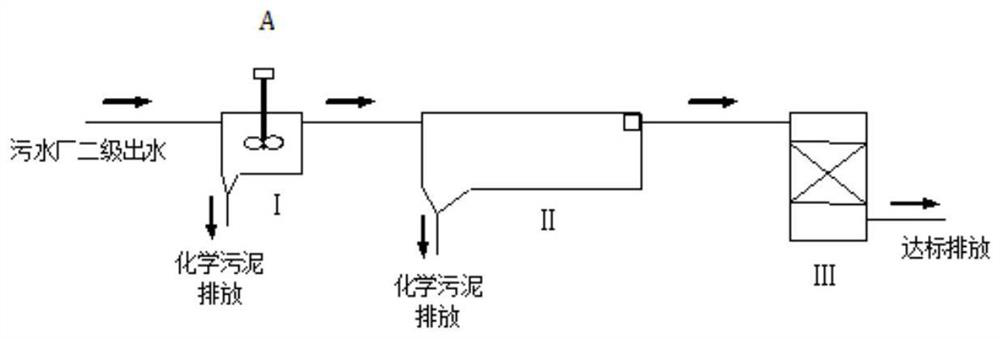
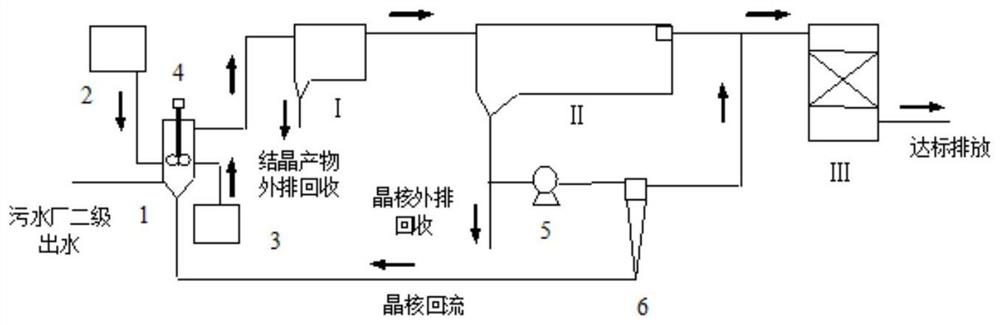
A method for recovering phosphorus in the secondary effluent of a sewage plant
A technology of secondary water effluent and recovery method, which is applied in the direction of water/sewage multi-stage treatment, water/sewage treatment, chemical instruments and methods, etc., and can solve problems such as large equipment or structures, and difficulty in improving the quality of phosphorus removal processes. , to achieve the effect of simple and easy process transformation, high recycling value and stable phosphorus removal effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] The concentration of phosphorus in the secondary effluent of the sewage plant is 1.05mg / L, and the treatment capacity is 2m 3 / h, the hydraulic retention time of the primary sedimentation tank and the secondary sedimentation tank are the same as the coagulation tank and sedimentation tank of the sewage plant, which are 20min and 2h respectively, and the corresponding device volumes are 670L and 4000L. The filtration rate of the filter tank is the same as that of the sewage plant filter tank, which is 20m / h. The hydraulic retention time of the forced agglomeration crystallizer is 5min, and the corresponding volume is 180L. The hydraulic retention time of the hydrocyclone concentrator 6 is 20s, the corresponding volume is 12L, and the initial seed crystal dosage is 50g / L.
[0048] After the reaction is stable, the flow rate of the return sludge pump is 0.5m 3 / h, lift 40m. The pH in the forced agglomeration crystallizer 1 is controlled at 8.5, Ca 2+ The dosage is cont...
Embodiment 2
[0051] The difference from Example 1 is that the phosphorus concentration in the secondary effluent is 2.62 mg / L (winter effluent from the sewage plant). The pH in the forced agglomeration crystallizer 1 is controlled at 8.5, Ca 2+ The dosage is controlled at 10mg / L, and the stirring speed is controlled at 50rpm. After the reaction is stable, the average particle size of seed crystal HAP is maintained at about 100 μm, and the number of seed crystals is stable at about 25 g / L.
[0052] The operation results show that after the reaction is stable, the phosphorus concentration in the effluent of the system is stable below 0.25mg / L, and the pH is stable at about 8.2, which meets the first-class A standard of the "Pollutant Discharge Standard for Urban Sewage Treatment Plants" (GB 18918-2002), and can also be It meets the Class IV standard of "Surface Water Environmental Quality Standard" (GB 3838-2002). The recycling rate of phosphorus in the system is above 90%.
Embodiment 3
[0054] The difference from Example 1 is that the phosphorus concentration in the secondary effluent is 0.8 mg / L (summer effluent from the sewage plant). The flow rate in the forced agglomeration crystallizer 1 is controlled at 12m / h, the pH is controlled at 8.8, and the Ca 2+ The dosage is controlled at 40mg / L, and the stirring speed is controlled at 100rpm. After the reaction was stable, the average particle size of seed crystal HAP was maintained at about 75 μm, and the number of seed crystals was stable at about 50 g / L.
[0055] The operation results show that after the reaction is stable, the phosphorus concentration in the effluent of the system is stable below 0.2mg / L, and the pH is stable at about 8.4, which meets the first-class A standard of the "Pollutant Discharge Standard for Urban Sewage Treatment Plants" (GB 18918-2002), and can also be It meets the Class IV standard of "Surface Water Environmental Quality Standard" (GB 3838-2002). The recycling rate of phospho...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com