A combined method of using indigenous microorganisms and plants to remove lead pollution in phosphate rock wasteland
A technology of microorganisms and waste land, applied in the restoration of polluted soil and other directions, can solve the problems of heavy metal pollution, slow growth and difficult application in the waste land of phosphate rock that have not been found, and achieve good application prospects and promotion value, low cost, targeted at strong effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
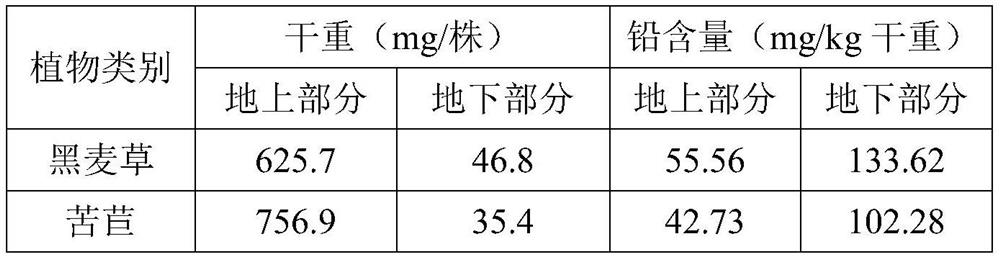
[0028] After sterilizing 500g of uncontaminated common soil, mix it with 20-50g of low-grade phosphate rock powder evenly, then spray lead nitrate solution with a concentration of 80-120mg / L, and stabilize it for 2-4 weeks to obtain a simulated soil sample. The microbial inoculum selected for inoculation is the indigenous high-efficiency lead-dissolving phosphorus-resistant microbial bacterial solution obtained by screening in step (b), namely the Pseudomonas bacterial solution. The bacterial solution was cultured to logarithmic phase before use.
[0029] Control group: 500g of sterilized simulated soil samples were put into plastic flowerpots with a diameter of about 11cm, and then ryegrass seedlings with a height of 5-6cm and chicory seedlings with a height of 1-2cm were transplanted to the same flower In pots, each pot is guaranteed to have 3-4 plants. Considering that the suitable cultivation temperature of the two plants is 20-35°C, cultivate at this temperature and wate...
Embodiment 2
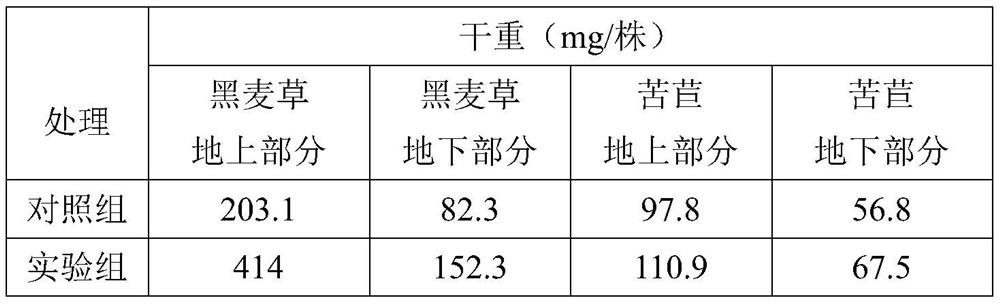
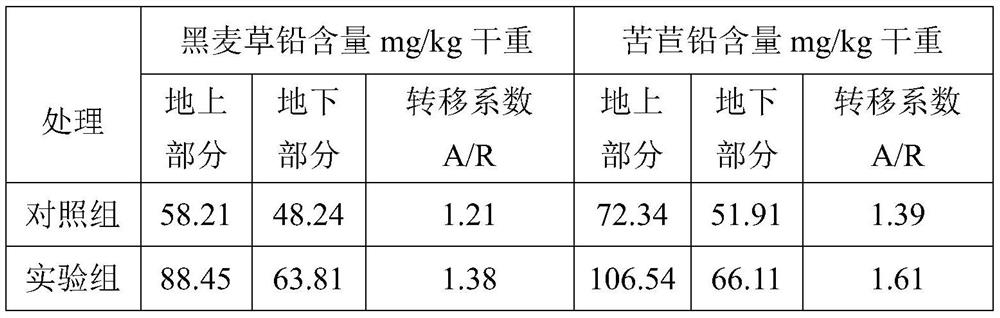
[0038] Considering that most of the lead in the soil is in the form of insoluble PbCO 3 exists, by adding a certain amount of PbCO to ordinary soil 3 way to simulate lead-contaminated soil. Mix 500g of uncontaminated common soil (sterilized in advance), 20-50g of low-grade phosphate rock powder and 1-3g of PbCO 3 Mix evenly to obtain a simulated soil sample.
[0039] Control group: 500g of sterilized simulated soil samples were put into a plastic flowerpot with a diameter of about 11cm, and then ryegrass seedlings with a height of 5-6cm and chicory seedlings with a height of 1-2cm were transplanted into the same flowerpot medium, 3-4 plants are guaranteed in each pot. The cultivation temperature is controlled at 20-35°C, the water content in the soil is kept at 60%-80% of the maximum water holding capacity in the field, and the bacterial liquid is not inoculated.
[0040] Experimental group: 500g of sterilized simulated soil samples were put into a plastic flowerpot with a...
Embodiment 3
[0048] Using the screened indigenous high-efficiency lead-tolerant phosphorus-dissolving microorganisms Pseudomonas and indigenous lead-enriching plants ryegrass and chicory as materials, and taking lead-contaminated phosphate rock waste soil samples (real soil samples) as the removal objects, the research was carried out. corresponding test.
[0049] Control group: 500g of sterilized real soil samples were put into plastic flowerpots with a diameter of about 11cm, and then ryegrass seedlings with a height of 5-6cm and chicory seedlings with a height of 1-2cm were transplanted to the same flower In pots, each pot is guaranteed to have 3-4 plants. Considering that the suitable cultivation temperature for both plants is 20-35°C, cultivate at this temperature and water regularly, keep soil water content at 60%-80% of the maximum water holding capacity in the field, and do not inoculate bacterial liquid.
[0050] Experimental group: put 500g of sterilized real soil samples into p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com