Device for pyridine mineralization simultaneous denitrification through nano-iron oxide
A ferroferric oxide and nanometer technology, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, aerobic and anaerobic process treatment, water pollutants, etc., can solve the problems of pyridine-containing wastewater degradation and low denitrification efficiency, and achieve good electron conduction Features, tight combination, and the effect of reducing the loss of iron
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
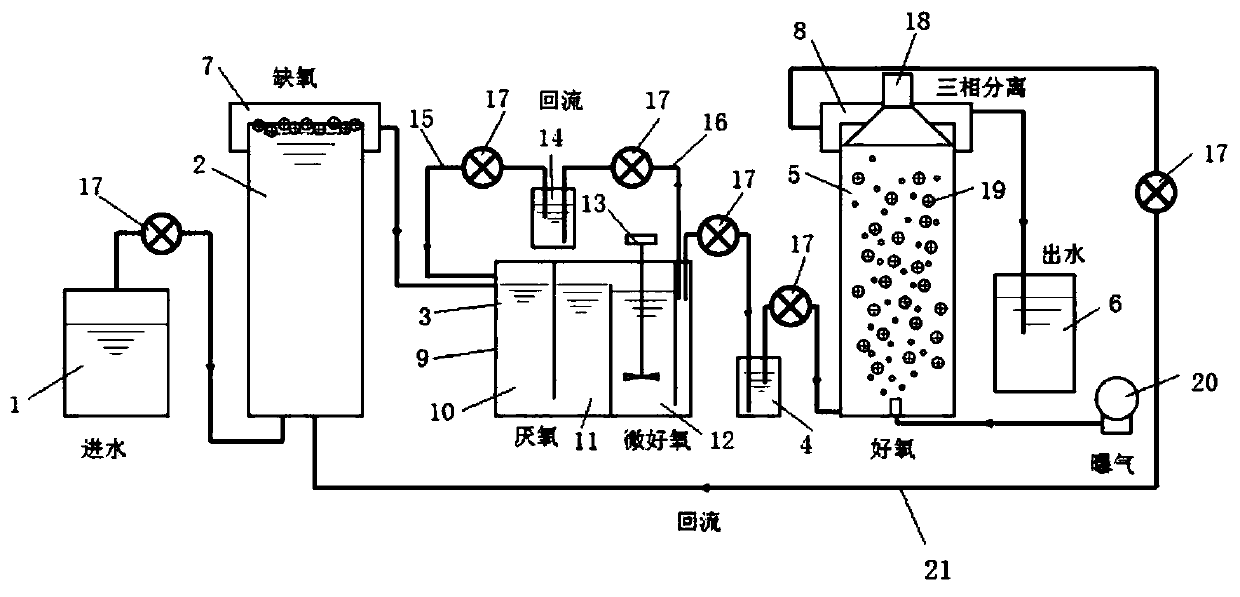
[0041] A device for synchronous denitrification of pyridine mineralization enhanced by using nanometer iron ferric oxide, including a water inlet tank 1, a UASB anoxic reactor 2, an ABR anaerobic baffle reactor 3, a first sedimentation tank 4, and a MBBR mobile bed biofilm aerobic device 5 and effluent pool 6; the upper end of the UASB anoxic reactor 2 is provided with a first overflow pool 7, and the upper end of the UASB anoxic reactor 2 passes through the first overflow pool 7 and ABR anaerobic reflux The reactors 3 are connected; the upper end of the MBBR moving bed biofilm aerobic device 5 is provided with a second overflow pool 8, one end of the second overflow pool 8 is connected with the outlet pool 6, and the other end of the second overflow pool 8 The first return pipe 21 is connected to the bottom of the UASB anoxic reactor 2 .
[0042] The ABR anaerobic baffle reactor 3 includes a first anaerobic zone 10, a second anaerobic zone 11, and a microaerobic zone 12 arran...
Embodiment 2
[0054] The first stage of reaction: This example takes pyridine-containing wastewater as the treatment object. The anaerobic sludge of the urban sewage treatment plant was used as the initial inoculation sludge, and nano-ferric oxide was added to the anaerobic sludge and stirred to mix the nano-ferric oxide and the sludge evenly. The activated sludge added with nano-ferric oxide is respectively put into each reactor of the device, so that the concentration of nano-ferric oxide in the reactor is 1000 mg / L. The temperature of the reactor is kept at 35±2°C, the total volume of the reactor is 14L, and the hydraulic retention time is 4 days. The pH of the reactor is 7.0-7.6, the concentration of pyridine in the wastewater is 500 mg / L, and the concentration of the added carbon source sodium acetate is 500 mg / L. The sludge concentration in the reactor is 8g / L, and the particle size of nano-ferric oxide is kept at about 50nm. The influent water passes through the anoxic-anaerobic-mi...
Embodiment 3
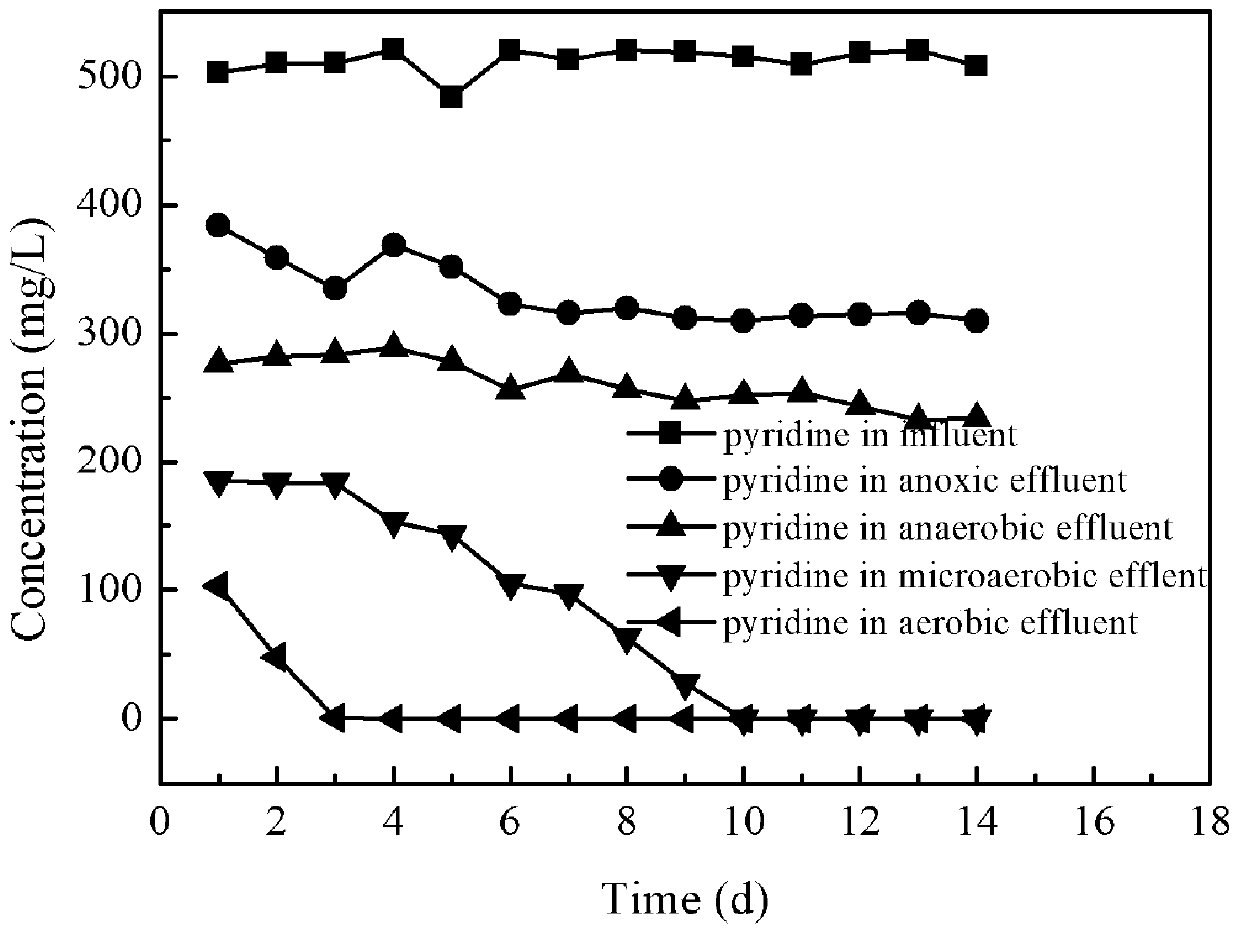
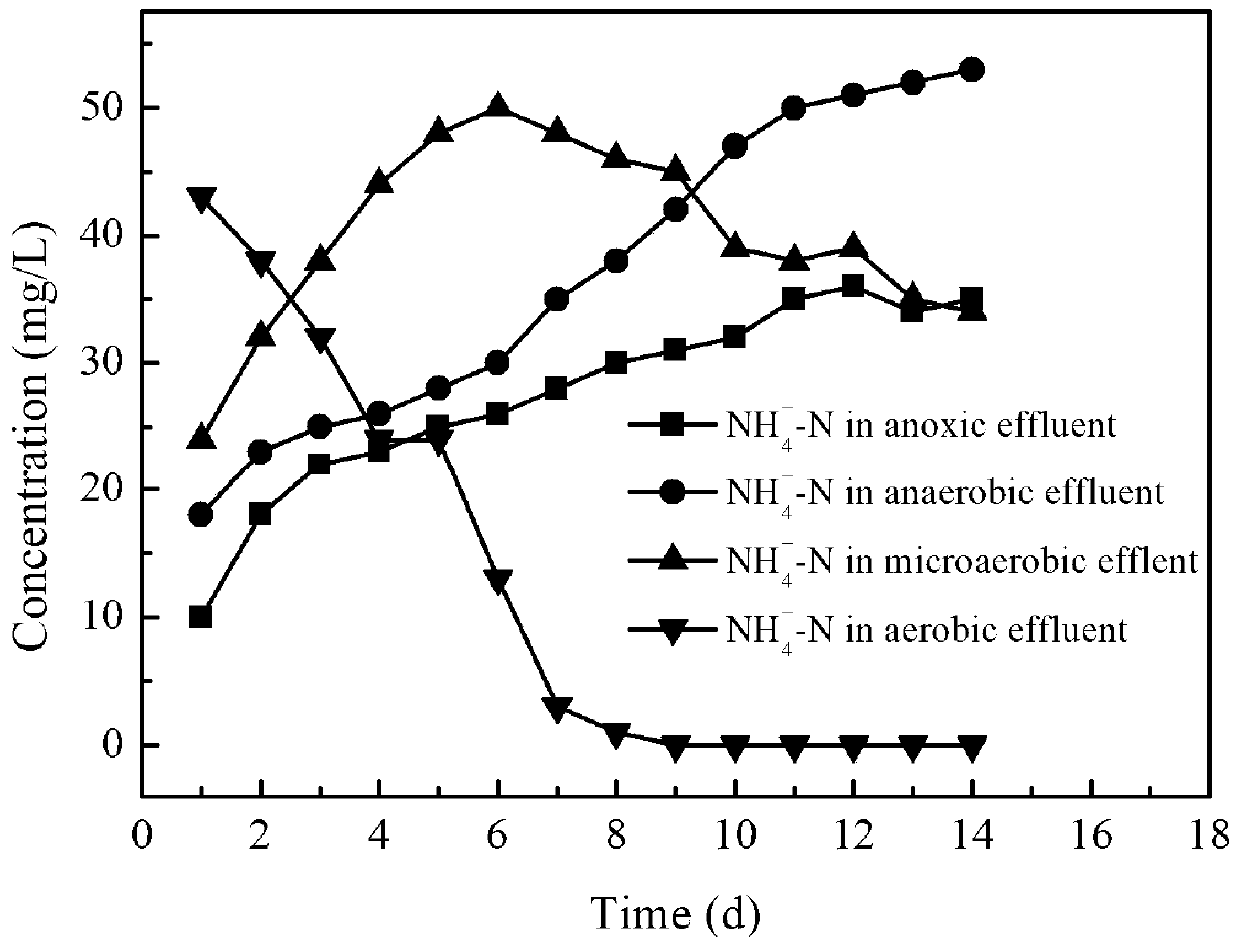
[0057] The second stage of reaction: this reaction stage is different from Example 2 in that no additional carbon source (external carbon source sodium acetate) is added to the influent, and pyridine is used as the only carbon source and nitrogen source for pyridine degradation. The concentration of pyridine in the waste water is 500 mg / L, and others are identical with embodiment 2.
[0058] Depend on Figure 5-7 As shown, with the removal of the easily degradable carbon source sodium acetate, the reaction device uses highly toxic pyridine as the only carbon and nitrogen source, and the pyridine degradation and nitrification effects are not inhibited but further improved. After anoxic and anaerobic degradation, the removal rate of pyridine was as high as 64.1±0.8%, and only 186 mg / L of pyridine remained in the anaerobic effluent, which indicated the good promotion effect of nano-ferric oxide.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| clearance rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com