Porous flat plate type radiator, porous flat plate type radiator system and manufacturing method of porous flat plate type radiator
A radiator, flat-panel technology, used in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, electric solid-state devices, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the problem of low heat dissipation efficiency of chip radiators, achieve high flatness, reduce contact thermal resistance, and efficient conduction Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
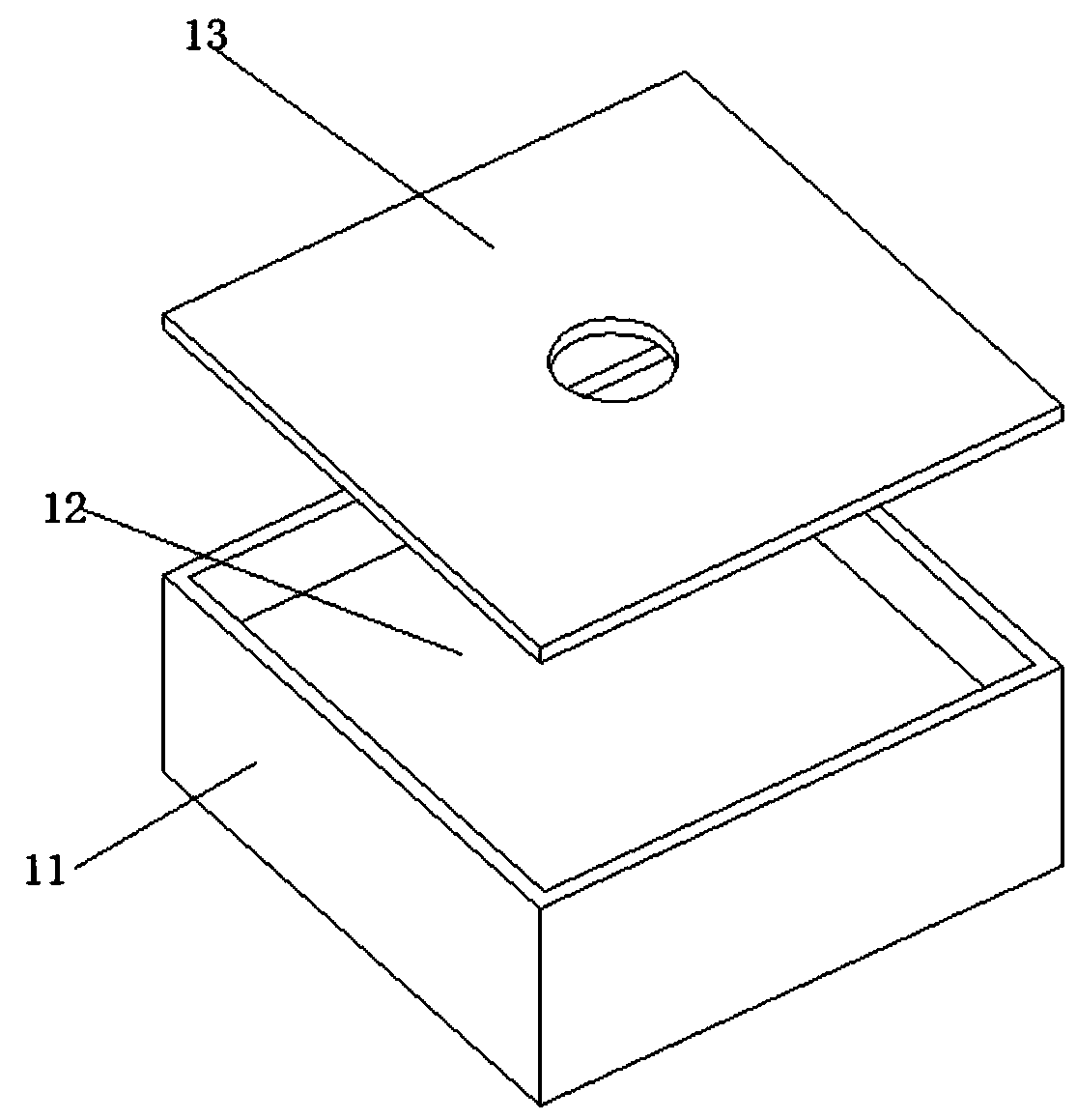
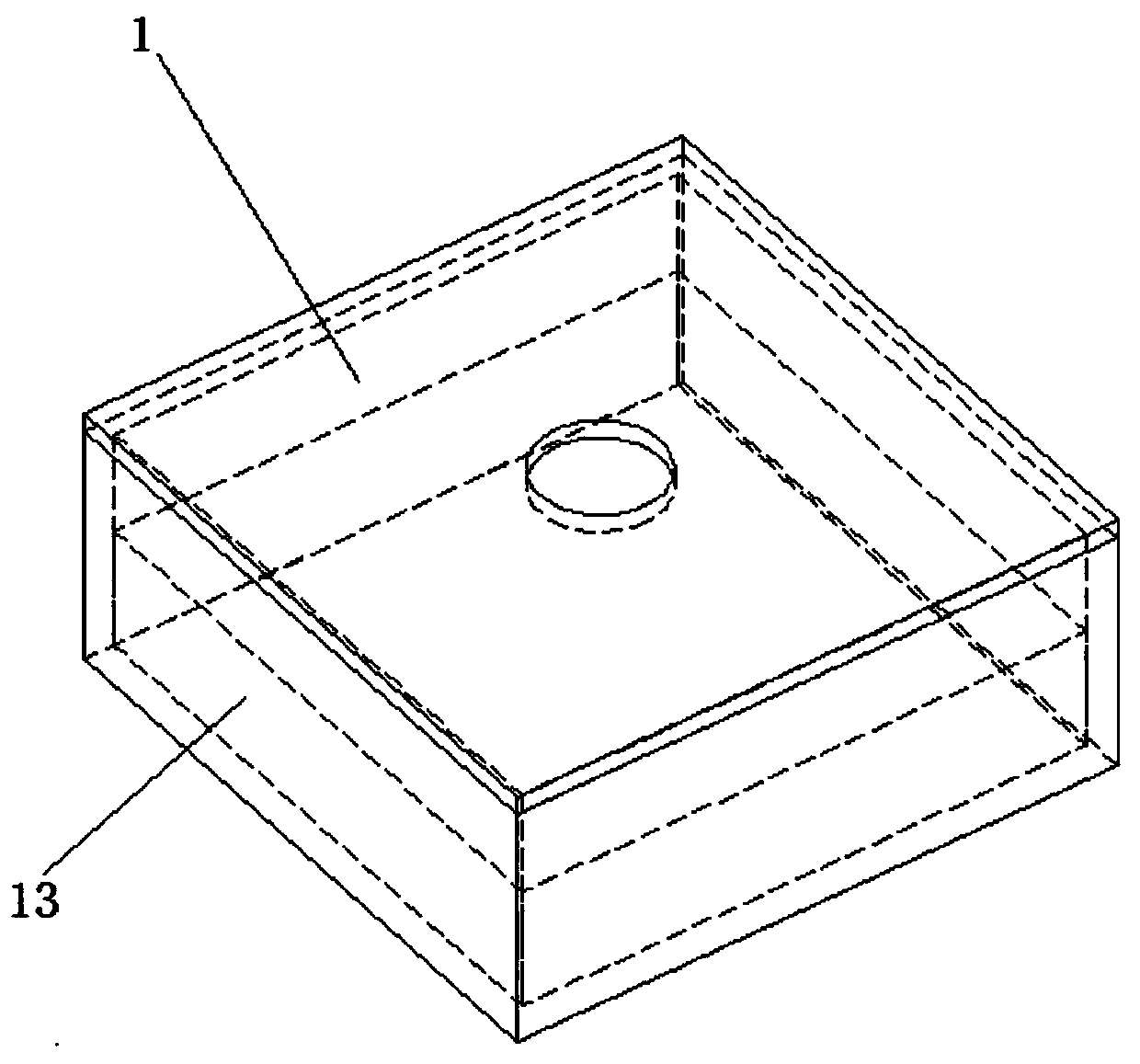
[0029] refer to Figure 1-2 As shown, the radiator provided in this embodiment includes a radiator body 1, a cavity 11 is formed inside the radiator body 1, and a porous structure 12 is formed on the bottom inner wall of the cavity 11; There is a heat pipe working medium; the outer surface of the bottom of the cavity 11 is ground into a plane, which serves as a heat transfer contact plane. By forming a porous structure on the inner wall of the bottom of the cavity 11 opposite to the heat transfer contact plane, heat conduction can be realized effectively and quickly, so that the heat generated by the heating element (such as CPU) that the heat transfer contact plane is in contact with can be quickly and efficiently Efficient conduction, the porous structure is the core of vaporization, which can effectively improve the heat transfer efficiency; at the same time, because the heat transfer contact plane is a plane formed by grinding, the flatness of its contact with the heating ...
Embodiment 2
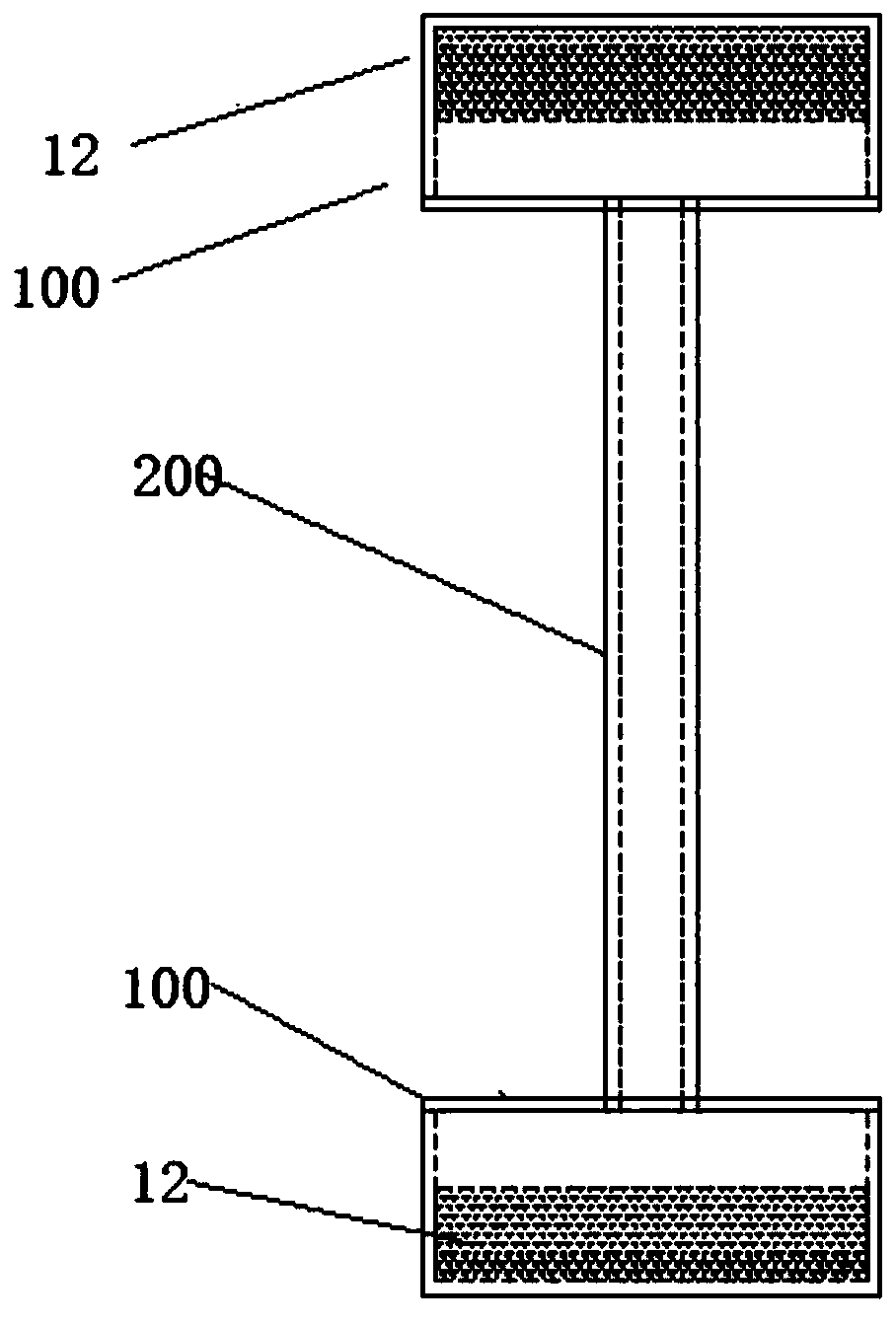
[0033] refer to image 3 As shown, it is a schematic structural diagram of the radiator system provided by this embodiment, which is mainly composed of two radiators 100 and a connecting pipe 200 communicating between the two radiators 100 . Wherein, the two radiators 100 used are the radiators described in Embodiment 1, and the heat pipe medium can be injected after the connecting pipe 200 communicates with the two radiators. Such as Figure 4 As shown, in a specific application, the heat transfer contact plane of one heat sink 100 is in contact with the chip 300, and the heat transfer contact plane of the other heat sink 100 is in contact with the cooling fan 400, so that the heat generated by the chip can be quickly dissipated. Passed to a fan for cooling. In addition, in order to further improve the heat transfer efficiency, the connecting pipe is also made of copper.
Embodiment 3
[0035] This embodiment provides a method for manufacturing a porous flat plate radiator, comprising the following steps:
[0036] Prepare a rectangular copper container;
[0037] Mix and stir 20%-80% of 10-100 micron copper fiber and 80%-20% of 10-100 micron copper powder;
[0038] Place the above-mentioned copper fiber copper powder mixture in the cavity;
[0039] Put the above-mentioned rectangular copper container containing copper fiber and copper powder into a vacuum sintering furnace for sintering, and the sintering vacuum degree is lower than 5×10 -2 Pa, the sintering temperature is 800-1000° and the temperature is kept for 0.5h to 1h, so that the copper fiber, copper powder and rectangular copper cavity are solid-phase metallurgically bonded, and the sintering forms a fine and uniform porous structure; due to the sintering of the copper cavity, a dense The uniform porous structure is conducive to the rapid and uniform conduction of heat, which can greatly improve the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com