Current sharing circuit and current sharing system when inverters are connected in parallel at high frequency
An inverter and parallel technology, applied in the direction of converting AC power input to DC power output, electrical components, output power conversion devices, etc., can solve the problems of reduced system power density, inconsistent heating of inverters, and uneven output current. , to suppress the circulation phenomenon, improve power density and overall work efficiency, and reduce maintenance costs.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
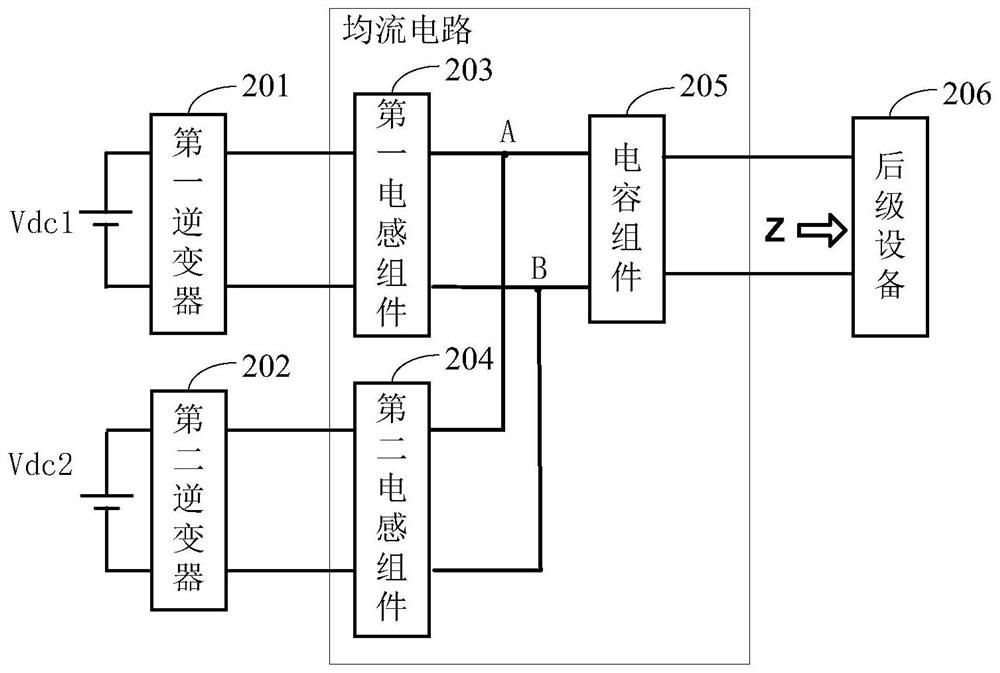
[0100] see figure 2 , is a circuit diagram of a current sharing circuit when inverters are connected in parallel at high frequency provided in this embodiment.
[0101] The current sharing circuit is applied to at least the following two inverters: the first inverter 201 and the second inverter 202 . The output terminal of the first inverter 201 and the output terminal of the second inverter 202 are connected in parallel at a common parallel point.
[0102] The method provided in the embodiment of the present application is suitable for high-frequency parallel connection of inverters. High-frequency parallel connection means that the midpoint voltage of the high-frequency output bridge arm of the inverter is connected in parallel, and the frequency is generally hundreds of Hz to hundreds of kHz. The high frequency output voltage of the inverter is different from the power frequency output voltage of the inverter. The high frequency output voltage of the inverter is usually ...
Embodiment 2
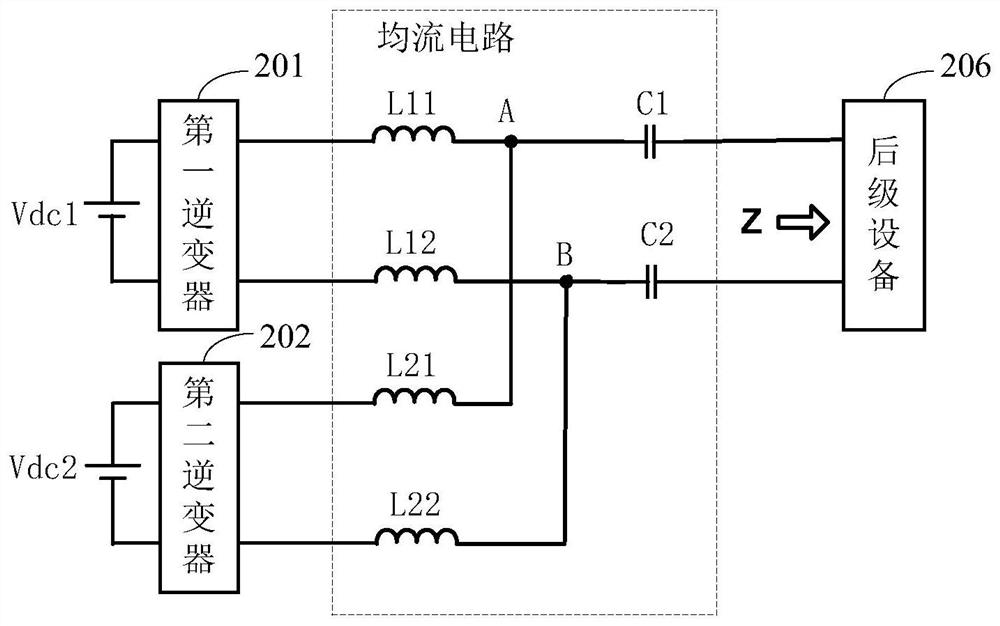
[0161] see image 3 , which is a circuit diagram of another current sharing circuit when inverters are connected in parallel at high frequency provided in this embodiment.
[0162] Such as image 3 As shown, the common parallel points include positive common parallel point A and negative common parallel point B.
[0163] The first inductance component includes: a first inductance L11 and a second inductance L12.
[0164] The first inductor L11 is connected between the positive output terminal of the first inverter and the positive common parallel point A; the second inductor L12 is connected between the negative output terminal of the first inverter and the negative common parallel point B.
[0165] The second inductance component includes: a third inductance L21 and a fourth inductance L22.
[0166] The third inductor L21 is connected between the positive output terminal of the second inverter and the positive common parallel point A; the fourth inductor L22 is connected b...
Embodiment 3
[0181] see Figure 5 , which is a circuit diagram of another current sharing circuit when inverters are connected in parallel at high frequency provided in this embodiment.
[0182] Wherein, the common parallel points include positive common parallel point A and negative common parallel point B.
[0183] The first inductance component includes: a first inductance L1.
[0184] The first inductor L1 is connected between the positive output terminal of the first inverter and the positive common parallel point A.
[0185] The second inductance component includes: a third inductance L3.
[0186] The third inductor L3 is connected between the positive output terminal of the second inverter and the positive common parallel point A.
[0187] The capacitor component includes: a first capacitor C1.
[0188] The first capacitor C1 is connected between the positive common parallel point A and the equipment connected to the rear stage of the inverter.
[0189]Compared with the current...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com