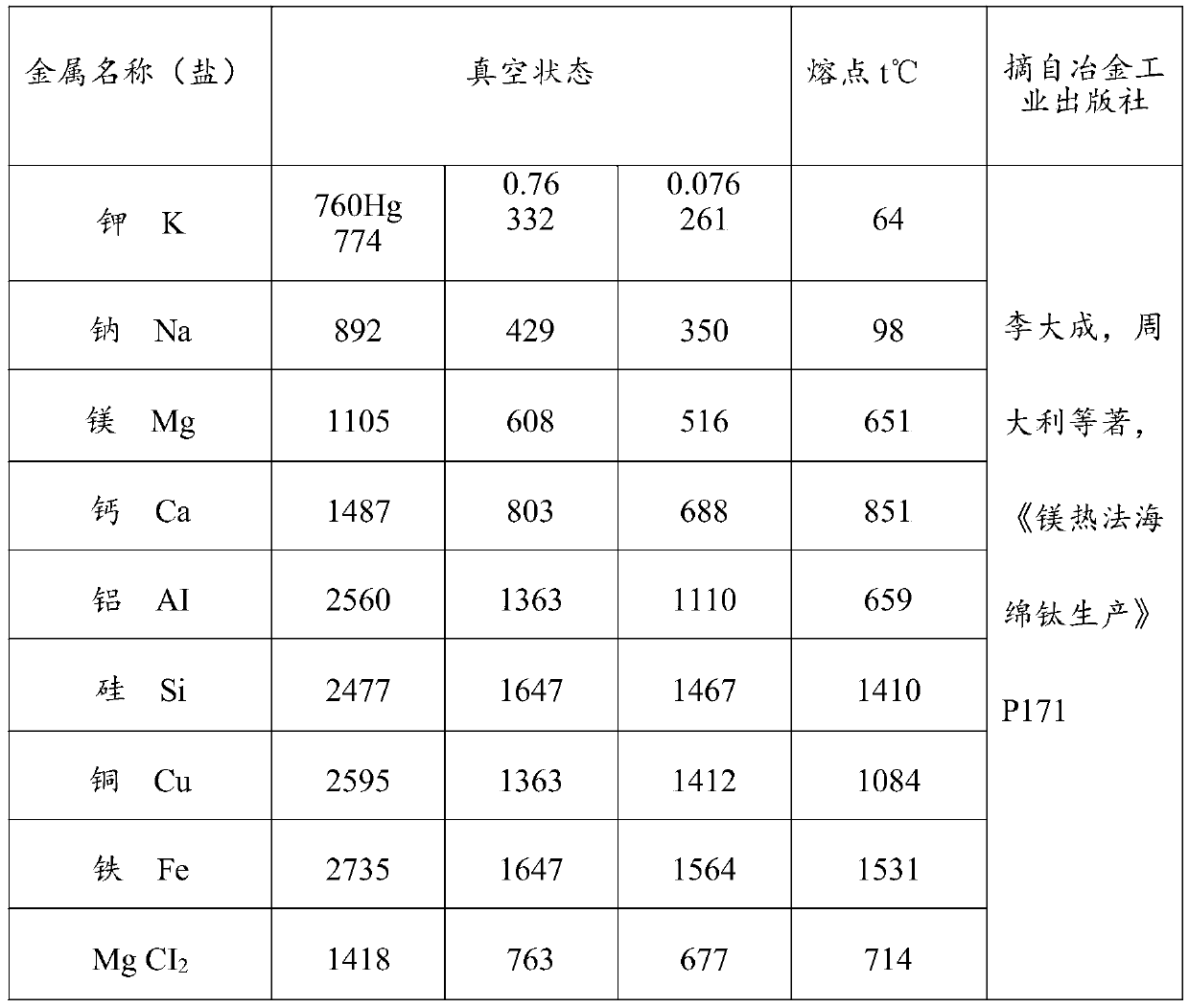
Method for recycling magnesium refining flux waste residues by means of boiling point differences
A technology of flux and waste slag, which is applied to the improvement of process efficiency, silicon oxide, calcium/strontium/barium halides, etc., and can solve the problems of resource waste and recovery costs, unsuitable for industrial production applications, uneconomical and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
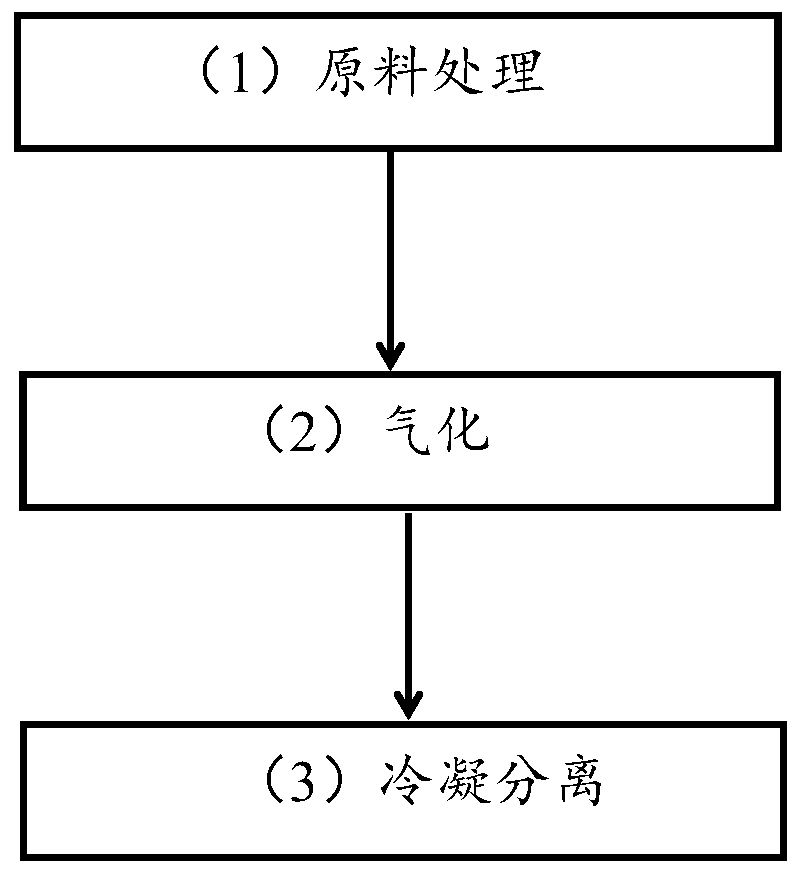
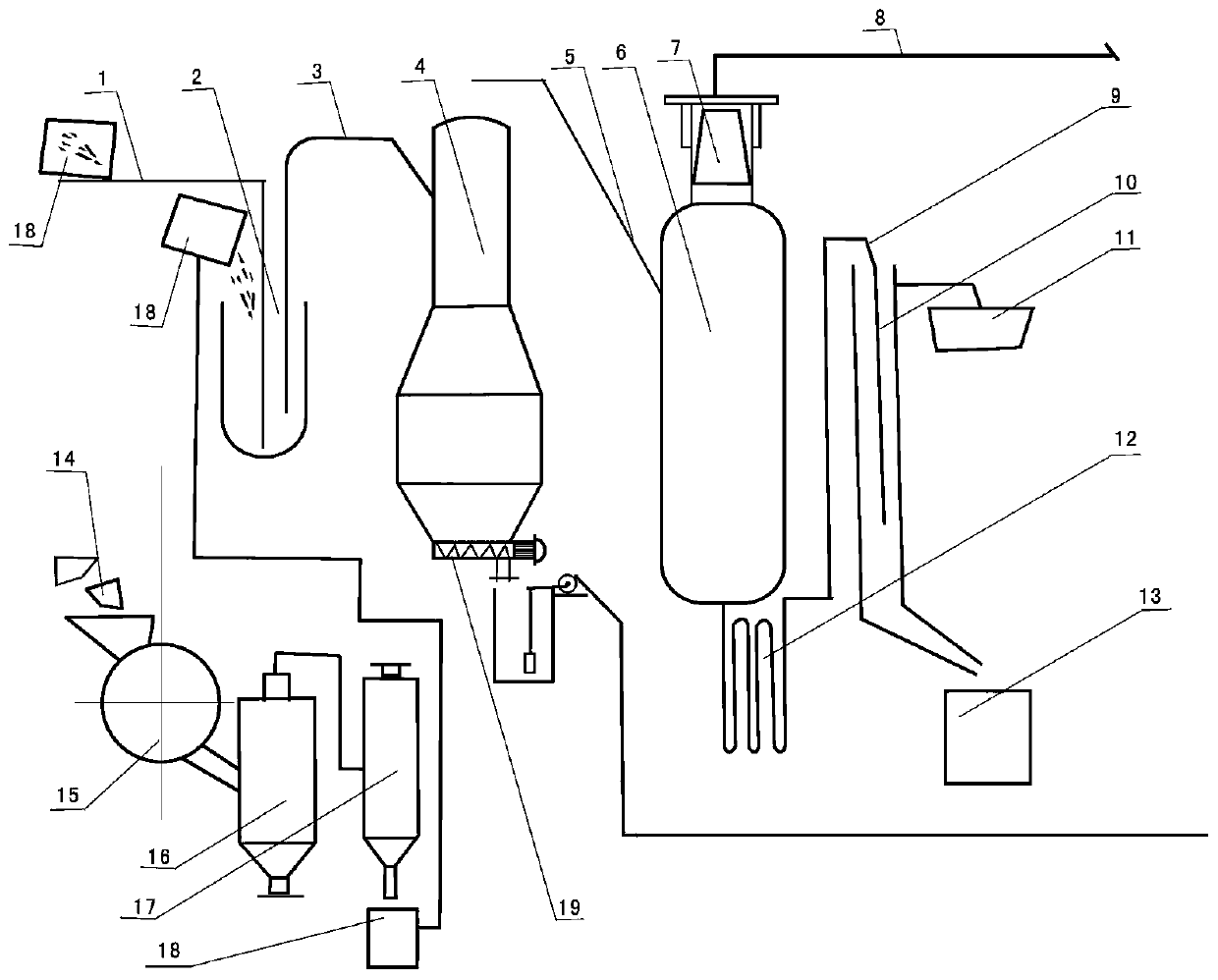
[0049] A method for recovering magnesium refining flux waste slag by using the difference in boiling point, the method specifically includes the following steps:
[0050] (1) Raw material treatment: the magnesium refining flux waste slag supplied by the magnesium smelter factory and the magnesium refining flux waste slag supplied by the external factory are respectively processed to obtain liquid magnesium refining flux waste slag with good fluidity;
[0051] Among them, the treatment of magnesium refining flux waste supplied by external factories includes the following steps: first crush and then pulverize the magnesium refining flux waste supplied by external factories on the spot, separate through powder separator to obtain flux slag powder with particle size below 10mm, and then moisture-proof packaging , Pull it back to our factory and transfer it to the heating pot, heat it to 800℃~850℃ to get liquid magnesium refining flux waste slag with good fluidity;
[0052] The tre...
Embodiment 2
[0056] A method for recovering magnesium refining flux waste slag by using the difference in boiling point, the method specifically includes the following steps:
[0057] (1) Raw material treatment: the magnesium refining flux waste slag supplied by the magnesium smelter factory and the magnesium refining flux waste slag supplied by the external factory are respectively processed to obtain liquid magnesium refining flux waste slag with good fluidity;
[0058] Among them, the treatment of magnesium refining flux waste supplied by external factories includes the following steps: first crush and then pulverize the magnesium refining flux waste supplied by external factories on the spot, separate through powder separator to obtain flux slag powder with particle size below 10mm, and then moisture-proof packaging , Pull it back to our factory and transfer it to the heating pot, heat it to 800℃~850℃ to get liquid magnesium refining flux waste slag with good fluidity;
[0059] The tre...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Granularity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com