A micromechanical resonator
A micromechanical resonator and resonator technology, applied in the field of resonators, can solve the problems of unpredictable and quantified changes in package stress, and achieve the effects of reducing energy loss, impact and energy loss.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
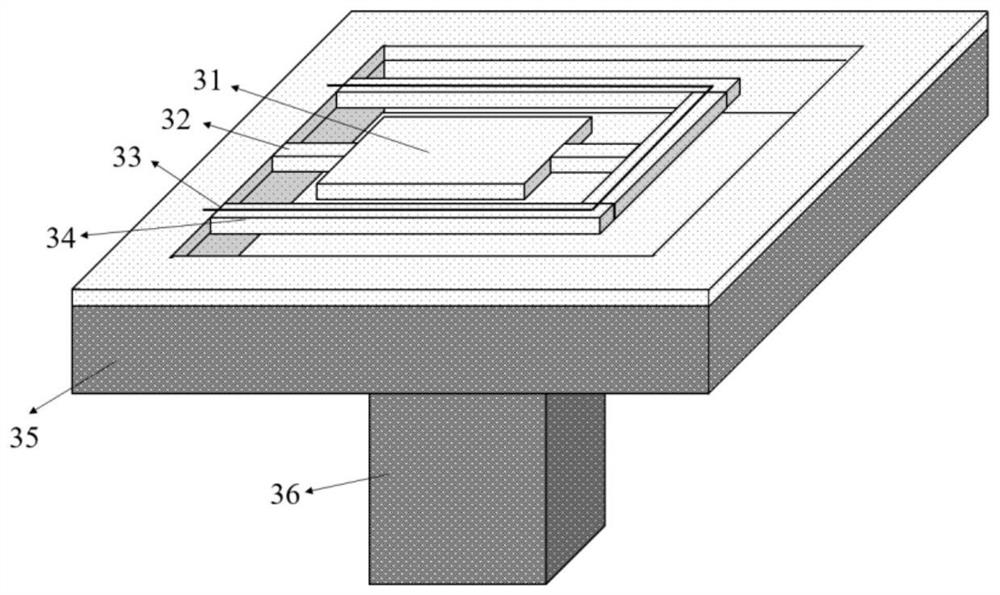
[0050] Figure 3-1 The structure of the resonator prepared in this embodiment is shown.
[0051] A micromechanical resonator comprising a substrate silicon chip 35 with a central prism structure 36, a resonator structure and a vacuum package structure,
[0052] in:
[0053] (1) A cavity is provided on the top surface of the substrate silicon wafer 35;
[0054] (2) The resonator structure includes a resonant vibrator 31, a support beam 32, an isolation frame 34 and a heating resistance wire 33; the resonant vibrator 31 is a rectangular plate structure, suspended in the cavity, and connected to the lining by two straight beam support beams 32 One side of the bottom silicon chip 35 and the "U"-shaped isolation frame 34, the support beam 32 is located at the vibration node of the resonator 31; the isolation frame 34 is connected to the inner wall side of the substrate silicon chip 35; the heating resistance wire 33 is located on the upper surface of the isolation frame 34 ;
...
Embodiment 2
[0069] Figure 3-2 The structure of the resonator prepared in this embodiment is shown.
[0070] The difference with Example 1 is:
[0071] One end of the resonant oscillator 31 in Embodiment 1 is connected to the isolation frame 34 through the support beam 32, and the other end is directly connected to the substrate silicon wafer 35 through the support beam 32; in this embodiment, the isolation frame 34 is a rectangular frame, and the resonant oscillator 31 is two Both ends are connected to the isolation frame 34 through the support beam 32.
[0072] Figure 5-2 The structural cross-sectional schematic diagram of the micromechanical resonator prepared for this embodiment, the specific manufacturing steps are as follows:
[0073] (1) Provide an SOI substrate with a cavity; this layer is composed of substrate silicon wafer 501, buried oxide layer silicon oxide 502 and resonant oscillator structure silicon layer 503 in sequence from bottom to top;
[0074] (2) deposit a bott...
Embodiment 3
[0079] Figure 3-3 The structure of the resonator prepared in this embodiment is shown.
[0080] The difference with Example 1 is:
[0081]The isolation frame 34 in Embodiment 1 is a U-shaped beam; while the isolation frame 34 in this embodiment is a snake-shaped folded beam.
[0082] Figure 5-3 The structural cross-sectional schematic diagram of the micromechanical resonator prepared for this embodiment, the specific manufacturing steps are as follows:
[0083] (1) Provide a substrate silicon wafer (SOI) with a cavity; this layer is composed of substrate silicon wafer 501, buried oxide layer silicon oxide 502 and resonator structure silicon layer 503 from bottom to top; (2) in SOI Deposit the bottom electrode layer 504 on the upper surface of the device layer, then prepare the piezoelectric film layer 505, and then prepare the top electrode layer 506 on the piezoelectric film 505;
[0084] (3) Deposit a sacrificial layer 515, which is made of silicon oxide, etch to make ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com