Microbial compositions and methods
A composition, microbiological technology, applied in the field of treatment of plants, plant parts or soil, capable of solving problems affecting plants, inconsistent performance, small crop benefits, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0157] Example 1. Origin and isolation of MON 201510
[0158] Microbial strain MON 201510 was isolated from the rhizosphere of crop plants grown in a controlled environment using soil obtained from a native grassland in Iowa, USA. By serial dilution into R2A medium (0.5g casamino acids, 0.5g dextrose, 0.5g peptone, 0.5g soluble starch, 0.5g yeast extract, 0.5g special sodium, 0.3g K 2 HPO 4 , 0.05gMgSO 4 ·7H 2 0, 15 g of agar and water in a final volume of 1000 mL) to isolate strains from the collected samples. Individual colonies formed on the medium surface from the sonicated cell slurries were picked for further analysis.
Embodiment 2
[0159] Example 2. Identification and sequencing of MON 201510
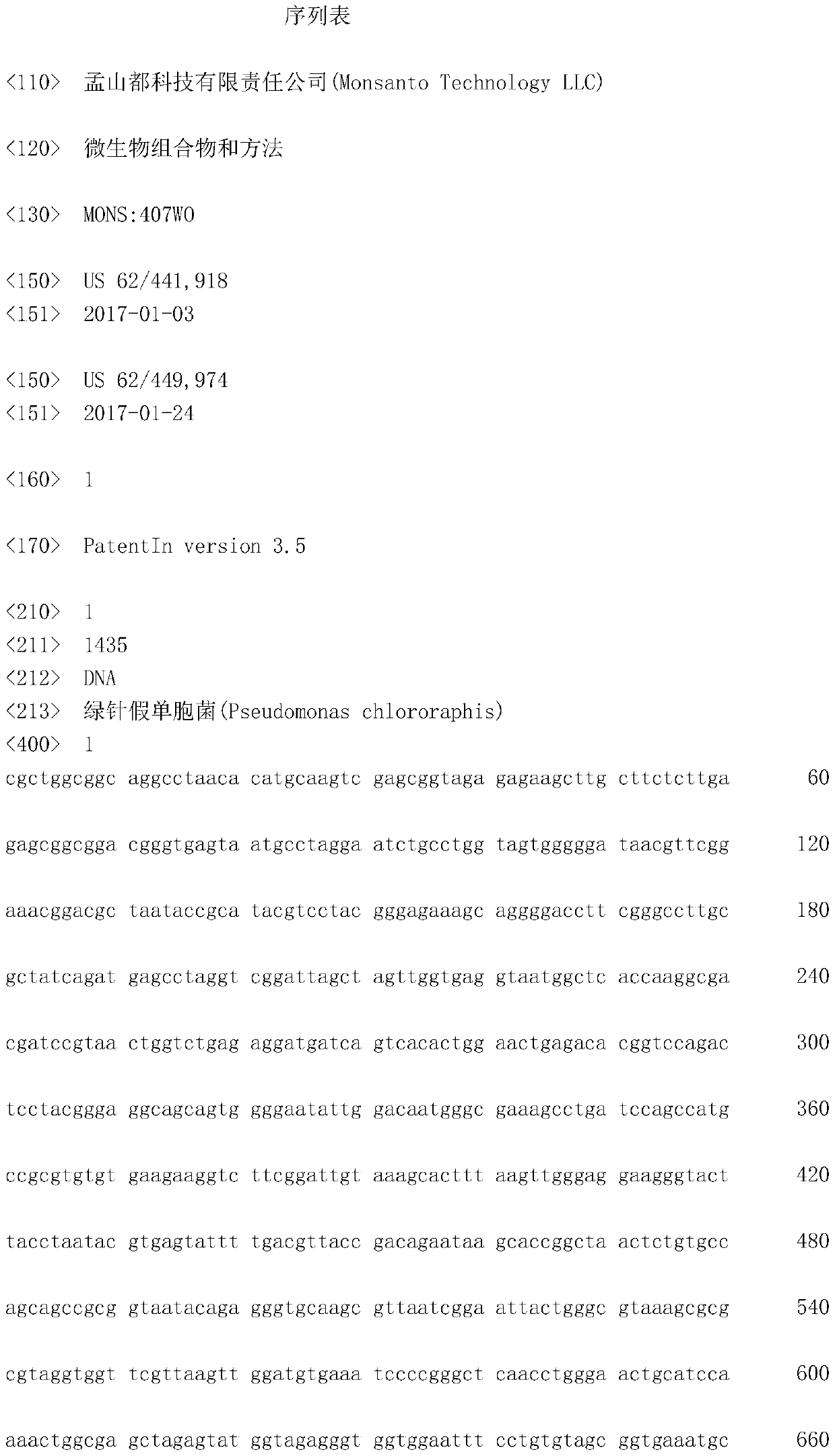
[0160] The MON 201510 isolate was identified as Pseudomonas chlorospinum by 16S ribosomal DNA (rDNA) sequencing. The 16S rDNA sequence was determined by genome-wide next-generation sequencing (NGS) and derivation of related 16S rDNA sequences. The 16S rDNA sequence of the MON 201510 isolate is provided as SEQ ID NO:1.
Embodiment 3
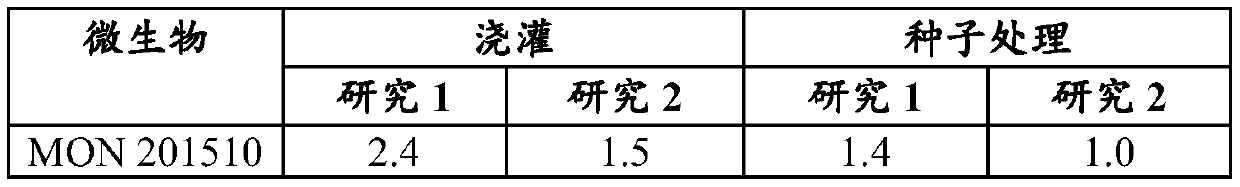
[0161] Example 3. Growth chamber assay for controlling sudden soybean death syndrome (SDS) on MON 201510
[0162] The isolated MON 201510 strain was grown in liquid culture and then frozen in 15% glycerol before use. Soybean seeds were broth-treated with a thawed broth suspension of the MON 201510 isolate at the time of sowing and evaluated in four studies in a growth chamber inoculation disease experiment. The same soybean variety was used for all experiments (maturation group 3.4). Experimental sites were inoculated immediately before planting using sterilized sorghum pellets that had been previously colonized with the SDS pathogen Fusarium cladoides. Control plants were left untreated and inoculated. Disease assessment was performed five weeks after inoculation using an ordinal scale (1-6), where 1 corresponds to asymptomatic plants and 5 corresponds to fully chlorotic and / or necrotic plants. A rating of 6 indicates failure to sprout.
[0163] All experiments utilized a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com