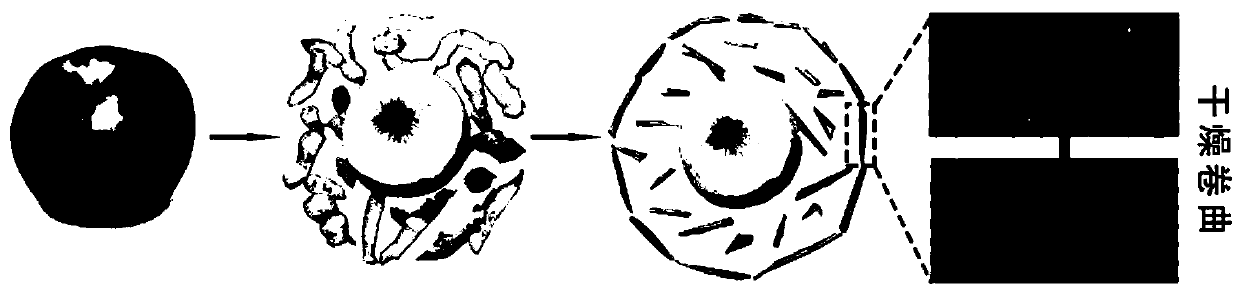
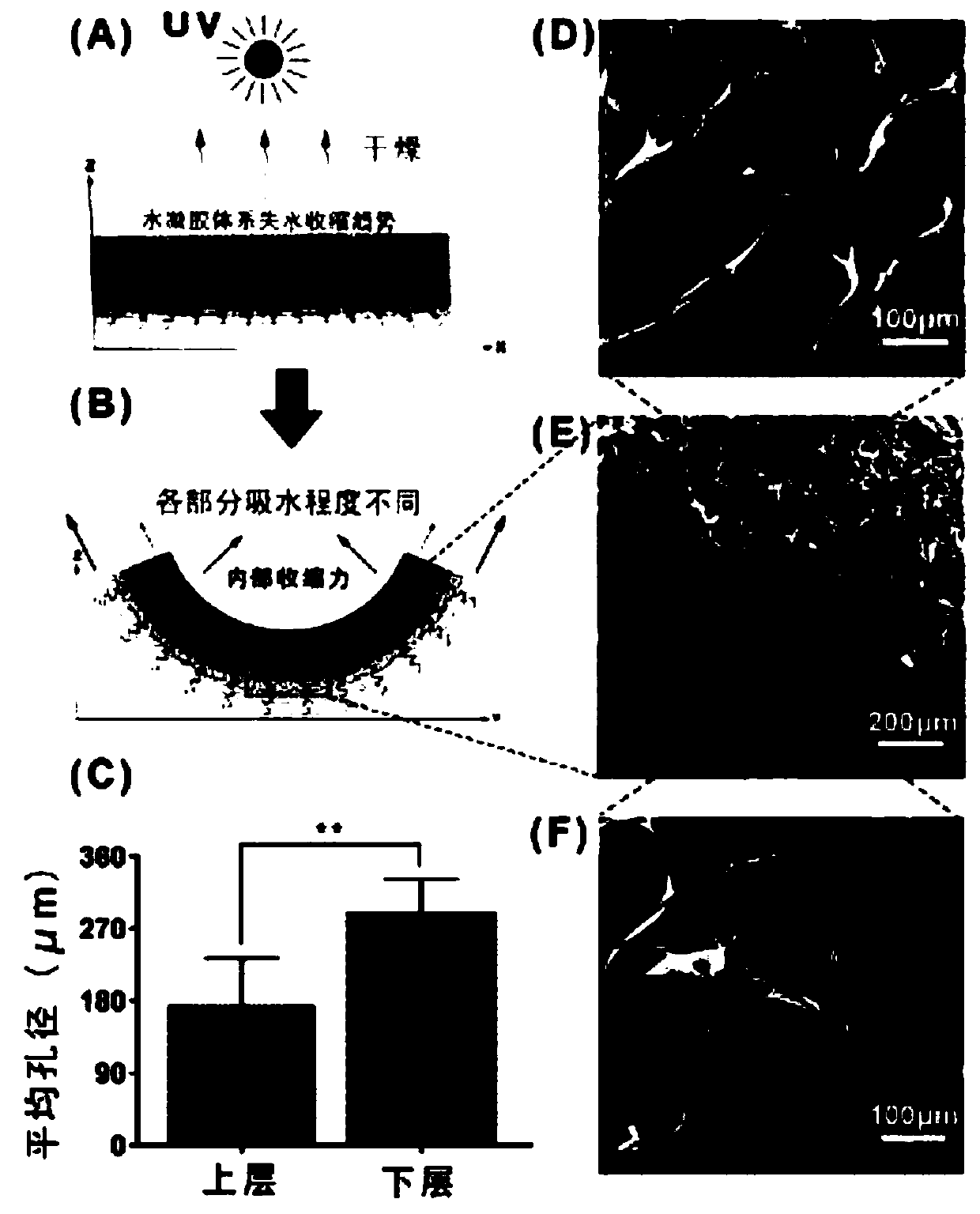
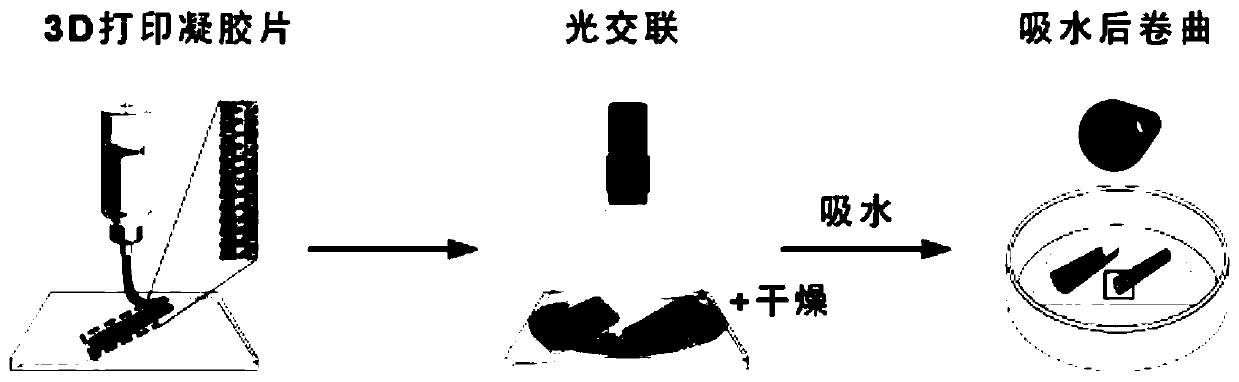
Hydrogel vascular micro stent and preparation method thereof
A hydrogel and hydrogel sheet technology, applied in the field of microvascular stents, can solve the problems of low survival rate and differentiation rate, cumbersome process, easy to destroy tissue structure, etc., and achieve high precision, controllability, and biocompatibility. The effect of good and huge development prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0032] The invention provides a method for preparing a hydrogel vascular microstent, comprising the following steps:
[0033] a) 3D printing the mixed solution of GelMA hydrogel and photoinitiator to obtain GelMA hydrogel sheet;
[0034] b) The GelMA hydrogel sheet obtained in step a) is self-crimped in imitation of apple peel to obtain a hydrogel vascular microstent.
[0035] In the present invention, firstly, the mixed solution of GelMA hydrogel and photoinitiator is 3D printed to obtain the GelMA hydrogel sheet. In the present invention, the GelMA hydrogel can be commercially available or self-made in the laboratory. In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the GelMA hydrogel is a laboratory product. In the present invention, the preparation method of the GelMA hydrogel is preferably specifically:
[0036] Dissolve gelatin in PBS, heat and stir continuously at 50°C-90°C, and add methacrylic anhydride to react at the same time; after the reaction is terminated,...
Embodiment 1
[0075] (1) Use 15wt% gel and 1wt% photoinitiator (Irgacure 2959, Sigma-Aldrich) to mix and use to obtain a GelMA-Irgacure 2959 solution, and print a rectangular shape on a glass slide with the help of a 3D printer (CELLINK AB, Sweden). GelMA hydrogel sheet (size 30mm×2mm×0.20mm);
[0076] The parameters of the 3D printer are: the pneumatic printing nozzle is 200 μm, the temperature of the printing head is 20° C., the temperature of the glass slide on the printing platform is 10° C., and the printing speed is 10 mm / s.
[0077] (2) After cross-linking the GelMA hydrogel sheet obtained in step (1) with 365nm ultraviolet light (XL-1000A) for 2min, then completely dry it at 25°C; then immerse the glass slide in water, and the GelMA hydrogel The sheet was peeled off from the glass slide, and the self-rolling phenomenon could be observed; finally, the successfully curled gel tube was immersed in water for 2 hours to remove excess photoinitiator, and then freeze-dried to obtain the hy...
Embodiment 2
[0082] (1) Use 10wt% gel and 1wt% photoinitiator (Irgacure 2959, Sigma-Aldrich) to mix and use to obtain a GelMA-Irgacure 2959 solution, and print a rectangular shape on a glass slide with the help of a 3D printer (CELLINK AB, Sweden). GelMA hydrogel sheet (size 30mm×2mm×0.20mm);
[0083] The parameters of the 3D printer are: the pneumatic printing nozzle is 200 μm, the temperature of the printing head is 20° C., the temperature of the glass slide on the printing platform is 10° C., and the printing speed is 10 mm / s.
[0084] (2) After cross-linking the GelMA hydrogel sheets obtained in step (1) with 365nm ultraviolet light (XL-1000A) for 0.5min, then completely dry them at 25°C; The film was peeled off from the glass slide, and the self-rolling phenomenon could be observed; finally, the successfully curled gel tube was immersed in water for 2 hours to remove excess photoinitiator, and then freeze-dried to obtain the hydrogel vascular microstent.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com