Ovum collection method and preparation used in bovine living body superovulation
A technique for in vivo egg collection and preparation, which is applied to the improved field of cattle in vivo superovulation egg collection, the preparation of cattle in vivo superovulation egg collection, and the improved field of cattle in vivo egg collection, can solve the problem that the fertilization rate and the cleavage rate are not significantly different, It is difficult to effectively increase the number of oocytes obtained and the blastocyst rate is low.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
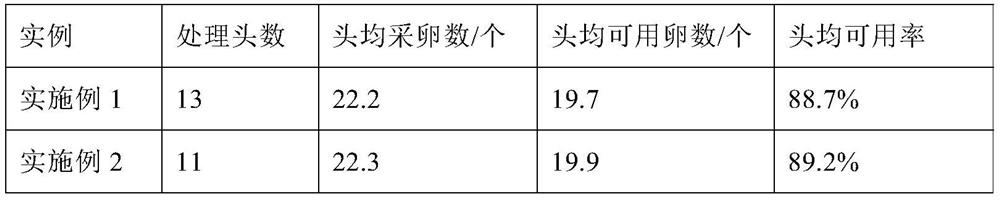
[0062] Example 1: Cattle live egg collection
[0063] 1. Superovulation treatment before egg retrieval
[0064] The cows with the number of follicles ≥ 20 with a diameter of less than 8 mm on both ovaries were screened as oocyte donor cows, and the cows were 2 to 5 years old; FSH preparations were injected in 4 equal doses within two days for superovulation, and each injection was performed. 12h interval, the dose of each injection is 0.5μg / kg bovine body weight in terms of FSH;
[0065] 2. Live egg collection
[0066] 48 hours after the last injection of the FSH preparation, in vivo egg collection was performed. The operation of in vivo egg collection was as follows:
[0067] (21) Preoperative preparation: adjust the equipment to the working state (the pressure of the egg suction vacuum pump is 50-90mmHg), inject about 5ml of egg suction liquid into the collection tube, place it in a thermostat, and adjust the temperature of the thermostat to 39°C; The transparent plastic...
Embodiment 2
[0074] Example 2: Cattle live egg collection
[0075] 1. Superovulation treatment before oocyte retrieval: each injection dose is calculated as 0.4 μg / kg bovine body weight in FSH, and the rest are treated with embodiment 1;
[0076] 2, live egg collection: handle with embodiment 1;
[0077] 3. Detection of oocytes: the same treatment as in Example 1.
[0078] FSH preparation: bovine follicle-stimulating hormone (50 μg / ml), nilestriol (FSH:nilestriol=100:15), poloxamer 188 (concentration 0.5 mg / ml).
[0079] Donor cattle: Holstein (dairy cattle breed), 11 heads.
Embodiment 3
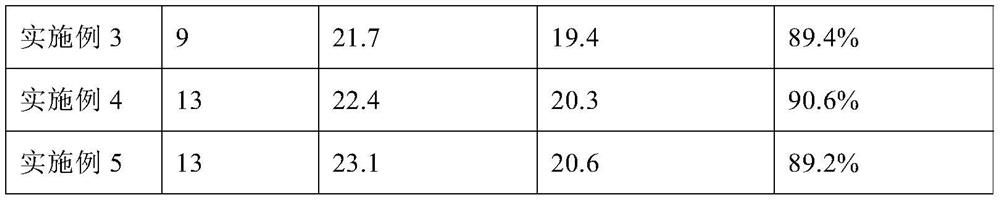
[0080] Example 3: Cattle live egg collection
[0081] 1. Superovulation treatment before oocyte retrieval: each injection dose is calculated as 0.6 μg / kg bovine body weight in FSH, and the rest are treated with embodiment 1;
[0082] 2, live egg collection: handle with embodiment 1;
[0083] 3. Detection of oocytes: the same treatment as in Example 1.
[0084] FSH preparation: bovine follicle-stimulating hormone (25 μg / ml), nilestriol (FSH:nilestriol=100:25), poloxamer 188 (concentration 0.3 mg / ml).
[0085] Donor cattle: Simmental (beef cattle breed), 9 heads.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com