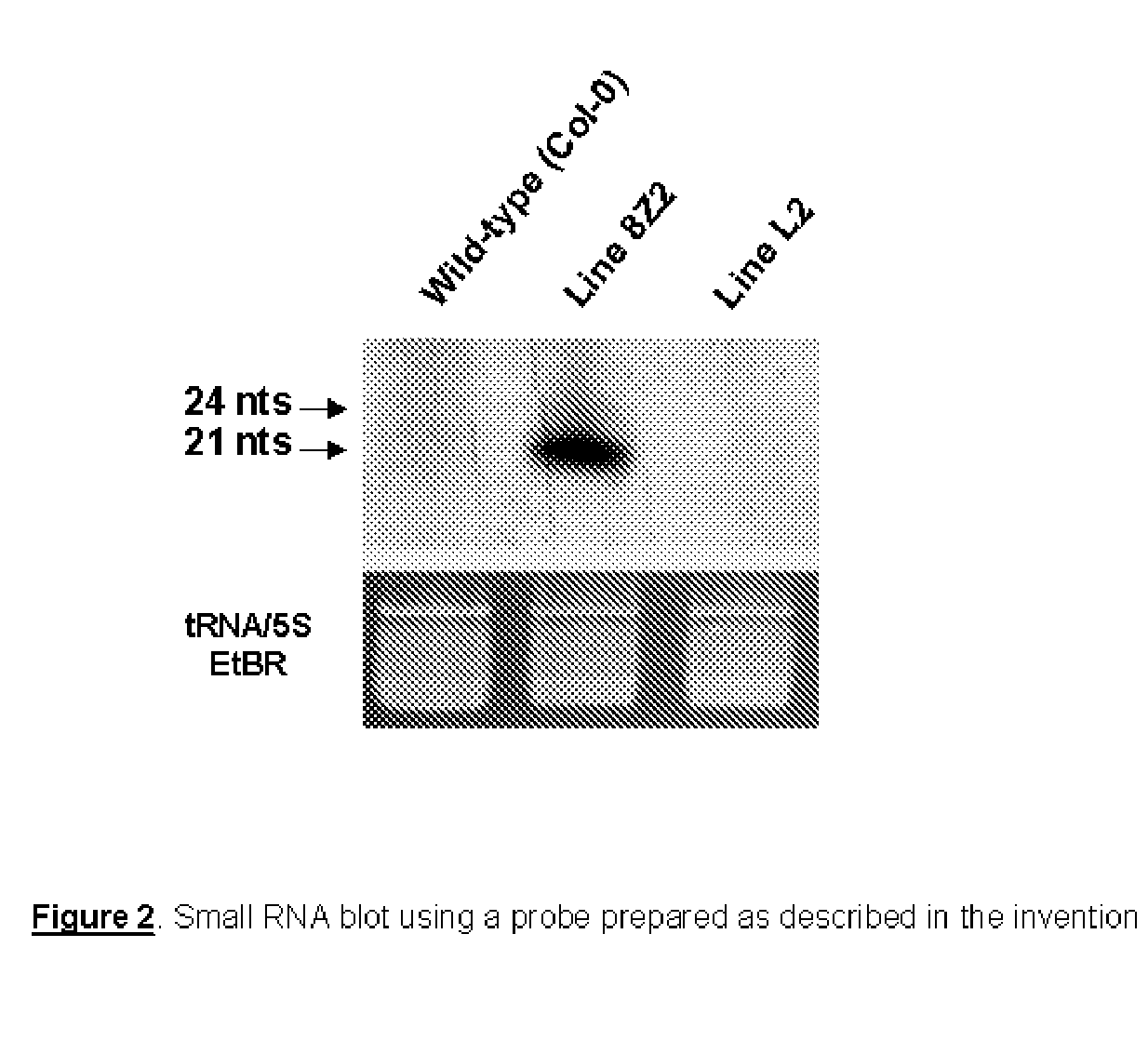
RNA probes
The invention is based in part on the generation of a double stranded RNA molecule substantially covering the whole transcribed region of a gene, and cleaving this using an RNA endonuclease to generate small RNA molecules which are already or may be subsequently labelled. The invention provides small labelled ribonucleic acid (RNA) fragments for use as probes to detect potentially small interfering ribonucleic acid (siRNA) fragments produced in vivo. The invention also provides uses of said small labelled RNA fragments and kits suitable for preparing said small labelled RNA fragments.
Owner:SI AMMOUR AZEDDINE +2
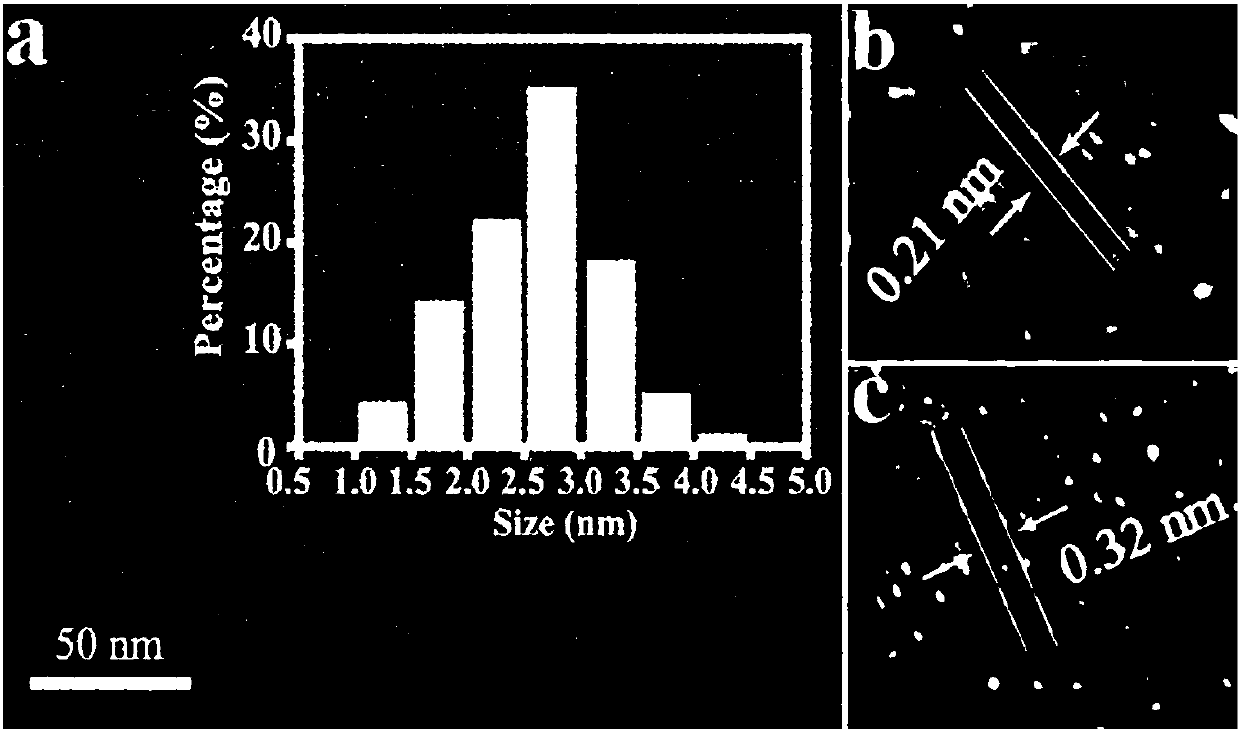
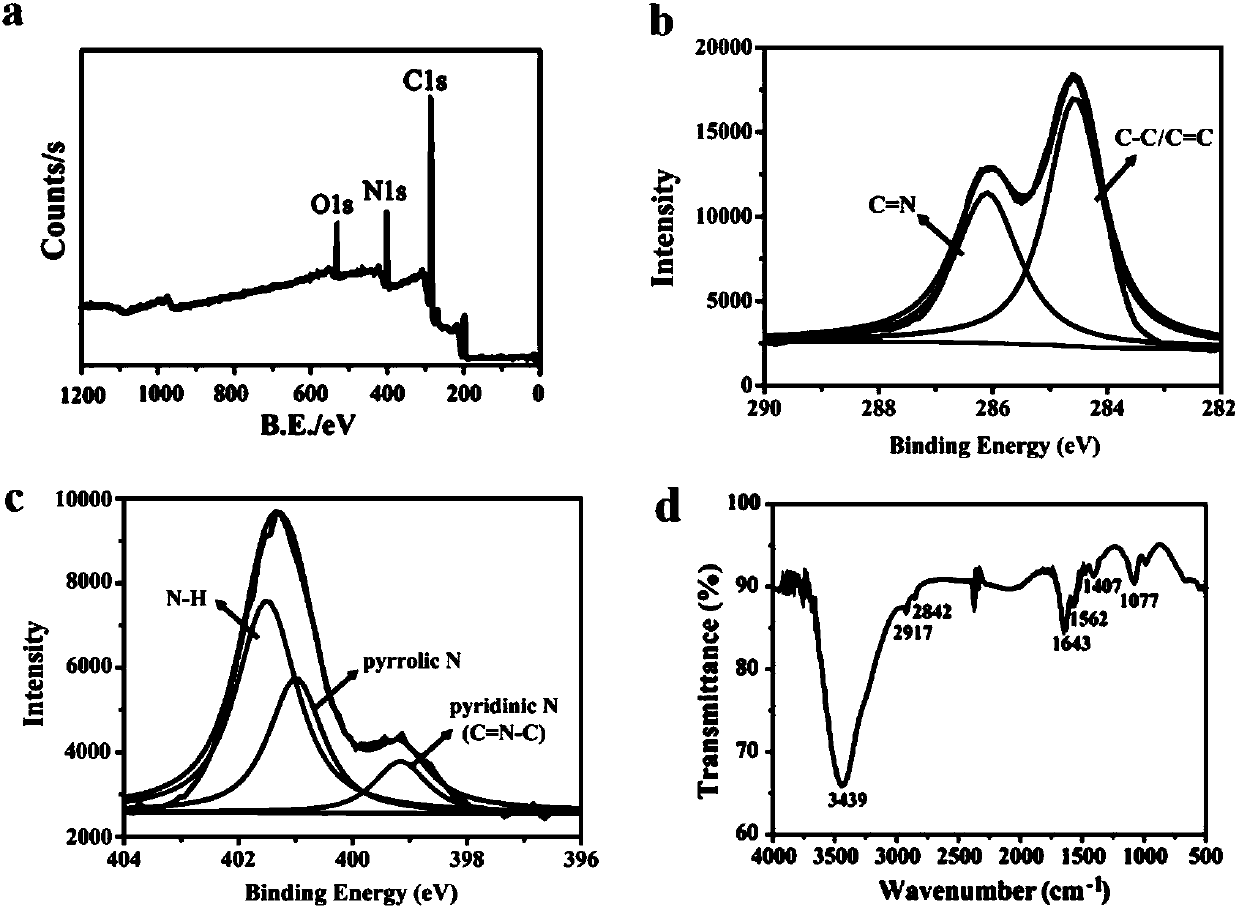
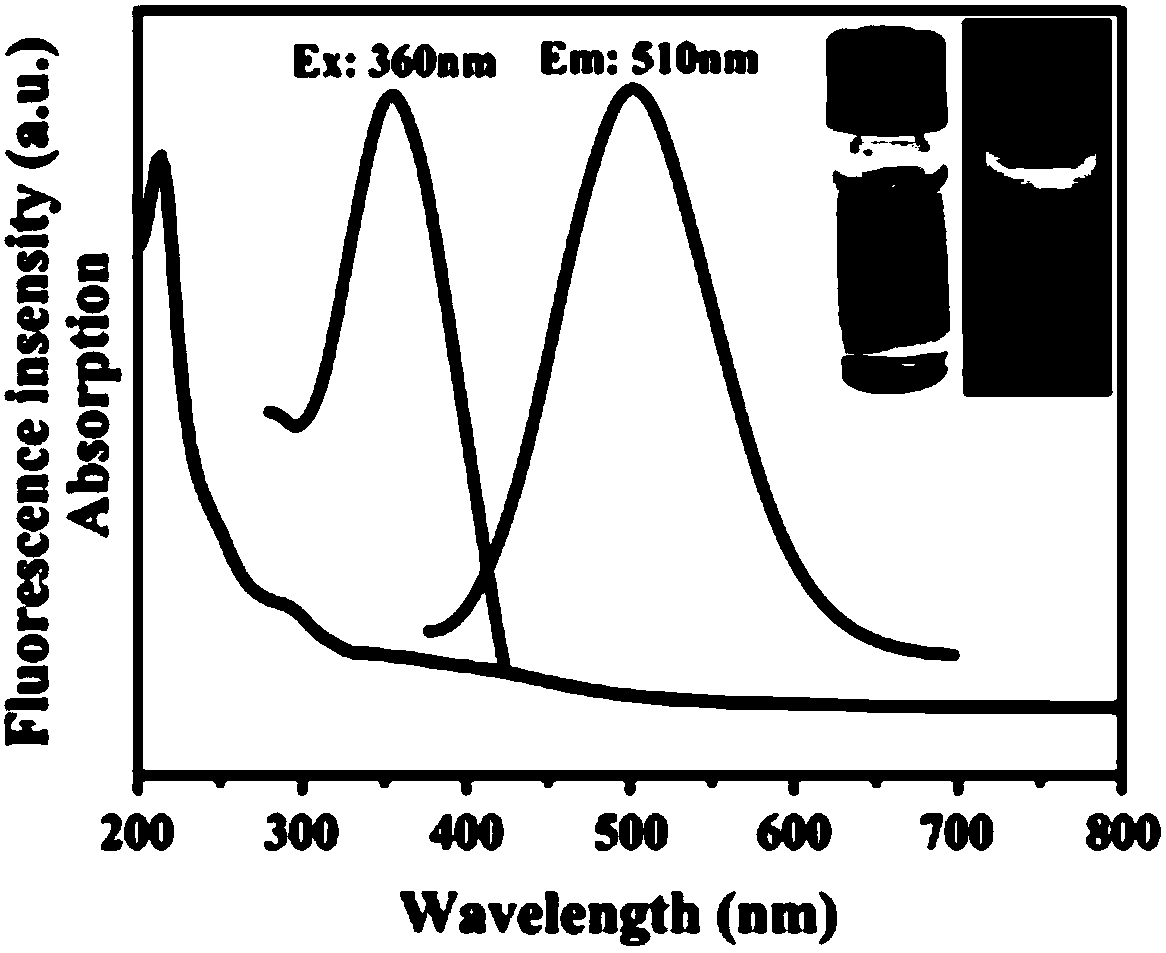
Preparation method of fluorescent carbon dot capable of imaging RNA in living cell for long time in targeting manner and product and application of preparation method
InactiveCN107601455AEasy to synthesizeGood resistance to photobleachingNanoopticsNano-carbonSynthesis methodsLiving cell
The invention relates to a preparation method of a fluorescent carbon dot capable of imaging RNA in a living cell for a long time in a targeting manner and a product and application of the preparationmethod, the fluorescent carbon dot is hydro-thermally synthesized from m-phenylenediamine, an amine compound and water as the raw materials; the synthesis method is simple, the conditions are controllable, the prepared carbon dot has the performances of strong green fluorescence emission, ultralow biotoxicity and strong photobleaching resistance, can image the RNA in the cell for a long time, canserve as an RNA probe to distribute and locate the RNA in the conventional cell, or is applied to the dynamic change of the RNA in the cell, and can further be used to indicate the state of the celland screen an anti-cancer drug taking RNA polymerase I as a target spot.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
miRNA detection chip, manufacturing method and application thereof
InactiveCN104293898ANucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzymatic hydrolysisReverse transcriptase
The invention relates to an miRNA detection chip, which comprises a substrate, a chromium film arranged on the substrate, a gold film located on the chromium film, 12- sulfydryl lauric acid self-assembled monolayer introduced by a self-assembly way on the gold film and an RNA probe combined with the self- assembly monolayer. The specific RNA sequence of the miRNA detection chip can hybridize with cDNA formed by miRNA reverse transcriptase to form a hybridization sequence. When the cDNA formed by reverse transcriptase of the miRNA to be tested can hybridize with the specific RNA sequence, a RNase H is used for enzymatic hydrolysis of the specific RNA sequence in the RNA-cDNA hybrid, and the released cDNA can repeatedly combine with specific RNA sequence on the chip surface, and then hydrolysis is carried out until the RAN probe on the chip surface is completely hydrolyzed, thus forming an amplification detection based on non-PCR. The amplification detection has simple operation, and can realize high throughput and rapid detection of miRNA In addition, the invention also relates to a manufacturing method and application of the miRNA detection chip.
Owner:SHENZHEN INT TRAVEL HEALTHCARE CENT +2
Method suitable for bastard halibut gonad frozen section mRNA in-situ hybridization
InactiveCN105648065AResolving later stages of gonadal differentiationResolve larger mature gonadsMicrobiological testing/measurementSaccharumDigestion
The invention relates to an mRNA in-situ hybridization technology, in particular to a method suitable for bastard halibut gonad frozen section mRNA in-situ hybridization. The method includes the steps that bastard halibut gonad is immobilized with an excess PFA solution with the concentration of 4% and permeated with an excess methanol solution with the concentration of 100% in sequence and then is preserved for a long term; the sample which is immobilized and then preserved is subjected to rehydration and 20-30% saccharose sedimentation, then is subjected to OCT embedding and frozen section preparing and is dried for 2-3 h at 55 DEG C, and a frozen section is obtained to serve as an in-situ hybridization sample; the sample is washed for 3-5 min with excess DEPC water to remove an OCT embedding agent in the sample frozen section; the sample frozen section is subjected to washing, proteinase K digestion and immobilization, then is subjected to pre-hybridization and then is mixed with a hybridization solution containing a bastard halibut RNA probe at 50-70 DEG C for overnight hybridization; after hybridization treatment, washing, antibody incubation, rewashing, light-proof color development, termination color development, re-immobilization and section encapsulation are carried out, and thus expression localization of bastard halibut gonad related genes at the mRNA level is achieved. By means of the method, the problem that direct gonad in-situ hybridization of bastard halibut gonadal tissue is difficult is solved, and expression localization of bastard halibut related genes in gonad at the mRNA level can be clearly described.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of flounder juvenile gonad mRNA in-situ hybridization
The invention relates to juvenile fish gonad mRNA in-situ hybridization technology, in particular to a method of flounder juvenile gonad mRNA in-situ hybridization. The method includes: taking a washed sample, and fixing the washed sample through a PFA solution of 4% in amount concentration; after fixing, using 100% methanol solution for storage of the sample at minus 20 DEG C, and using the fixed and stored sample after being treated as an in-situ hybridization sample; performing rehydration, washing, protease K digestion and fixing on the in-situ hybridization sample, subjecting the in-situ hybridization sample to washing and pre-hybridization, and mixing with hybridization liquid containing a flounder RNA probe after pre-hybridization for hybridization overnight at 50-70 DEG C; washing after hybridization, performing antibody incubation, re-washing, light-avoiding color rendering, color rendering stopping, re-fixing, re-washing, and settling with 20-30%; subjecting a settling sample to OCT embedding, and performing freeze slicing to realize marking of flounder juvenile gonad mRNA in-situ hybridization. By implementing the method, positioning (mRNA level) of flounder related genes in gonad can be clearly described, and breakthrough progress is made.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and apparatus for detection or identification of DNA
InactiveUS20050048501A1High sensitivityEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationDNAEnzyme
DNA is detected using complementary RNA probes and an enzyme that attacks and hydrolyzes the RNA probes only when it has hybridized with target DNA. A low concentration of target DNA can therefore successively hydrolyze a larger amount of RNA whose loss may then be detected to indirectly determine the presence of the target DNA.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Embryonic stem cell markers for cancer diagnosis and prognosis
InactiveUS20100009858A1Reduce in quantityImprove forecast accuracySugar derivativesNucleotide librariesTumour tissueCancers diagnosis
A method of predicting the development of a cancer in a patient, comprises procuring a sample of tumour tissue from the patient, determining the expression pattern of embryonic stem cell genes in the tissue, comparing the expression pattern with the corresponding expression pattern of embryonic stem cell genes in tumour tissue of reference patients with known disease histories. Also disclosed are microarrays and DNA / RNA probes for use in the method.
Owner:CHUNDSELL MEDICALS AB
Method and kit for detecting ribonuclease
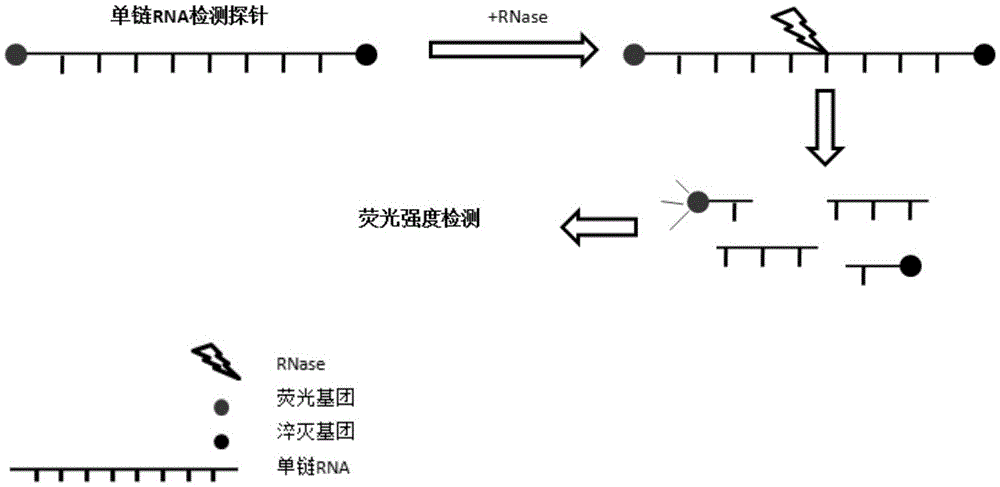
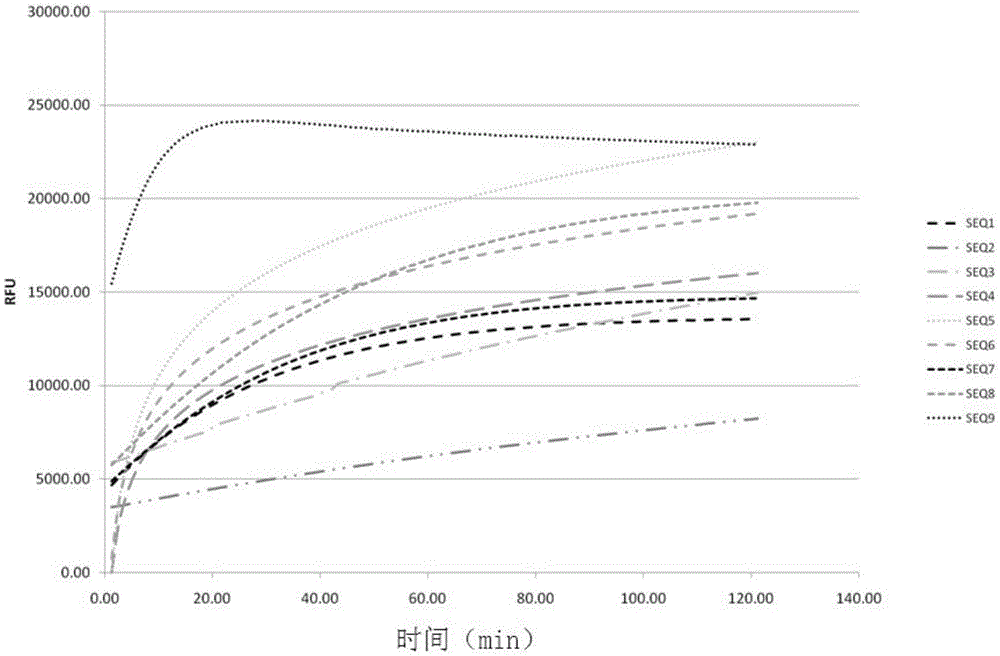
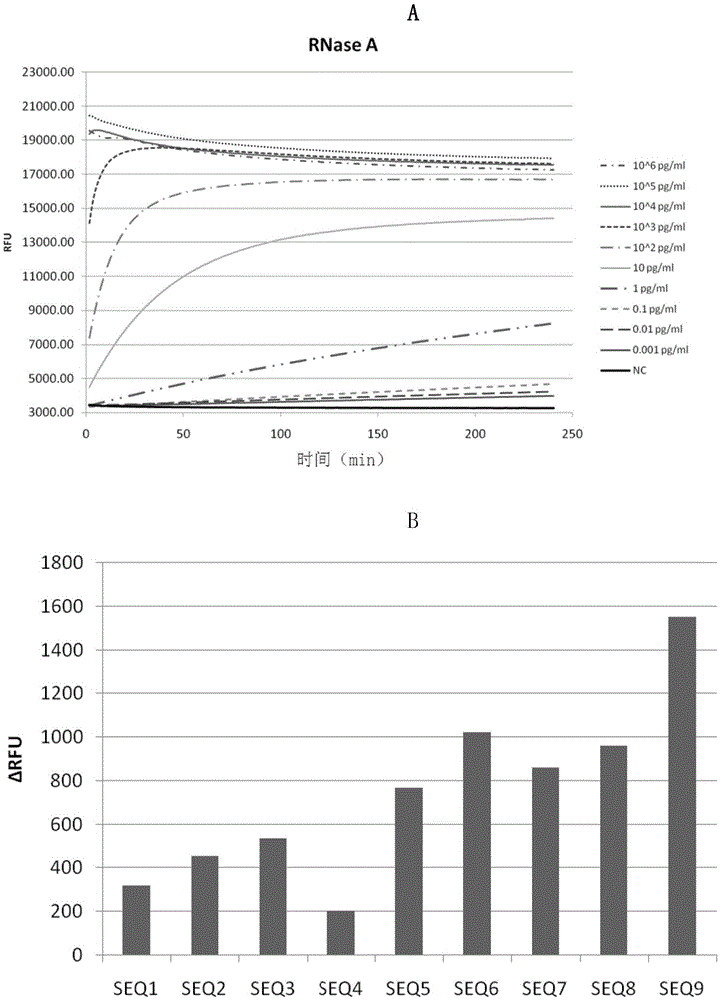
The invention discloses a method and kit for detecting ribonuclease. The method includes the following steps of firstly, designing and synthesizing an RNA probe; secondly, evenly mixing a to-be-detected sample and a reaction system with the RNA probe to obtain reaction liquid; thirdly, detecting the fluorescence intensity of the reaction liquid, and determining whether ribonuclease is contained in the to-be-detected sample according to the fluorescence intensity. The method has the advantages that flexibility is high (0.1 pg / ml RNase A, 100 times higher than Ambion); real-time observation can be achieved; thirdly, high-throughput detection can be conducted, wherein a large number of samples can be detected at the same time; reaction is small in volume, low in cost, easy and rapid (about 1 hour), and the method is suitable for conventional quality control of laboratories; a board spectrum is achieved, wherein content and relative content of different types of ribonuclease in different samples can be detected; safety is achieved, wherein no harmful compounds are used.
Owner:GUANGZHOU RIBOBIO
Solid phase technique for selectively isolating nucleic acids
InactiveUS20100121044A1High purityIncrease ionic strengthSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBio moleculesNucleotide
A method of isolating target nucleic acid molecules from a solution comprising a mixture of different size nucleic acid molecules, in the presence or absence of other biomolecules, by selectively facilitating the adsorption of a particular species of nucleic acid molecule to the functional group-coated surface of magnetically responsive paramagnetic microparticles is disclosed. Separation is accomplished by manipulating the ionic strength and polyalkylene glycol concentration of the solution to selectively precipitate, and reversibly adsorb, the target species of nucleic acid molecule, characterized by a particular molecular size, to paramagnetic microparticles, the surfaces of which act as a bioaffinity adsorbent for the nucleic acids. The target nucleic acid is isolated from the starting mixture based on molecular size and through the removal of magnetic beads to which the target nucleic acid molecules have been adsorbed. The disclosed method provides a simple, robust and readily automatable means of nucleic acid isolation and purification which produces high quality nucleic acid molecules suitable for: capillary electrophoresis, nucleotide sequencing, reverse transcription cloning the transfection, transduction or microinjection of mammalian cells, gene therapy protocols, the in vitro synthesis of RNA probes, cDNA library construction and PCR amplification.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
Preparation method of gene DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) sequence capture probe
ActiveCN103898210AEfficient preparationImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationDeoxyadenosine monophosphateBiotin
The invention discloses a preparation method of a gene DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) sequence capture probe. According to the technical scheme, the method comprises the following steps: 1) designing two partially complementary primers and carrying out annealing treatment so as to form a partially double-chain structured split joint, and carrying out a coupled reaction between the split joint and an ordinary PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification product (A1) of a target gene so as to obtain a target gene (A2) two ends of which are provided with joints; 2) designing corresponding primers according to the sequences of the joints and amplifying the target gene (A2) so as to obtain an amplification product (A3) with a T7 promoter; and 3) quantifying the product (A3), and adding NTP (Nucleotide Triphosphate) with biotin labels (wherein biotins are labeled on the NTP is labeled with biotins but ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate), CTP (Cytidine Triphosphate) and DTP (Deoxyadenosine Triphosphate) are not labeled with biotins) into the product (A3) under a certain condition so as to carry out an in-vitro transcription reaction, thereby finally obtaining an RNA (Ribose Nucleic Acid) probe with biotin labels (gene DNA sequence capture probe).
Owner:HANGZHOU D A GENETIC ENG
Detection kit for mutation of pathogenic genes, susceptibility genes and possibly-related genes of autism
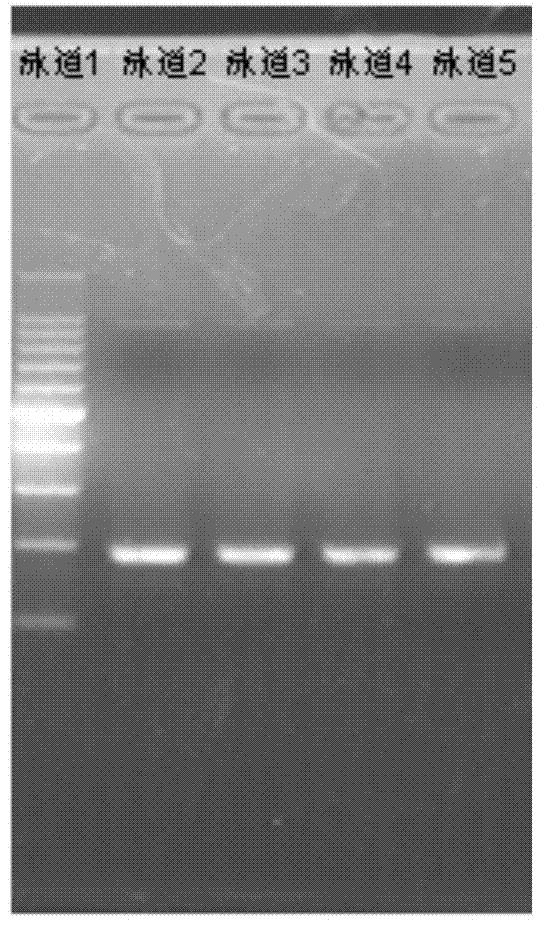
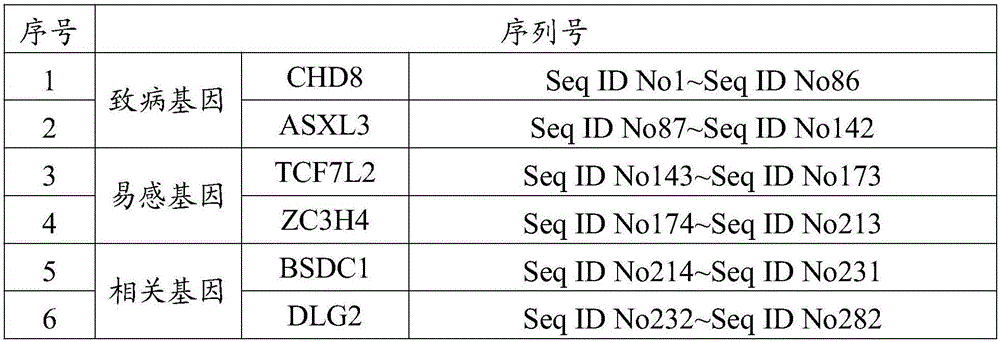
The invention provides a detection kit for mutation of pathogenic genes, susceptibility genes and possibly-related genes of autism. The detection kit is characterized by comprising a RNA probe set, primers, a blocking buffer solution, a RNA enzyme blocking solution, a hybrid buffer solution, a binding buffer solution, a SSC rinsing solution with one unit concentration, a SSC rinsing solution with 0.1 unit concentration, a PCR reaction solution and a TE buffer solution, wherein the RNA probe set comprises 282 RNA probes, and the sequences of the RNA probes are as shown in SEQ ID No. 1 to SEQ ID No. 282. The detection kit for detecting the pathogenic genes, susceptibility genes and possibly-related genes of autism in the invention can simultaneously detect six pathogenic / susceptibility genes related to autism, and is applicable to molecular genetic diagnosis of individual patients with autism and to risk prediction of neonatal autism when parents of a patient of autism give birth to another child.
Owner:天津中科安迪生物科技发展有限公司
Thyroid cancer pathogenicity-related gene fusion and mutation detection kit
ActiveCN106591431AAccurate diagnosisRaw materials are widely availableMicrobiological testing/measurementHybridization probeTE buffer
Disclosed is a thyroid cancer pathogenicity-related gene fusion and mutation detection kit. The thyroid cancer pathogenicity-related gene fusion and mutation detection kit is characterized by comprising an RNA probe set, primers, blocking buffer, an RNA enzyme blocking solution, hybridization buffer, binding buffer, 1x SSC rinse liquid, 0.1x SSC rinse liquid, PCR reaction liquid and TE buffer, wherein the RNA probe set comprises 161 RNA probes with the sequences shown as Seq ID No.1-161. The thyroid cancer pathogenicity-related gene fusion and mutation detection kit is capable of detecting 5 disease-related pathogenic genes simultaneously, providing conditions for precise diagnosis and treatment of individuals suffering from thyroid cancer and evaluating cancer risks of thyroid nodule patients.
Owner:INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Positioning marking method for primordial germ cells (PGCs) of scophthalmus maximus at embryonic development stage
ActiveCN104278078AEasy to placeEasy to collect and storeMicrobiological testing/measurementYolkPlant Germ Cells
The invention relates to a positioning marking method of PGCs, and concretely relates to a positioning marking method for primordial germ cells (PGCs) of scophthalmus maximus at embryonic development stage. The method comprises: acquiring embryo samples of scophthalmus maximus at all stages, fixing, using methanamide with the concentration of 50% to store the samples at -20 DEG C to 40 DEG C for usage; removing oolemma of all above embryo samples of scophthalmus maximus at all stages, using 1*PBST-methanol eluants with different concentrations to perform gradient dewatering processing, and storing at -20 DEG C to -40 DEG C; employing gradient methanol o process the embryo samples at all stages and subjected to above dewatering processing for rewatering, then using a 1*PBST buffer to wash, and after eluting, pre-hybridizing at 60-65 DEG C for 1-2 h; after prehybridization, hybridizing in a hybridization liquid containing a scophthalmus maximus RNA probe at 60-65 DEG C for a night; and after hybridization, washing, performing antibody incubation and color development, and further performing positioning marking. The invention provides the relatively convenient and practical sample storage method, the problem that oolemma and yolk are difficult to remove because methanol dewatering and storage are performed during conventional embryo integral in-situ hybridization is solved, and a protease K digestion step is saved, and the operation steps are simplified.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for detecting target DNA sequence, gene chip adopting same and application of gene chip
InactiveCN102010911AAvoid false negativesAvoid False Positive ResultsMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisHeteroduplex
The invention discloses a method for detecting a target DNA sequence. The method comprises the following steps: 1) an RNA probe contacts with a target DNA to be annealed, wherein one end of the RNA probe is fixed on a substrate, the RNA probe contains a detection sequence close to the fixed end and a marking sequence close to the free end and the target DNA has a segment which is complimentary tothe detection sequence in the RNA probe; 2) ribonuclease is used to hydrolyze the obtained DNA after annealling, wherein the RNA component in the RNA heteroduplex releases the target DNA and the marking sequence of the RNA probe; and 3) the free target DNA and marking sequence are removed through washing, the marking DNA with a marker is bound with the RNA probe of the detection sequence to perform sequence analysis on the target DNA, wherein the RNA probe is not hydrolyzed and is fixed on the substrate, and the marking DNA is complimentary to the marking sequence of the RNA probe. By adopting the method to detect the target DNA, the target gene does not require PCR amplification and the target DNA is directly detected, thus avoiding adopting the false negative and false positive results of the PCR amplification and increasing the detection accuracy rate.
Owner:深圳博睿祥晖企业管理咨询有限公司
RNA probes
InactiveUS20070184464A1Microbiological testing/measurementOther foreign material introduction processesIn vivoDouble stranded rna
The invention is based in part on the generation of a double stranded RNA molecule substantially covering the whole transcribed region of a gene, and cleaving this using an RNA endonuclease to generate small RNA molecules which are already or may be subsequently labelled. The invention provides small labelled ribonucleic acid (RNA) fragments for use as probes to detect potentially small interfering ribonucleic acid (siRNA) fragments produced in vivo. The invention also provides uses of said small labelled RNA fragments and kits suitable for preparing said small labelled RNA fragments.
Owner:SI AMMOUR AZEDDINE +2
Detection probe, preparation method thereof, and application
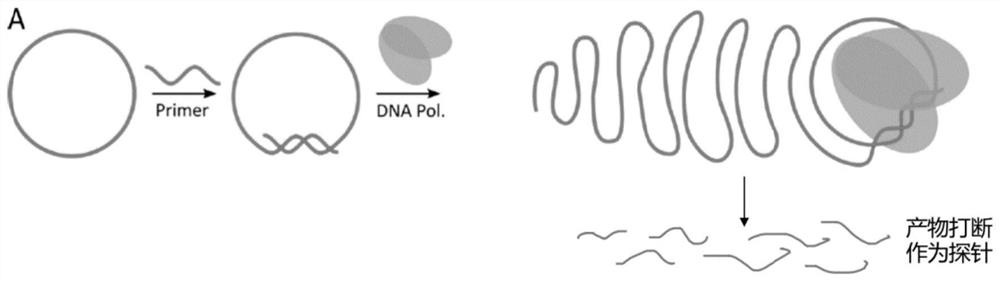
ActiveCN111996235AImprove uniformityAvoid the problem of cumulative error rateMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesMinicirclePlasmid
The invention discloses a detection probe, a preparation method thereof, and application, and belongs to the field of biology. According to the preparation method disclosed, full-length probe fragments are obtained through amplification by combining minicircle plasmids with a rolling circle amplification method, and the probes with different length requirements are further prepared through ultrasonic interruption. The method can be used for producing DNA probes or RNA probes, and the preparation method is simple, the yield is high, the cost is low, and the preparation period can be shortened to one day. Besides, the lengths of the probes prepared by the method is not limited, the probes with different targets and different lengths can be provided as required, the homogeneity is good, and the purity is high, so that the capture performance of the probes is greatly improved, the sequencing uniformity and depth of a target area are better, and the experiment cost is further reduced.
Owner:广州鼓润医疗科技有限公司
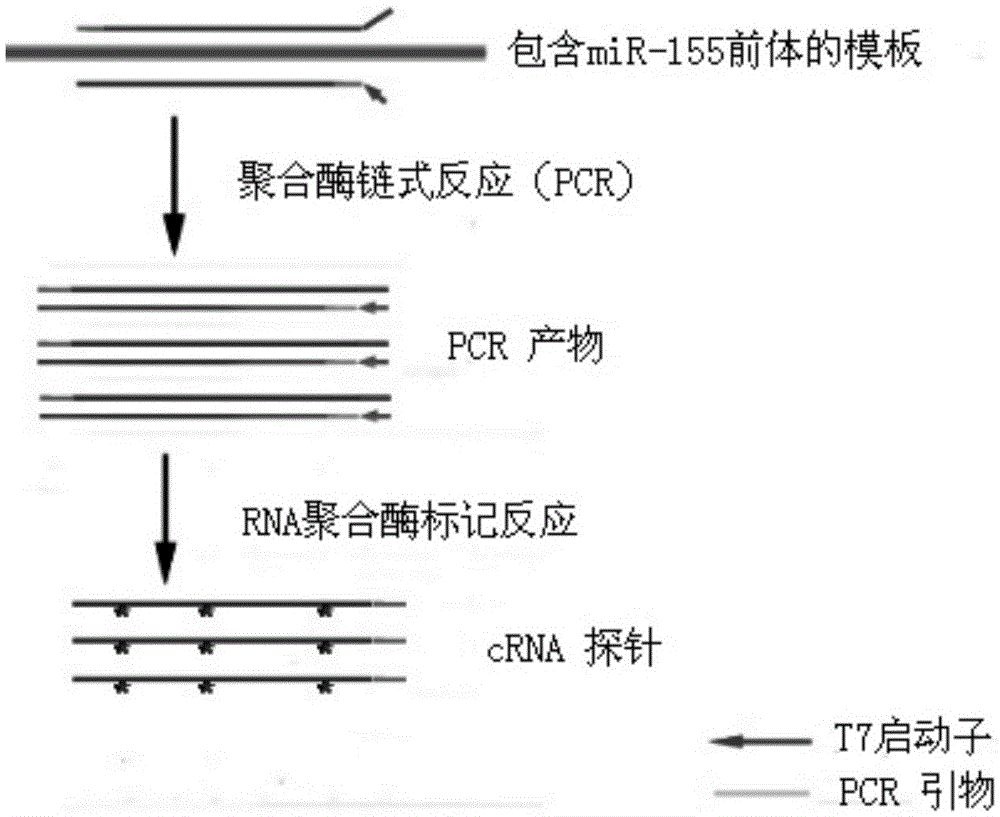
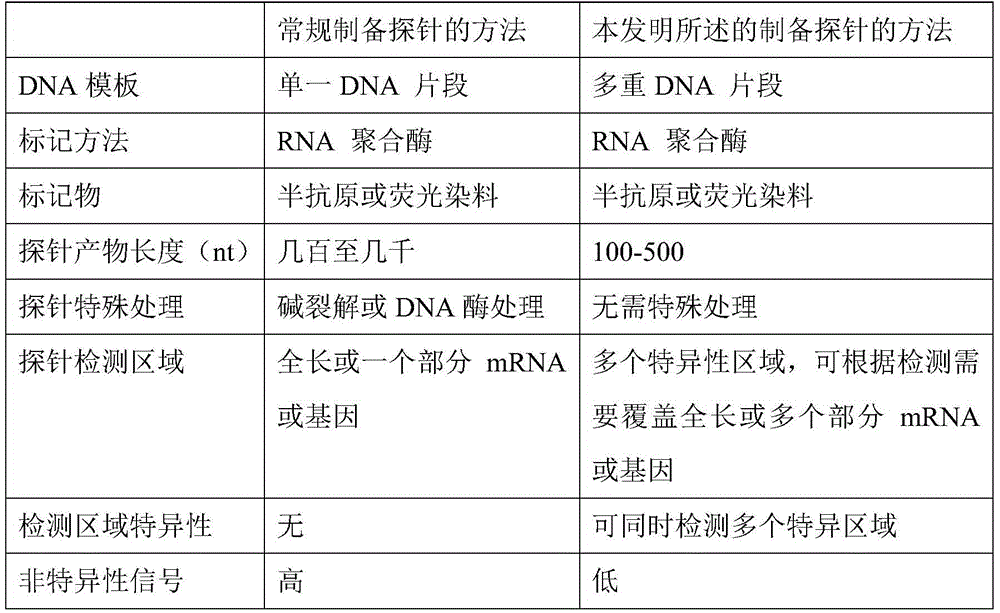
Method for preparing RNA (ribonucleic acid) probe by using miR-155 precursor as template
InactiveCN105586335AImprove test efficiencyShorten detection timeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationComplementary deoxyribonucleic acidDNA fragmentation
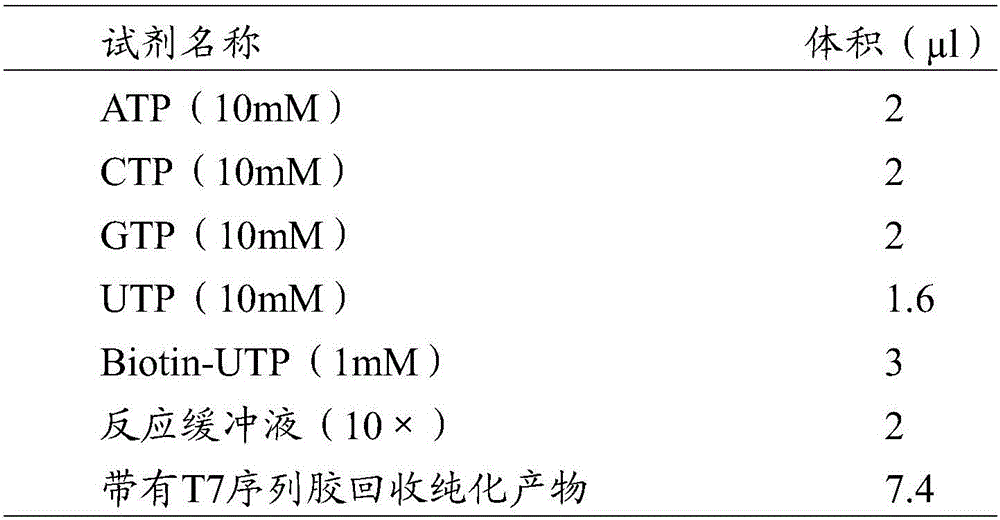
The invention relates to a method for preparing an RNA (ribonucleic acid) probe by using an miR-155 precursor as a template. The method comprises the following steps: designing at least one pair of primers according to the sequence of the miR-155 precursor, wherein the PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification product of the primers is a multiplex DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) segment, and the multiplex DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) segment can comprise all target sequences; carrying out PCR amplification on the miR-155 precursor cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) plasmid by adopting the primers in the step A to obtain the multiplex DNA segment, purifying, and mixing to obtain the template; adding an RNA polymerase and a biotin-labeled UTP (uridine triphosphate) to react, doping UTP into the product, and purifying to obtain the RNA probe. The cRNA (complementary ribonucleic acid) probe can be completely covered on all the target sequences. The probe preparation method simplifies the probe preparation steps, and greatly shortens the whole experimental time. The probe has the advantages of higher specificity, higher stability, weaker background signals and higher sensitivity. On such basis, the invention provides a kit for quickly detecting pancreatic-cancer-related miR-155 expression.
Owner:GUANGZHOU FULENGEN
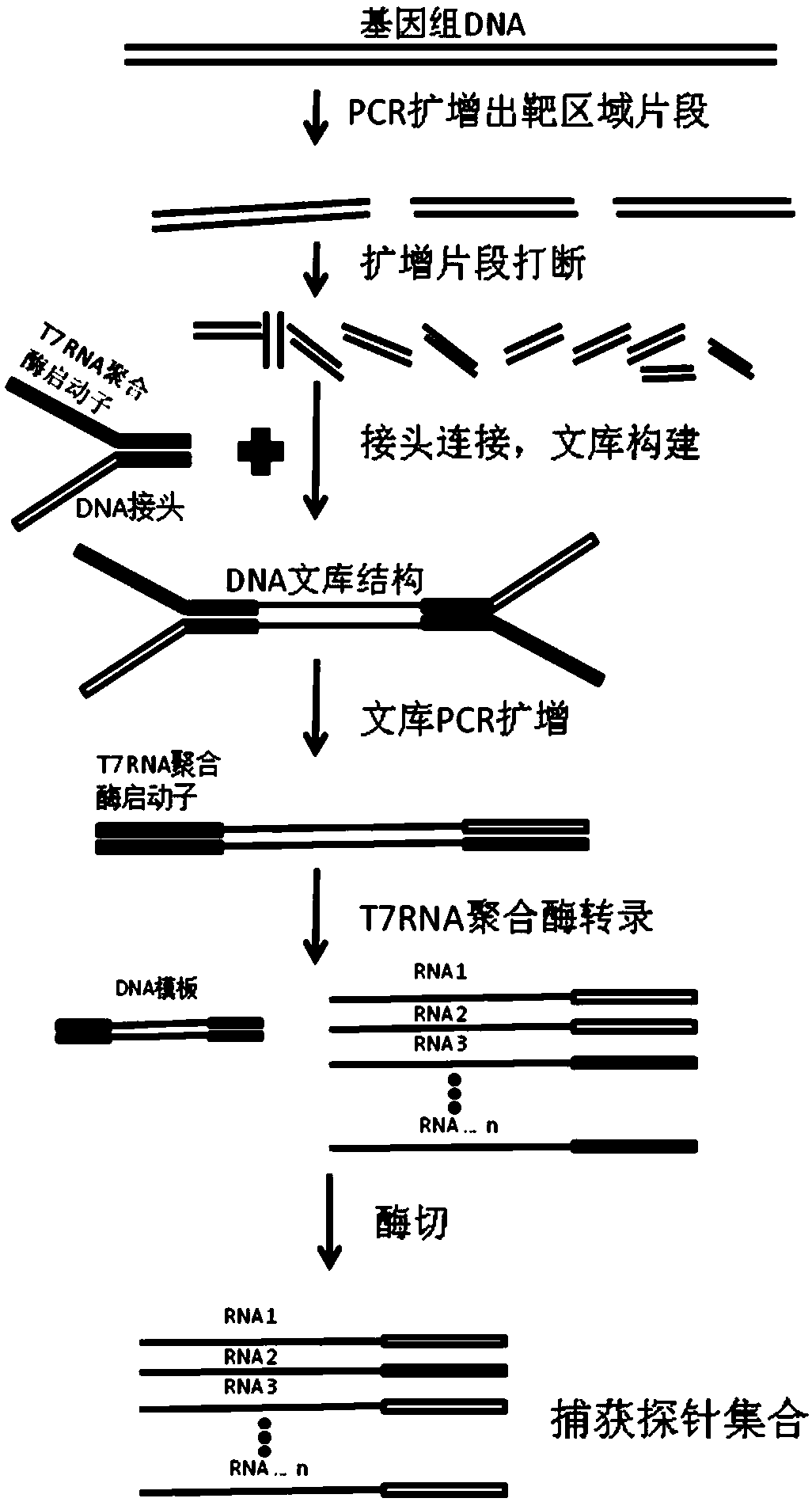
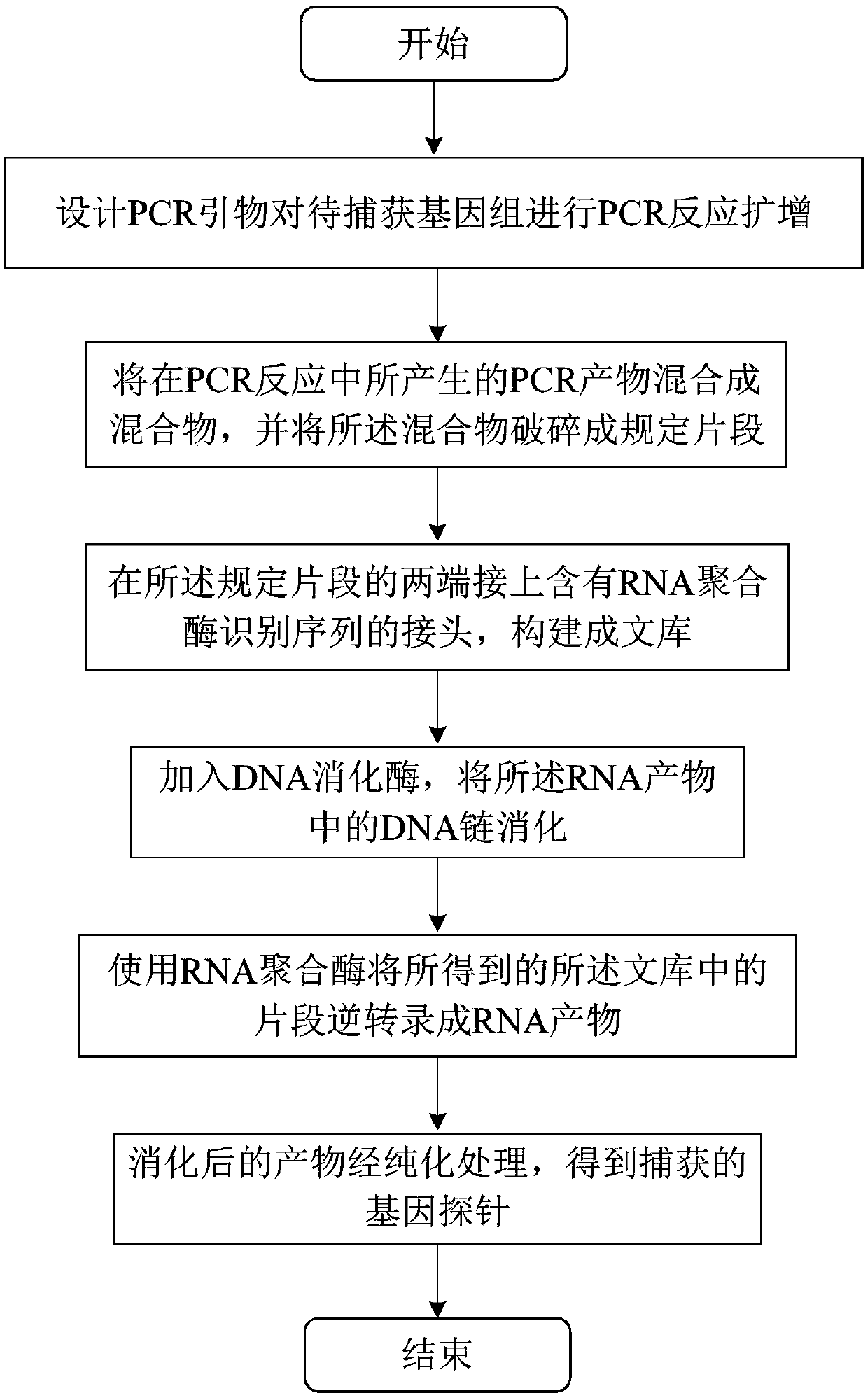
Preparation method of capture probe of large-fragment genome as well as kit
PendingCN108676847AImprove binding efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementFault toleranceLarge fragment
The invention provides a preparation method of a capture probe of a large-fragment genome. The preparation method comprises the following steps: designing a PCR primer and performing PCR reaction amplification on a to-be-captured genome; mixing PCR products generated by the PCR reaction into a mixture and crushing the mixture into regulated fragments; connecting joints containing RNA polymerase identification sequences at the two ends of the regulated fragments to construct a library; transcribing the fragments in the obtained library into RNA products by using RNA polymerase; adding DNA digestive enzyme and digesting DNA chains in the RNA products; and performing purification treatment on the digested products to obtain the captured gene probe. Amplification products of the to-be-capturedarea gene are crushed into the regulated fragments, and the gene probe (RNA probe) with proper length is obtained through the subsequent reaction. The RNA with the length range is not liable to selfannealing to form a secondary structure, and the joint efficiency is high when the probe is used. Therefore, higher fault tolerance is achieved while the specificity is guaranteed, and higher sensitivity is achieved.
Owner:深圳人体密码基因科技有限公司 +1
Gene detection probe group and screening method for 50 kinds of hereditary diseases of newborn
InactiveCN109234386AAccurate detectionQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFluorescenceScreening method
The invention discloses a gene detection probe group and a screening method for 50 kinds of genetic diseases of newborns, comprising a detection probe box, wherein the detection probe box is internally provided with a DNA probe, an RNA probe and a label probe; the specific detection method comprises the following steps of: S1, cleaning tissue of newborns; S2, then one membrane of 0.02 mm being cut, and the membrane being soaked in 100% methanol for 10s, and then the membrane becoming translucent, and then soaked in transfer buffer. Six filter papers of the same size being cut, and the blood membrane being shaken in 100% methanol for 5min; S3, labeling it with a labeling probe, and then inserting the DNA probe into the detected membrane, and simultaneously putting isotope, biotin or fluorescent dye into the membrane; S4, inserting RNA probe into the membrane, and injecting SP6 RNA polymerase and T7 RNA polymerase into the membrane at the same time for detection; S5, analysis of the synthetic results of color rendering calculation. The method of the invention has the advantages of accurate detection, low cost and short detection period, and is worth popularizing.
Owner:王伟青
Soluble rna polymerase protein and methods for the use thereof
InactiveUS20060154237A1HydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementPolymerase LModified nucleosides
A polymerase protein originating from a eukaryotic cell and involved in the RNA silencing pathway is for the first time provided in a purified soluble form that possesses a detectable RNA polymerization activity. This polymerase is useful in methods and kits for in vitro RNA synthesis. A polymerase of the invention copies ssRNA templates to produce two types of reaction products: short and long RNA copies. It can also copy ssDNA templates. The polymerization does not require a primer for the initiation of RNA synthesis, although RNA synthesis can be also initiated in the presence of a primer. In addition to standard nucleotides polymerase of this invention also accepts a number of modified nucleotides. The polymerase is useful in many downstream applications such as production of labeled RNA probes or generation of trigger RNA molecules to induce RNA interference effects in living cells or suitable in vitro systems.
Owner:RNA LINE
RNA aptamer-based theophylline quantitative detection method
ActiveCN107543919AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMaterial electrochemical variablesAptamerElectrochemical response
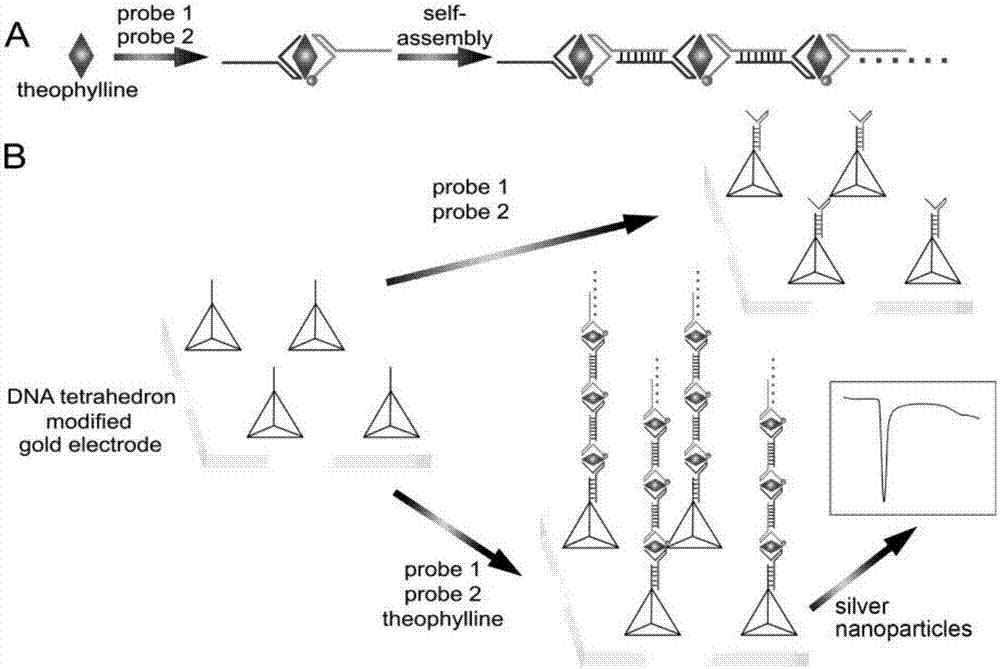
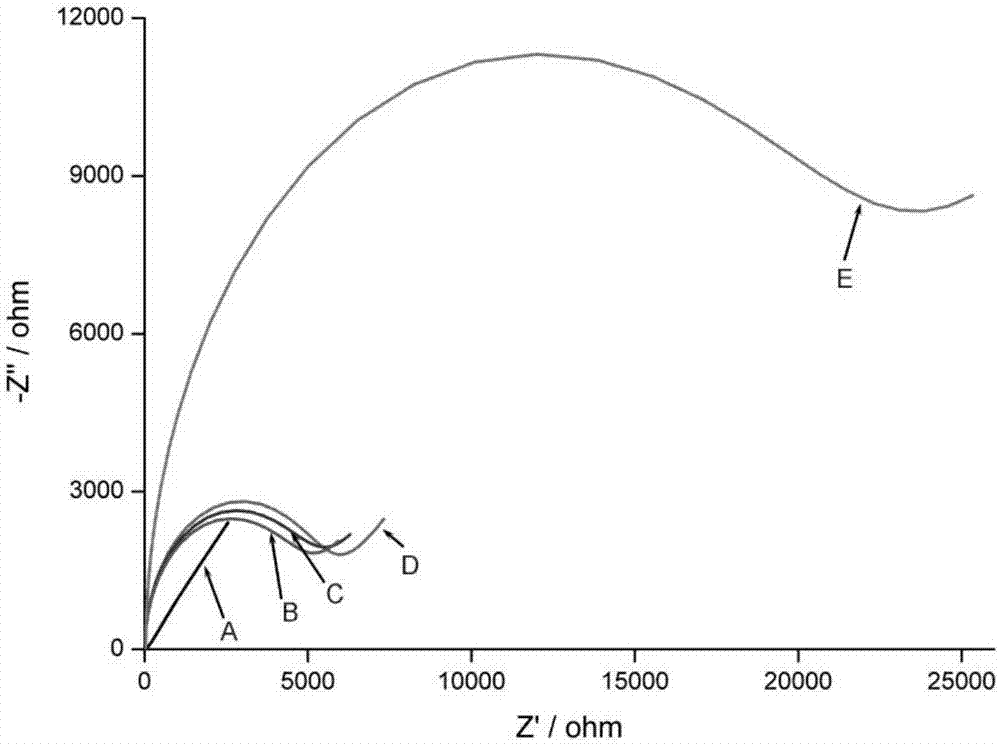
The invention discloses a RNA aptamer-based theophylline quantitative detection method, which comprises the following steps: two RNA probes are adopted to specifically capture theophylline and a sandwich structure is formed, wherein one RNA probe 1 is also used for combining an electrode, and the other RNA probe 2 is combined with electric signal module; and content of theophylline is obtained bymeasuring electrochemical response value of the modified electrode, wherein the two RNA probes have fragments capable of complementary pairing such that sandwich fragments can be connected in series end to end to finally form a linear long-chain. By combining specific recognition function of the aptamer, molecular interface assembling function of DNA tetrahedron and electrochemical stripping voltammetry performance of silver nanoparticles, high-sensitivity, high-specificity and low-interference electrochemical detection of theophylline is realized.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Preparation method of double-stranded DNA probe for liquid-phase hybrid capture and sequencing
InactiveCN110982875AConsistent abundanceEasy to makeMicrobiological testing/measurementDouble strandGC-content
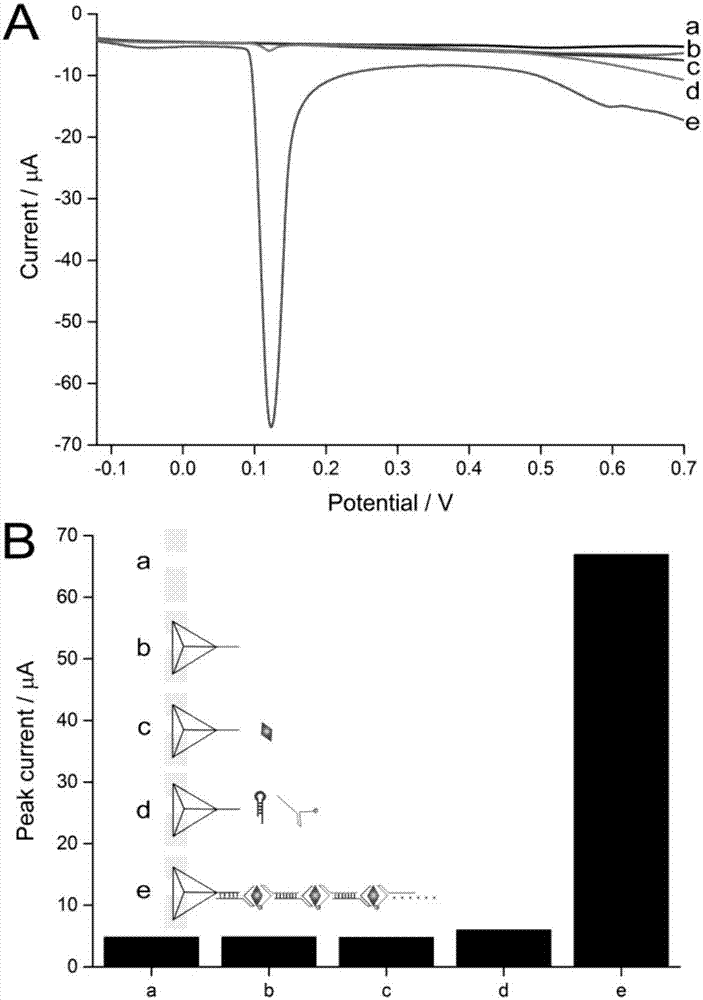
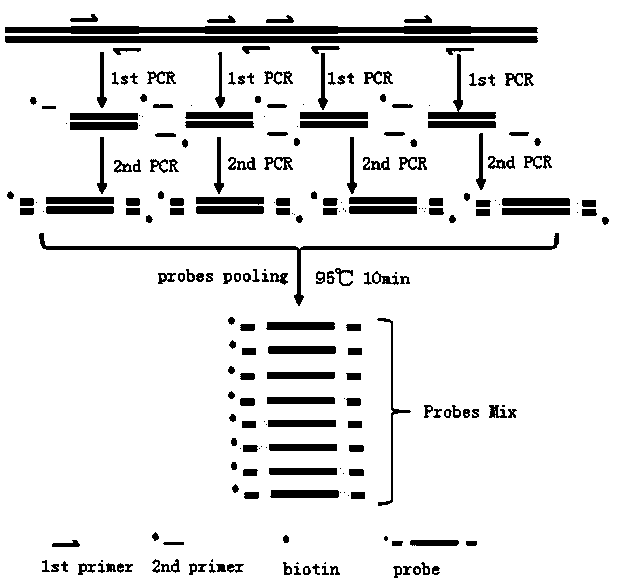
The invention discloses a preparation method of a double-stranded DNA probe for liquid-phase hybrid capture and sequencing. The method comprises the following steps of: designing and synthesizing target region specific primers and 5'-biotin modified universal primers, amplifying original probes through a first round of PCR by taking the specific primers and DNAs containing a targeting sequence astemplates; then, amplifying biotin-modified probes by using the universal primers and the original probes as templates; purifying each probe with qualified quality control by using nucleic acid purification magnetic beads; performing balanced mixing on each probe to form a probe pool; and subjecting the probe pool to heating denaturation so as to finish the preparation process of the double-stranded DNA probe. According to the method, the double-stranded DNA probe with a length of 240 bp can be prepared without depending on an expensive synthesis platform; probe synthesis efficiency is not influenced by GC content and length; preparation process is simple; and preparation cost is low. Each probe is independently prepared and subjected to quality control, so the abundance of each probe in the probe pool is consistent. When the double-stranded DNA probe is used, harsh environment and operation requirements of RNA probes are discarded, and positive and negative double strands of DNAs of atarget library can be captured at the same time.
Owner:张科
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com