Preparation method of 3D bioprinting ink with adjustable gel-sol phase transition temperature
A phase transition temperature, 3D printing technology, used in tissue regeneration, prosthesis, medical science, etc., can solve the problems of mismatched cell growth temperature and poor mechanical properties of hydrogel materials, and achieve enhanced mechanical properties and balance accuracy. , The effect of the simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
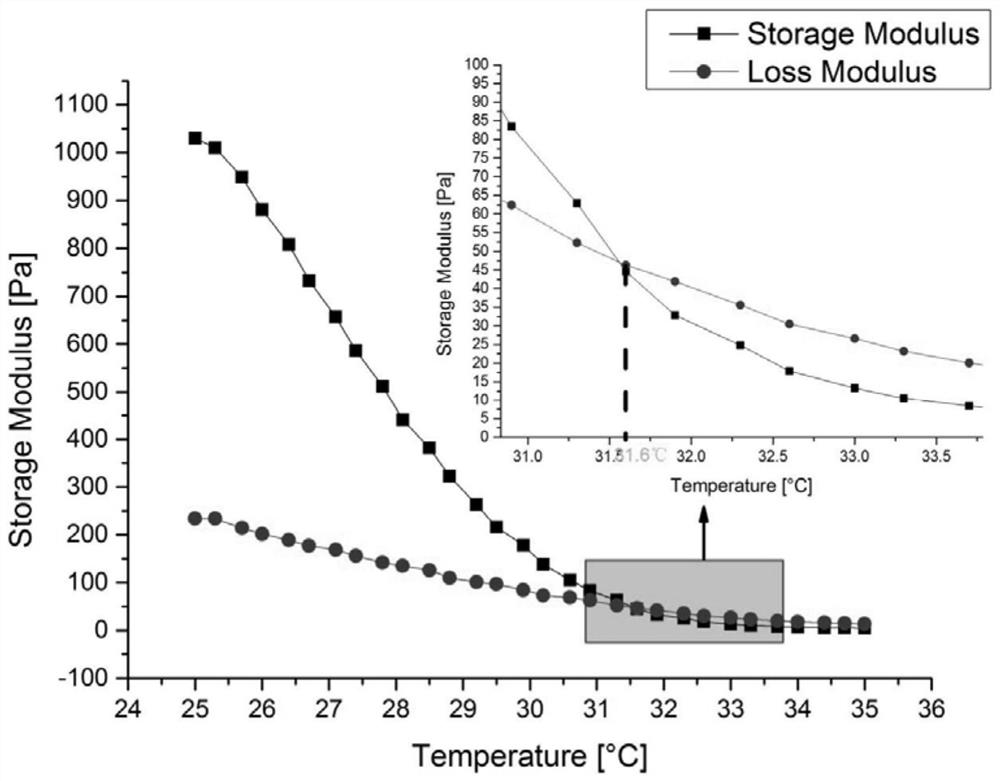
[0038] Example 1: Swell 4g of gelatin powder in a beaker filled with 20ml of deionized water for 30min, put the second beaker into a water bath magnetic stirrer with a water temperature of 78°C and heat and stir at a speed of 20r / min for 30min to obtain a concentration of 20.0% (W / V) gelatin aqueous solution, add 1g sodium alginate powder, 25ml deionized water in the beaker that fills gelatin aqueous solution, the heating temperature of magnetic stirrer keeps constant, and the rotating speed is adjusted to 10r / min, heating and stirring 80min, finally Obtain the sodium alginate of concentration about 2.2% (W / V) and the gelatin composite solution of concentration about 8.8% (W / V); Gradually lower to 20°C, take out and refrigerate for later use. 3D cartilage hydrogel scaffolds were printed at room temperature using a cell-controlled assembly machine. Place the printed scaffold in 4% CaCl 2 cross-linked in solution, the scaffold was removed from the CaCl 2 The solution was take...
Embodiment 2
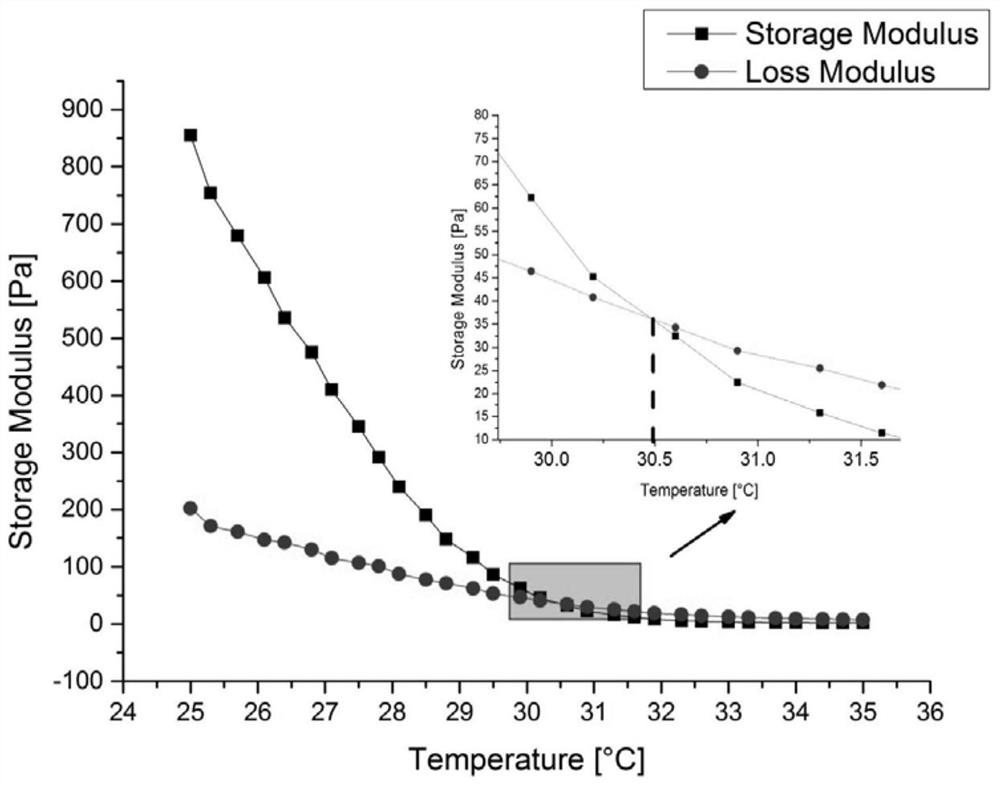
[0039] Embodiment 2: 4g gelatin powder is filled in the beaker of 20ml deionized water and swells 30min, and the beaker is put into the water bath magnetic stirrer that water temperature is 78 ℃ and is heated and stirred at the speed of 20r / min for 30min to make concentration be 20.0% ( W / V) gelatin aqueous solution, add 1g sodium alginate powder, 25ml deionized water in the beaker that is filled with gelatin aqueous solution, the heating temperature of magnetic stirrer keeps constant, and the rotating speed is adjusted to 14r / min, heats and stirs 90min, finally obtains A compound solution of sodium alginate with a concentration of about 2.2% (W / V) and gelatin with a concentration of about 8.8% (W / V); adjust the heating temperature of the magnetic stirrer to 28°C, and set the speed to 0r / min, and compound The temperature of the solution gradually decreased to 28°C along with the water temperature; again, the heating temperature was set to 78°C, and the rotation speed was set to...
Embodiment 3
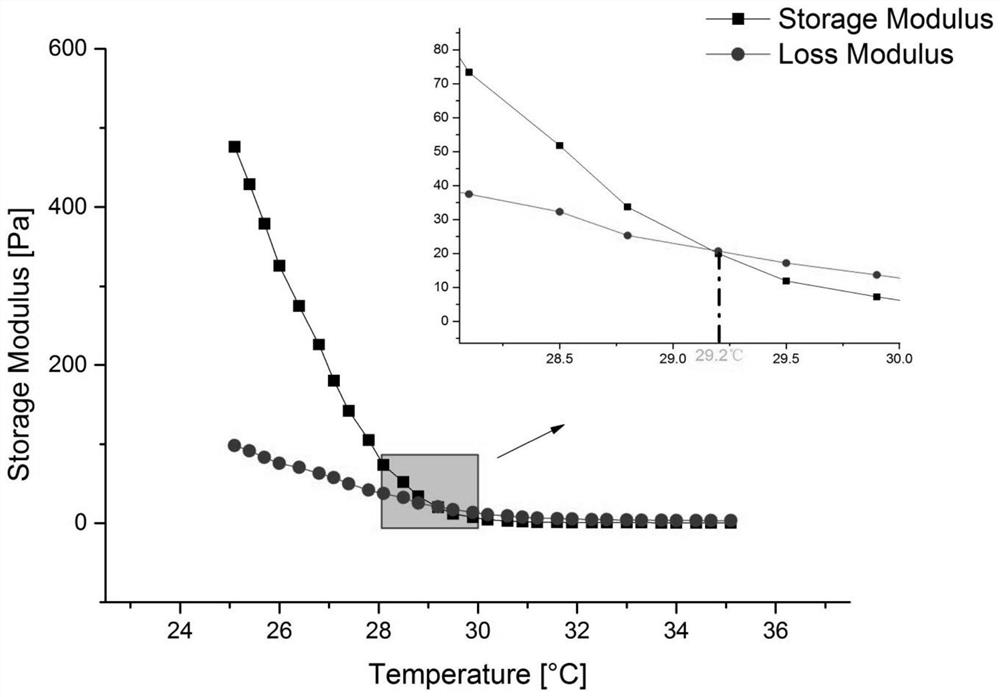
[0040]Example 3: Swell 4g of gelatin powder in a beaker filled with 20ml of deionized water for 30min, put the second beaker into a water bath magnetic stirrer with a water temperature of 78°C and heat and stir at a speed of 20r / min for 30min to obtain a concentration of 20.0% (W / V) gelatin aqueous solution, add 1g sodium alginate powder, 25ml deionized water in the beaker that is filled with gelatin aqueous solution, the heating temperature of magnetic stirrer keeps constant, and the rotating speed is adjusted to 14r / min, heating and stirring for 90min, finally Obtain a sodium alginate with a concentration of about 2.2% (W / V) and a gelatin composite solution with a concentration of about 8.8% (W / V); the heating temperature of the magnetic stirrer is adjusted to 28°C, and the rotating speed is set to 0r / min, The temperature of the composite solution gradually decreased to 28°C along with the water temperature; the heating temperature was set to 78°C again, the rotation speed wa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com