Methods, kits, mutant genotypes for earlier rice flowering time
A technology of flowering time and mutated genes, applied in the field of molecular genetics, can solve problems such as unclear function
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach
[0042] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
[0043] Unless otherwise specified, the examples follow conventional experimental conditions, such as the Molecular Cloning Experiment Manual of Sambrook et al. (Sambrook J & Russell DW, Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2001), or the conditions suggested by the manufacturer's instructions. Unless otherwise specified, the chemical reagents used in the examples are all conventional commercially available reagents, and the technical means used in the examples are conventional means well known to those skilled in the art.
Embodiment 1
[0044] Example 1 Rice OsFBO14 Gene Sequence and gRNA Sequence
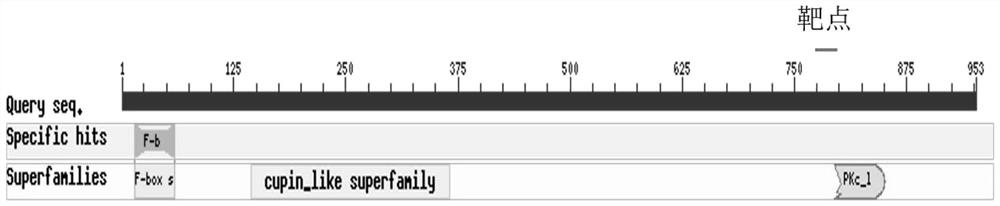
[0045] The sequence of the coding region of the rice OsFBO14 (LOC_Os03g27250) gene is shown in SEQ ID NO.9, and the protein encoded by it contains the F-box domain ( figure 1 ), the sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.10. There is no information about the function of this gene in rice and the specific traits it controls. In order to clarify the function of the gene in rice, the present invention intends to use the CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing method to mutate the OsFBO14 gene sequence and knock out the function of the gene in rice. The present invention selects the sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1 as the target region for CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing, and synthesizes a gRNA sequence (see SEQ ID NO.2 for the sequence).
Embodiment 2
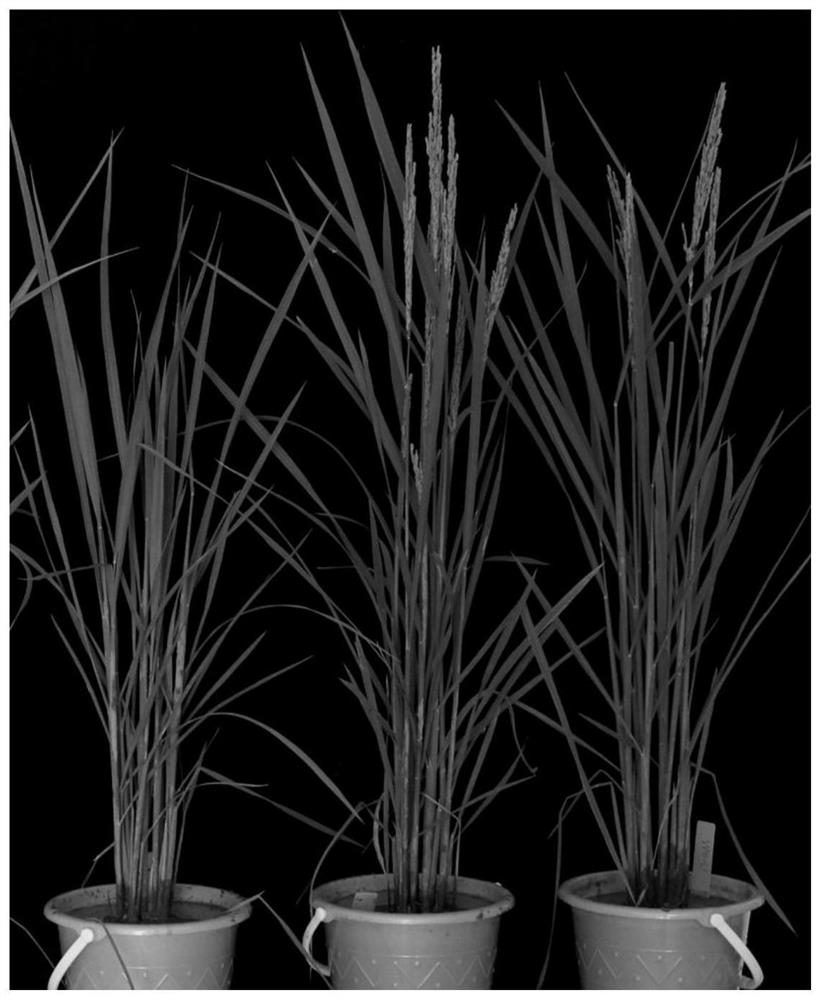
[0046] Example 2 The function of rice OsFBO14 gene and the use of CRISPR / Cas9 method to advance rice flowering time
[0047] 1. Construction of CRISPR / Cas9 vector.
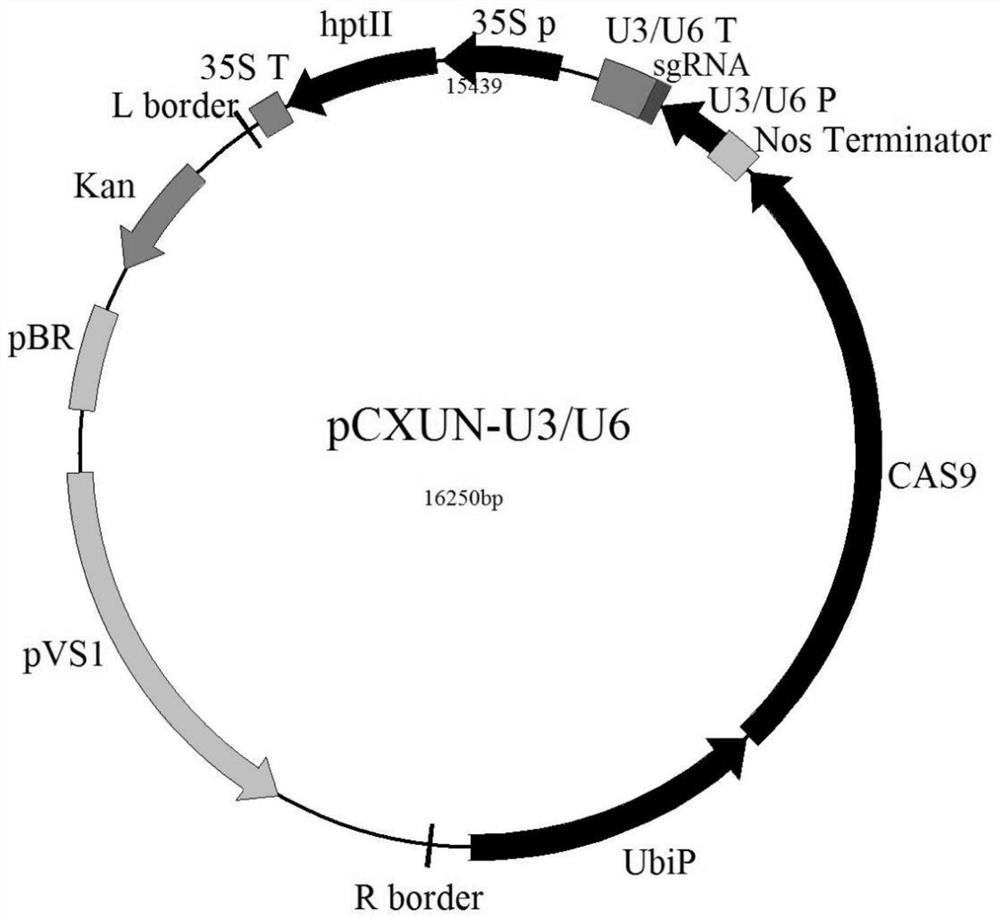
[0048] The present invention selects the japonica rice variety Zhonghua 11 (ZH11, bred and provided by the Institute of Crop Science, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences) as the receptor for gene editing. The Escherichia coli strain was from Tran1-T1 Phage Resistant Competent, purchased from Quanshijin Biotechnology Co., Ltd. Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain EHA105 was purchased from Shanghai Shifeng Biotechnology Co., Ltd. The sgRNA backbone vector pCXUN-U6 was obtained from Zhao Yunde's laboratory at the School of Cell and Developmental Biology at the University of California. The main reagents Taq enzyme was purchased from TIANGEN, endonuclease XbaI was purchased from NEB; KT, 6-BA, IAA, NAA, 2,4-D were purchased from Sigma; Cn, Hn, AS were purchased from GiBco; other inorganic reagents were from Sinopha...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com