Thermal transistor based on liquid metal phase change
A liquid metal and transistor technology, applied in the field of electronics, can solve the problems of complex processing technology, solid components are not suitable for flexible equipment, etc., to achieve the effect of lowering the production threshold, improving production efficiency and flexibility characteristics, and improving efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
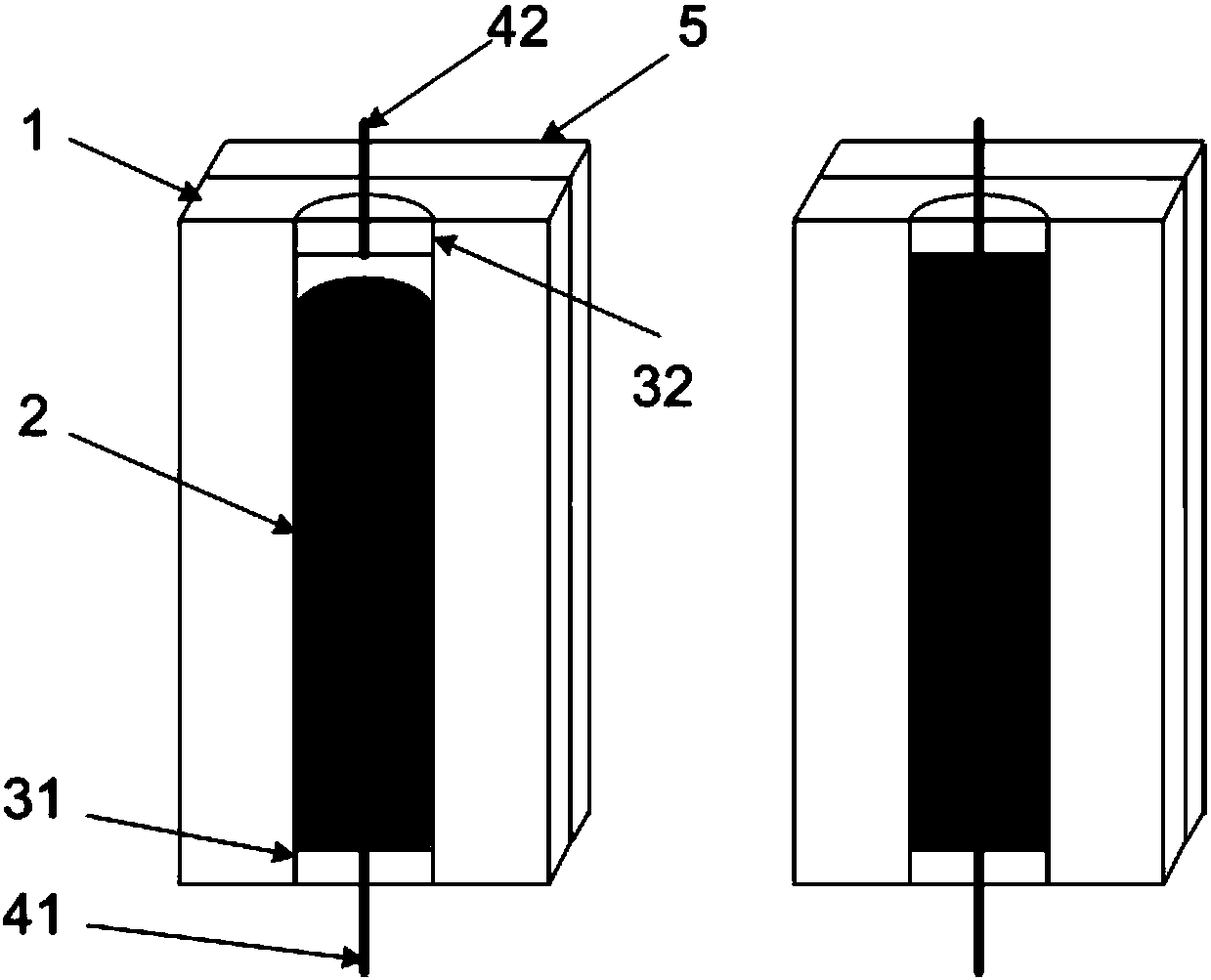
[0029] Such as figure 1 As shown in the figure, a thermal transistor based on liquid metal phase transition is shown, including a package structure 1, a cavity 2 is arranged inside the package structure 1, and liquid metal is arranged in the cavity 2, so Both ends of the cavity 2 are respectively provided with a first contact electrode 31 and a second contact electrode 32, the first contact electrode 31 is connected to a first external electrode 41, and the second contact electrode 32 is connected to a second external electrode 42; A contact electrode 31 is in contact with the liquid metal; a temperature control device 5 is provided outside the package structure 1, and the temperature control device 5 is used to control the temperature of the liquid metal so that the liquid metal undergoes solid-liquid phase transition When it is separated from or in contact with the second contact electrode 32 . Other structures and properties in this embodiment are the same as those of the ...
Embodiment 2
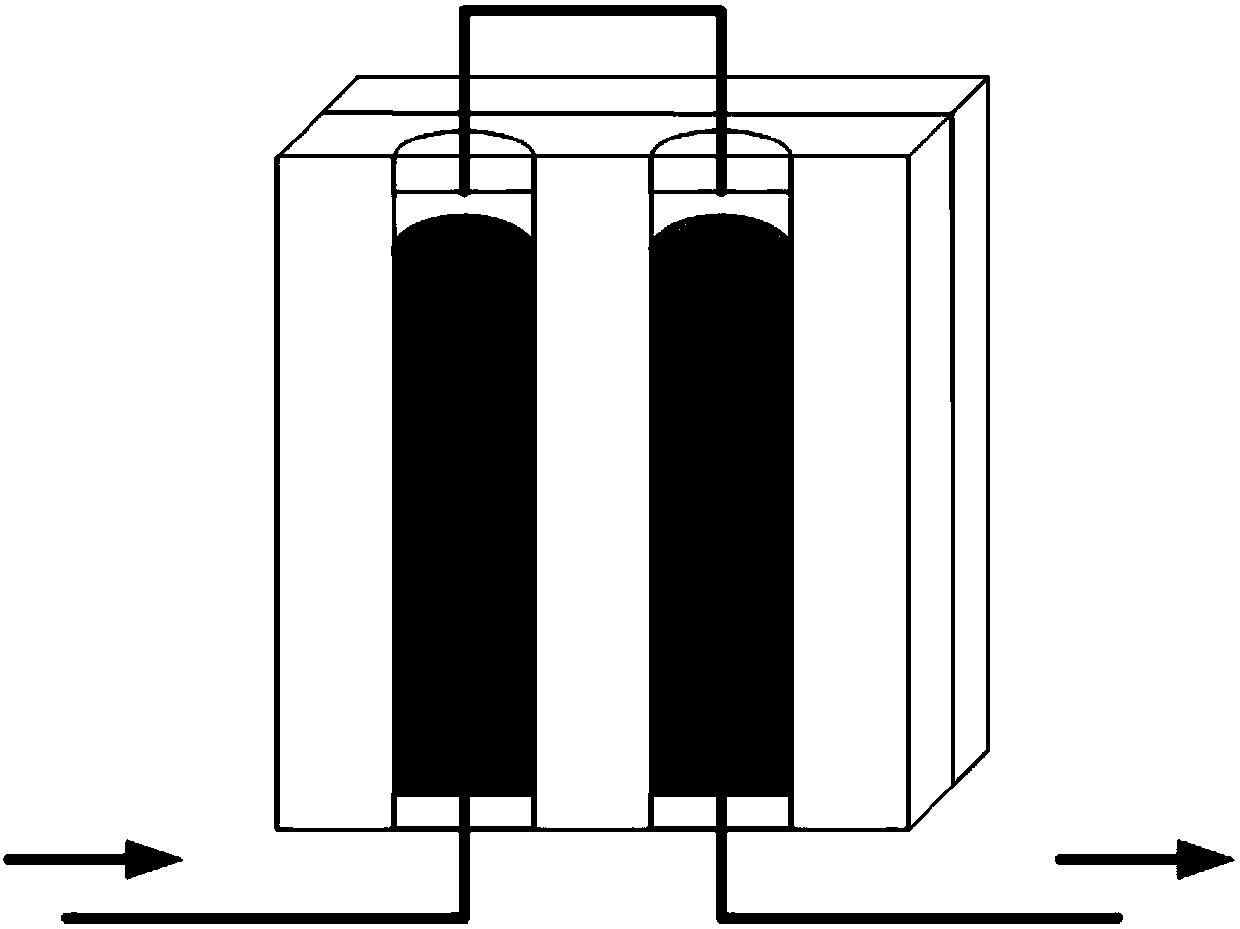
[0032] Such as figure 2 As shown in the figure, a circuit logic control schematic diagram of a series thermal transistor based on liquid metal phase transition is shown. Two liquid metals with different melting points, such as gallium, are respectively placed in the two cavities 2 inside the package structure 1. (Ga, melting point 30°C) and gallium indium alloy (GaIn 24.5, melting point 15°C). Initially, both liquid metals are in a liquid state, only in contact with the first contact electrode 31 and the first external electrode 41 at the bottom, and the circuit is in a disconnected state. When the temperature control device 5 cools the cavity 2 from one side, the Ga with a higher melting point undergoes a solid-liquid phase transition first, and contacts the first contact electrode 32 and the first external electrode 42 at the upper end, and the line is turned on. The other is still disconnected, so the outer circuit is still disconnected. When the temperature is graduall...
Embodiment 3
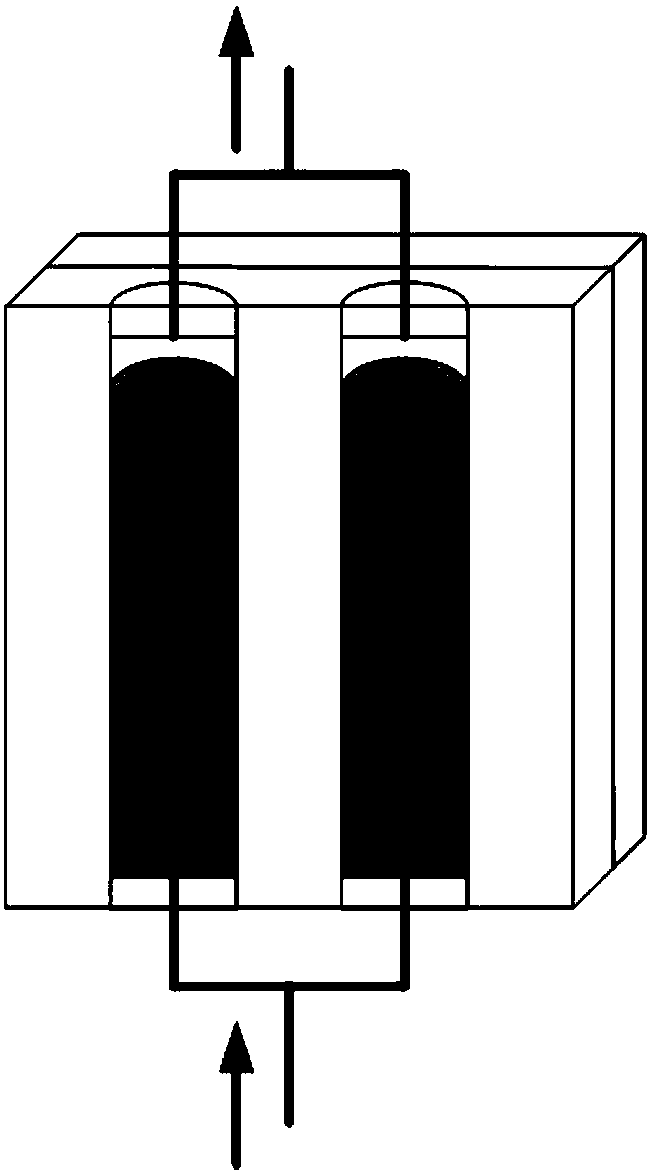
[0035] Such as image 3 As shown in the figure, a schematic diagram of circuit logic control of a parallel thermal transistor based on liquid metal phase transition is shown. Two liquid metal phase transitions with different melting points are respectively placed in two cavities 2 inside the package structure 1. Materials, such as gallium (Ga, melting point 30°C) and gallium indium alloy (GaIn 24.5 , melting point 15°C). Initially, both liquid metals are in a liquid state, only in contact with the first contact electrode 31 and the first external electrode 41 at the bottom, and the circuit is in a disconnected state. When the temperature control device 5 cools the cavity 2 from one side, the Ga with a higher melting point undergoes a solid-liquid phase transition first, and contacts the second contact electrode 32 and the second external electrode 42 at the upper end, and the line is turned on. The other is still off, so the external circuit is on. When the temperature is g...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com