Non-axisymmetric rotary tungsten electrode GTAW and pulse laser composite welding method
A pulsed laser, axisymmetric technology, used in laser welding equipment, welding equipment, metal processing equipment, etc. Uniformity and other problems, to achieve the effect of improving welding quality and manufacturing efficiency, improving energy efficiency, and increasing the volume of deposited metal
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
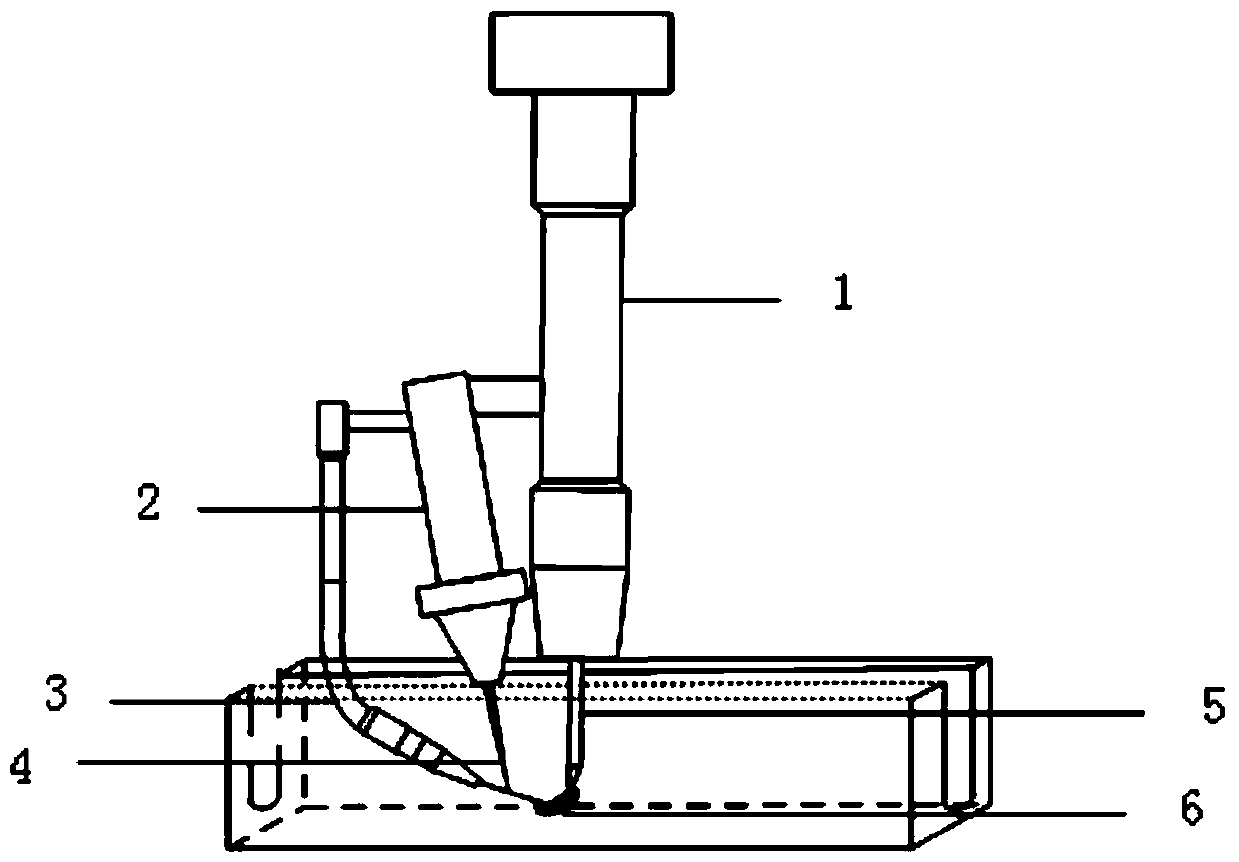
[0033] A non-axisymmetric rotating tungsten electrode GTAW and pulse laser composite welding method, the welding system based on it includes a pulse laser system, a welding torch system, and a wire feeding device; the 9% Ni steel with a thickness of 36mm to be welded in this embodiment has a U-shaped slope Narrow gap welding at the mouth.
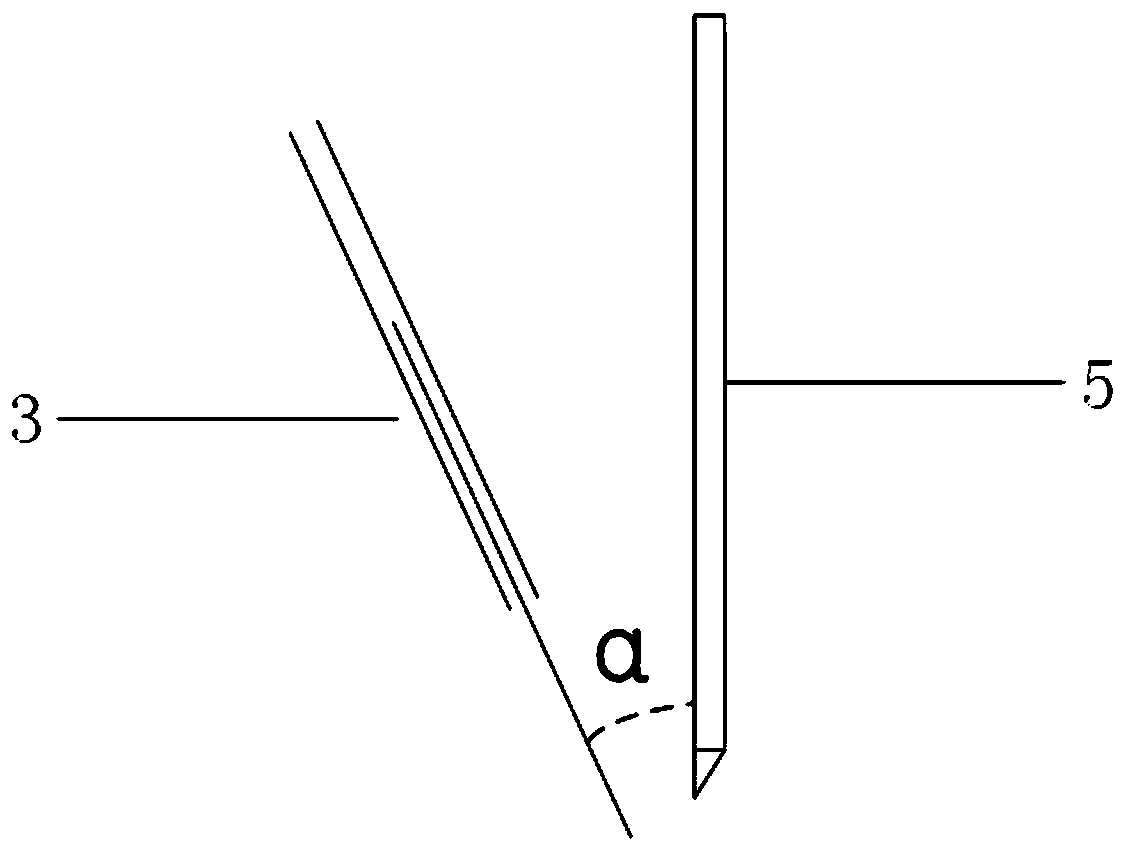
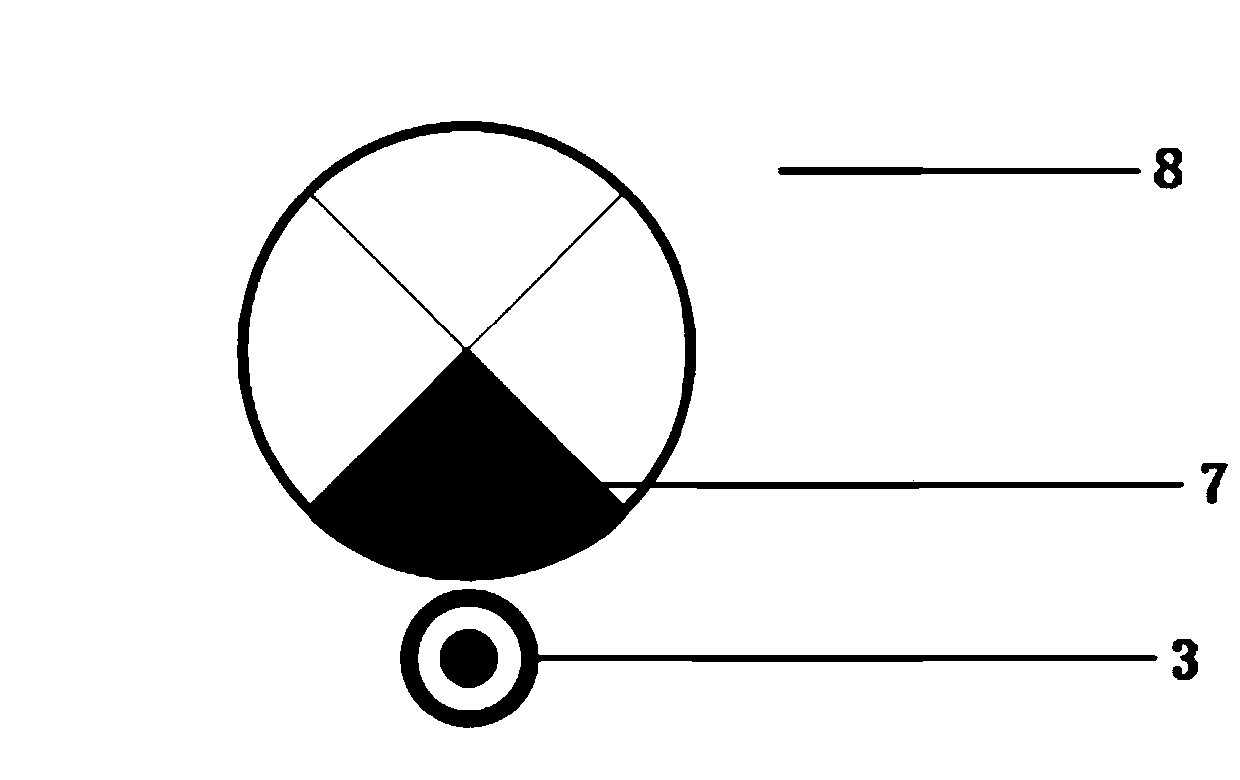
[0034]The welding torch system includes a central rotating shaft, a motor system, and an external motor control box. The external motor control box controls the switch of the motor and the rotation rate of the central rotating shaft. The central rotating shaft is connected to the tungsten pole, and one end of the tungsten pole is Non-axisymmetric tip; the tungsten pole rotates with the rotation of the central rotation axis. Due to the asymmetry of its rotation, the arc can always periodically heat the substrate and the metal on both sides according to the minimum voltage principle; while the tungsten pole controlled by the motor control box ...
Embodiment 2
[0044] A non-axisymmetric rotating tungsten electrode GTAW and pulsed laser composite welding method, the basic system of which is as described in Embodiment 1, the difference is that the welding system based on it also includes a self-adjusting system, and the self-adjusting system includes a visual sensor detection system , Control system, the visual sensor detection system is used to detect the size of the tungsten electrode arc to reflect the position of the rotating arc, the visual sensor detection system includes an industrial high-speed camera; the control system is used to receive the feedback of the arc position and adjust the power of the pulse laser.
[0045] Step (4) also includes setting up an industrial high-speed camera in front of the welding to collect the arc shape in real time, adjusting the appropriate camera angle so that the arc is in the middle of the field of view, the pixel size is 640*640, adjusting the frame rate of the camera to 3000fps, and the expos...
Embodiment 3
[0047] A non-axisymmetric rotating tungsten pole GTAW and pulse laser composite welding method, the equipment and steps are as described in Example 1, the difference is that the waveform of the pulse laser is a sinusoidal wave, and the peak and base values remain unchanged.
[0048] In this embodiment, the position of the non-axisymmetric rotating tungsten arc can be detected in real time by the visual sensor, and the power of the pulsed laser can be self-adjusted according to the set waveform. When the high-speed camera detects that the cross-sectional area of the arc column shrinks, the rotating arc reaches the welding wire. When the rotating arc reaches the two side walls and the position away from the welding wire end and the middle position, the pulse laser power increases. Compared with the steep drop of the square wave, the slow drop of the sine wave can reduce the arc resistance of the arc to the droplet at the end of the welding wire, make the droplet fall down fas...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Peak power | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com