Prevention of muscular dystrophy by crispr/cpf1-mediated gene editing
A technology for muscular dystrophy and dystrophin, which is applied in the field of treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, and can solve problems such as the inability to correct DMD mutations and restore the expression of dystrophin
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0262] Example 1 - Materials and methods
[0263] The pLbCpf1-2A-GFP and pAsCpf1-2A-GFP plasmids were generated. From the (Addgene plasmid #69988) pY016 plasmid (Zetsche et al., 2015) (pcDNA3.1-hLbCpf1) kindly provided by Feng Zhang and the (Addgene plasmid #69982) pY010 plasmid (Zetsche et al., 2015 ) (pcDNA3.1-hAsCpf1) PCR amplified human codon-optimized LbCpf1 and AsCpf1, respectively. The Cpf1 cDNA and T2A-GFP DNA fragments were cloned into the backbone of the pSpCas9(BB)-2A-GFP(PX458) plasmid (Ran et al., 2015), which was kindly provided by Feng Zhang (Addgene plasmid #48138), and the plasmid was cloned with AgeI / EcoRI cut to remove SpCas9(BB)-2A-GFP. In-Fusion HD Cloning Kit (Takara Bio) was used. Cpf1 guide RNA (gRNA) targeting the human DMD or mouse Dmd locus was subcloned into newly generated pLbCpf1-2A-GFP and pAsCpf1-2A-GFP plasmids using BbsI digestion and T4 ligation. Detailed primer sequences can be found in Table C, genomic target sequences can be found in ...
Embodiment 2
[0284] Example 2 - Results
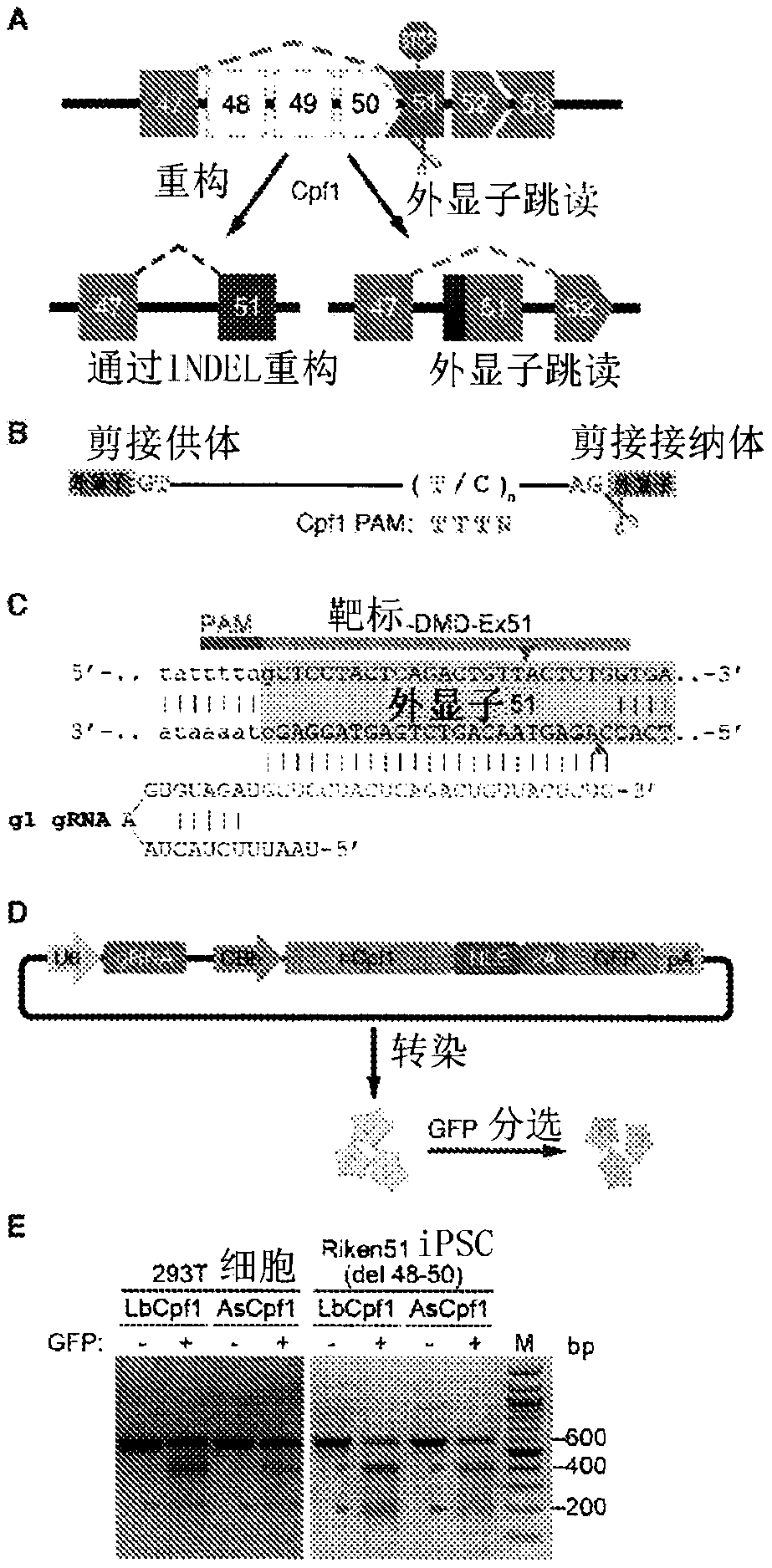
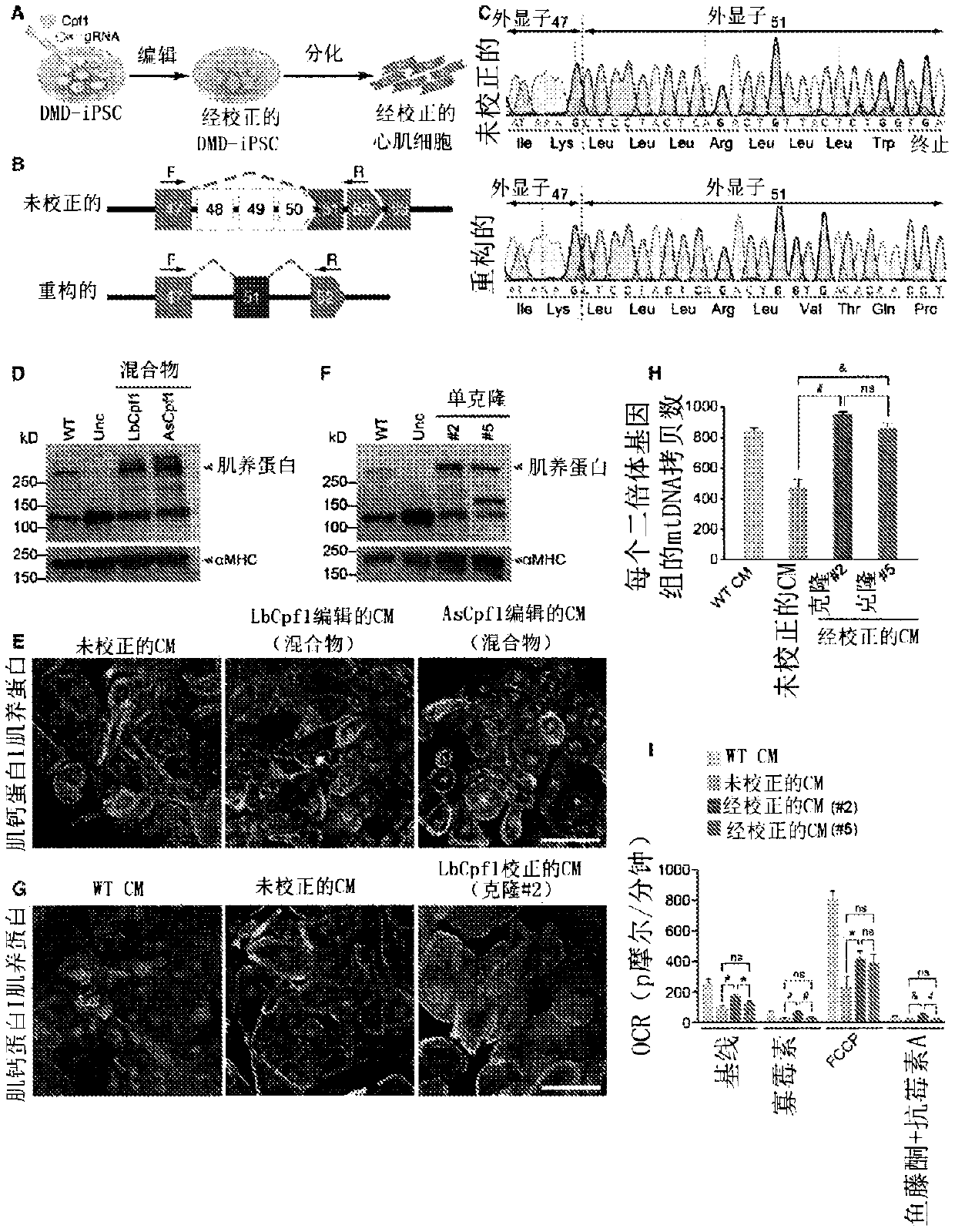
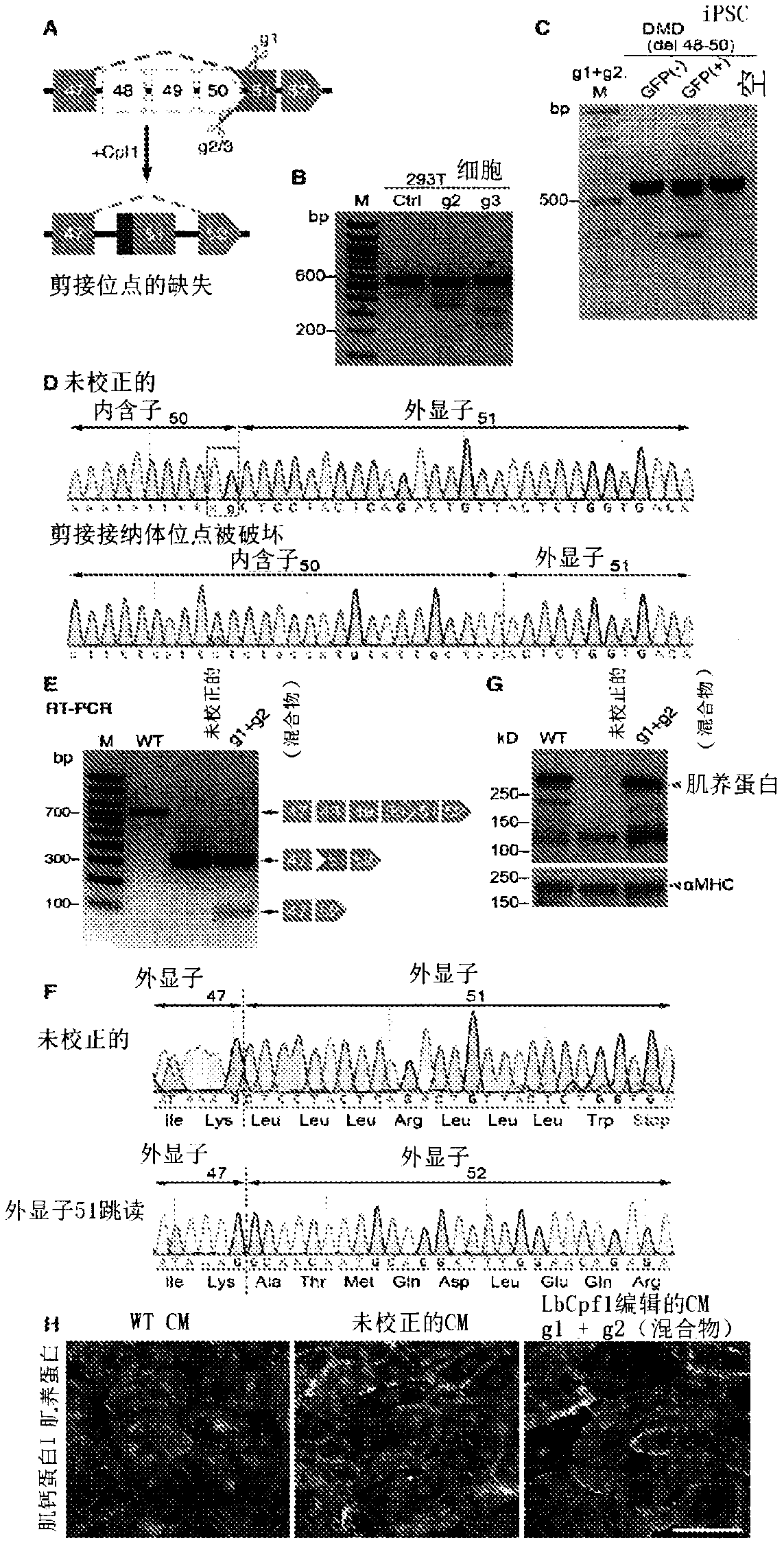
[0285] Correction of DMD iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes by Cpf1-mediated genome editing. Exon deletions preceding exon 51 of the human DMD gene disrupt the open reading frame (ORF) by juxtaposing exons out-of-frame and represent the most common type of human DMD mutation (Aartsma-Rus et al., 2009). In principle, skipping of exon 51 could restore the DMD ORF in 13% of DMD patients with exon deletion (Cirak et al., 2011). To test the potential of Cpf1 to correct this type of "hot spot" mutation, the inventors used DMD fibroblast-derived iPSCs (Riken HPS0164, abbreviated as Riken51), which have a deletion of exons 48 to 50, introducing exon A premature stop codon within 51 (Fig. 1A).
[0286] The splice acceptor region is generally T / C rich (Padgett, 2012), which generates an ideal PAM sequence for genome editing by the Cpf1 endonuclease (Fig. 1B). To rescue dystrophin expression in Riken51 iPSCs, the inventors used Cpf1 gRNA to target exon 51, introd...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com