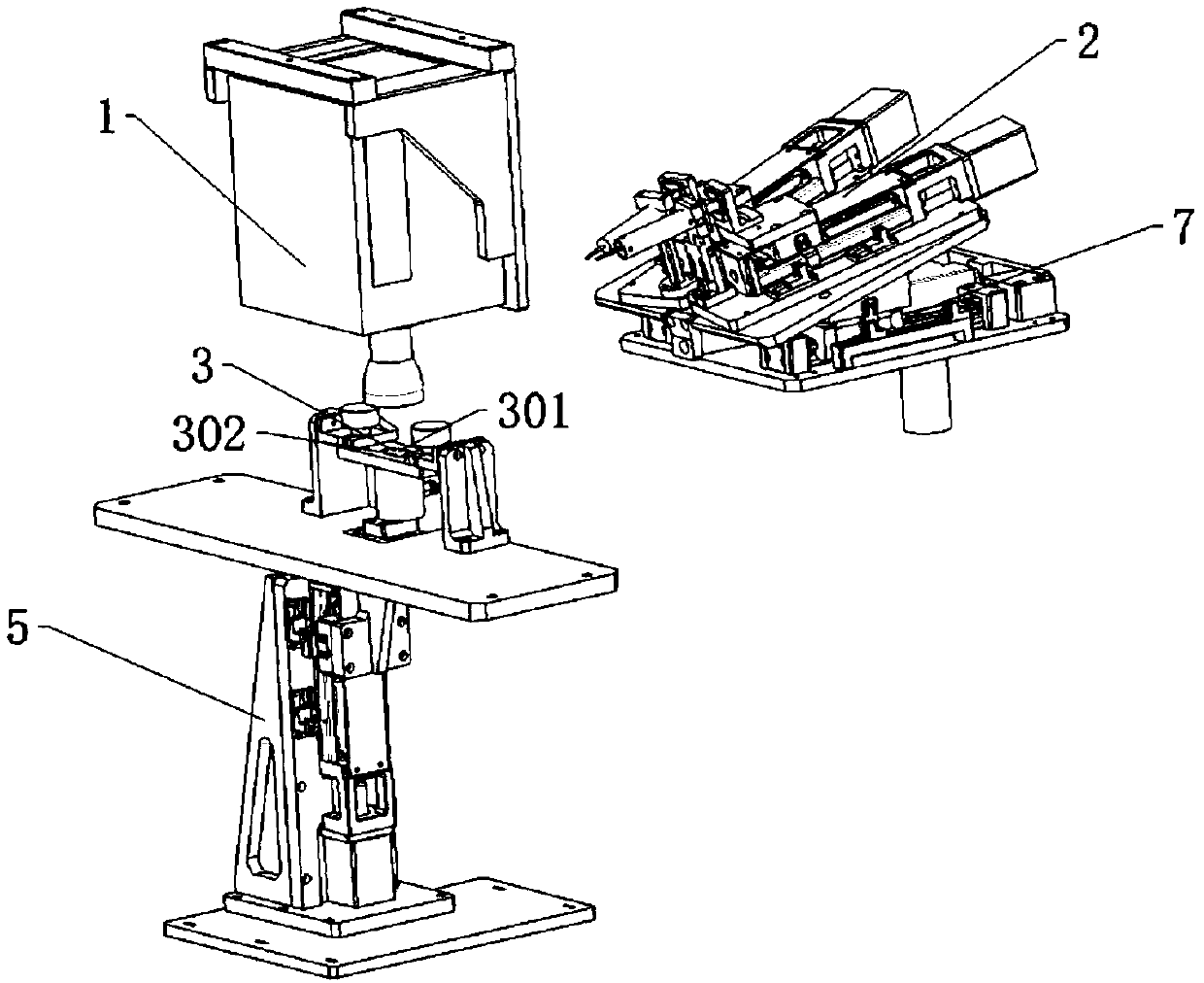
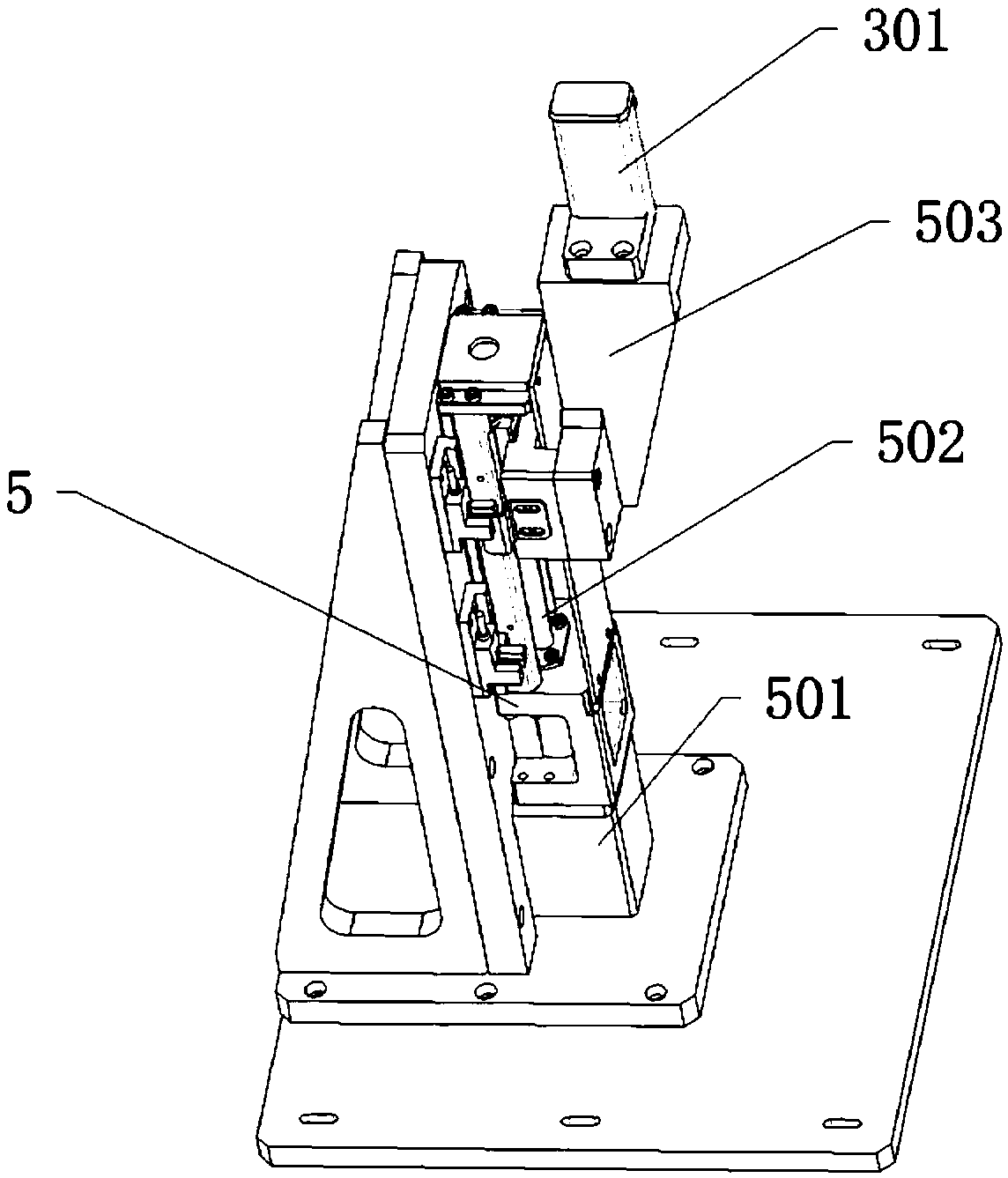
3D printing system
A 3D printing and optical system technology, applied in the field of 3D printing systems, can solve problems such as poor mechanical properties, inability to realize mixed processing of various materials, and limited applications
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0223] Example 1: 3D printed skin for injury repair
[0224] For example Figure 10 , 11 As shown in 12 and 13, the material to be printed is first modeled, and then the model is programmed and then printed. For example, the model established as Figure 10 and 12 as shown, Figure 10 For the leather model, Figure 12 Combine the epidermis and dermis. Figure 11 It is a schematic diagram of the printing process taking 3 layers as an example. For example, the black one represents the bracket that needs to be printed, which is similar to the structure of a three-dimensional cube, and the 12 sides of the bracket use the printed bracket, and the bracket forms a hollowed-out three-dimensional structure 102, forming a unit for printing the bracket, multiple The combination of elements forms a porous structure in the form of cantilever beams. The whole unit can form a dermis support of any size, for example, the diameter can be 8 mm, the thickness of the epidermis is 1 mm, a...
Embodiment 2
[0236] Example 2: 3D printing cartilage repair
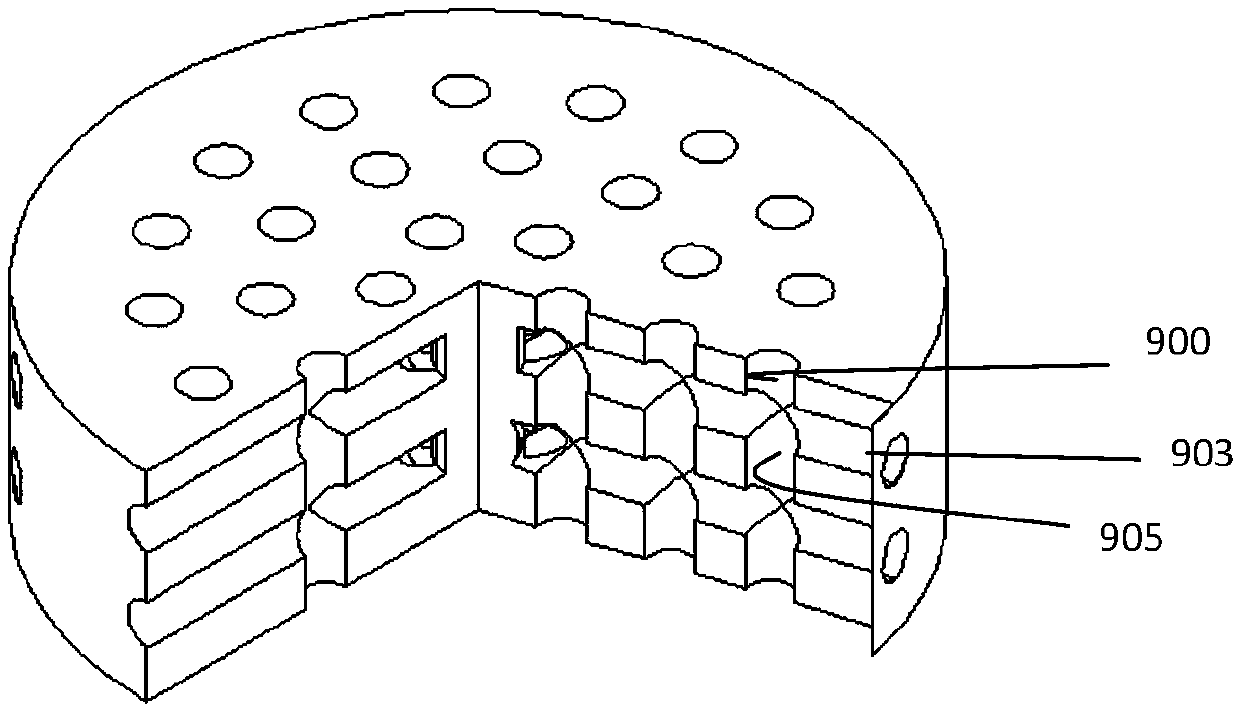
[0237] For example figure 1 , 18 As shown, the printed material is modeled first, and then the program is controlled according to the established model, and then printed. For example, the model established as figure 1 and 18 as shown, Figure 18 It is a model of a cartilage support, which includes an upper support 901 and a lower support 902, wherein the upper support has 30 round holes 900, and the side also has 30 round holes 903, and each round hole crosses the same, for example, each of the above round holes 900 and the side The circular holes 903 are connected, for example figure 1 can be seen. The diameter of the scaffold is 4mm, the thickness of the upper layer is 1mm, and the thickness of the lower layer is 2mm. In fact, the lower layer also has corresponding 30 holes which are the same as the 30 holes in the upper layer, and next time there are no side holes.
[0238] This design is to use the scaffold for ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com