Split gate CSTBT with PMOS current clamping and manufacturing method of split gate CSTBT
A separation gate and current technology, which is applied in the field of separation gate CSTBT and its production, can solve the problems of excessive saturation current, degradation of breakdown characteristics of CSTBT, etc., to improve saturation current, improve short-circuit safety working ability, and improve carrier distribution Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
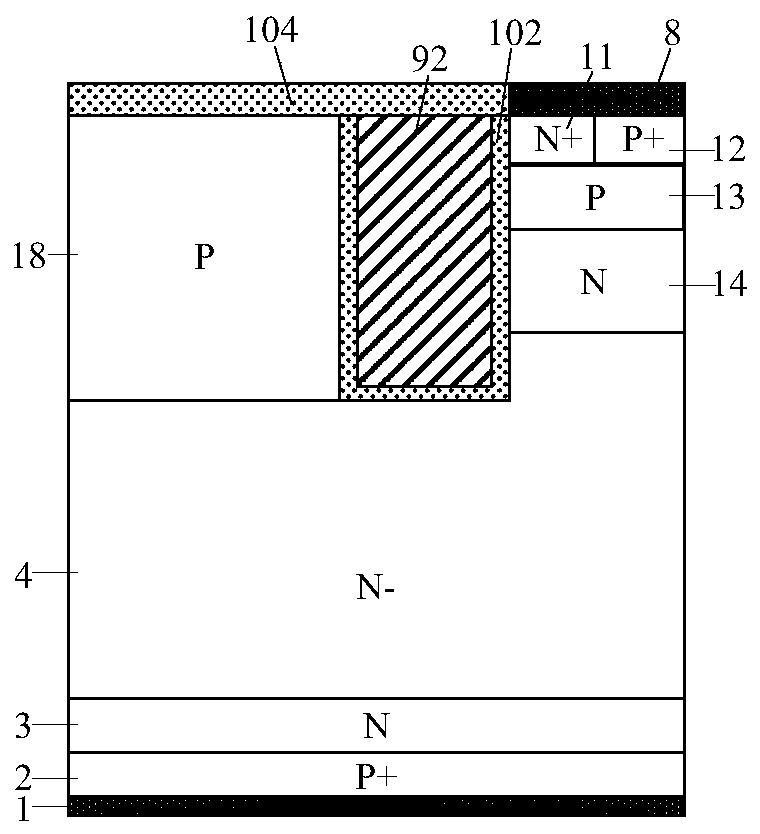
[0053] A split-gate CSTBT with PMOS current clamping, its half-cell structure is as follows figure 2 As shown, it includes: back collector metal 1, P-type collector region 2 located on and connected to the back collector metal 1, N-type field stop layer 3 located on and connected to the P-type collector region 2 and An N-drift region 4 located on and connected to the N-type field stop layer 3; a P-type buried layer 5 located on and connected to the N-drift region 4 and an N-type charge located on and connected to the N-drift region 4 Storage layer 14; N-type doped layer 6 located on the top of the P-type buried layer and connected to it; P-type doped layer 7 located on the top of the N-type doped layer 6 and connected to it; located on the top of the N-type charge storage layer and connected to it The P-type base region 13; the N+ emitter region 11 and the P+ emitter region 12 that are independent of each other and placed side by side on the top of the P-type base region; Th...
Embodiment 2
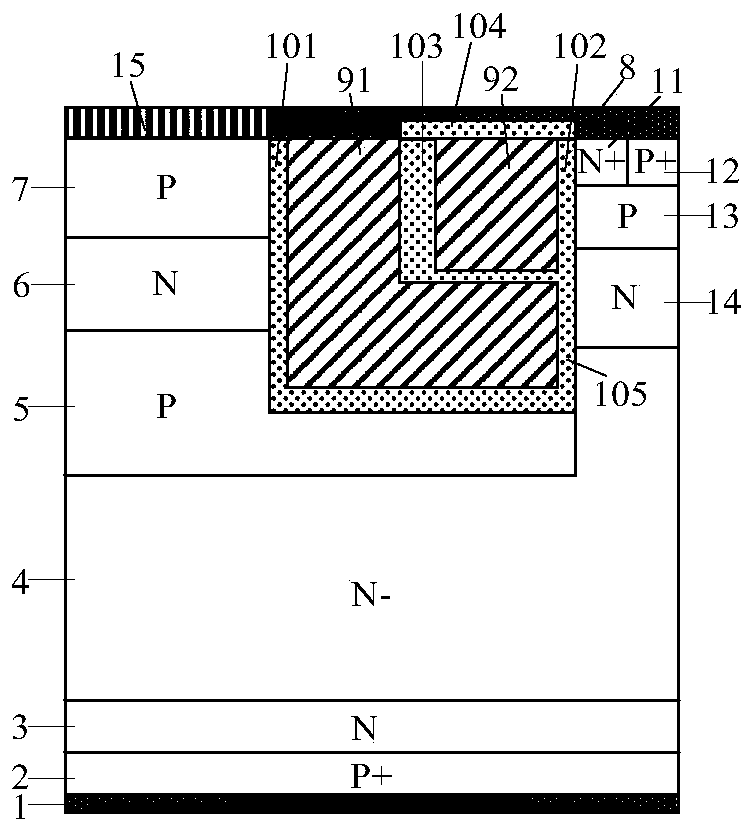
[0055] A split-gate CSTBT with PMOS current clamping, its half-cell structure is as follows image 3 As shown, this embodiment introduces a Schottky contact metal 15 connected to the P-type doped region 7 on the basis of the first embodiment, and the rest of the structure is the same as that of the first embodiment.
[0056] The Schottky contact metal 15 introduced in this embodiment has the same potential as the emitter metal 1 , and the introduction of the Schottky contact metal 15 can reduce the conduction voltage drop of the PMOS and reduce the switching loss of the device.
Embodiment 3
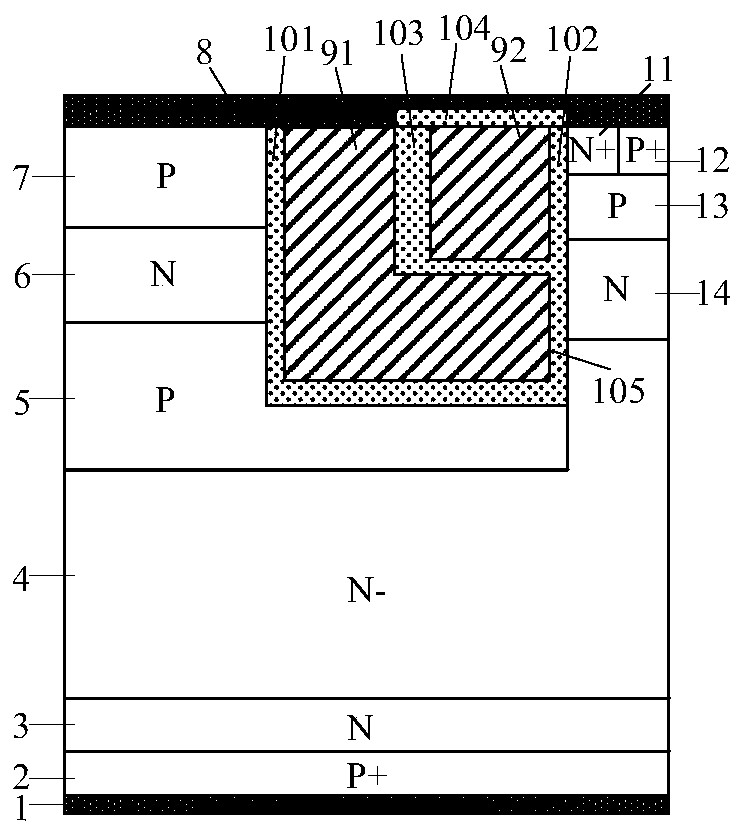
[0058] A CSTBT with a PMOS current clamping separation gate, and its half-cell structure is as follows Figure 4 As shown, in this embodiment, on the basis of embodiment 1, the P-type buried layer 5 is extended below the N-type charge storage layer 14, and the rest of the structure is the same as that of embodiment 1.
[0059] In this embodiment, the purpose of extending the P-type buried layer 5 to the bottom of the N-type charge storage layer 14 is that when the mesa of the structure increases, the P-type buried layer 5 can still transfer the drift region below the N-type charge storage layer 14 to the bottom of the N-type charge storage layer 14. depletion, so that the potential of the N-type charge storage layer 14 is determined by the potential of the P-type buried layer 5, and the structure can reduce the saturation current by adjusting the concentration of the P-type buried layer.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com