Method for producing chitosan oligosaccharide through solid-state fermentation of aspergillus oryzae
A solid-state fermentation, Aspergillus oryzae technology, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, fermentation, etc., can solve the problem of low yield of chitosan
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] Example 1: Optimization of moisture content in the culture medium
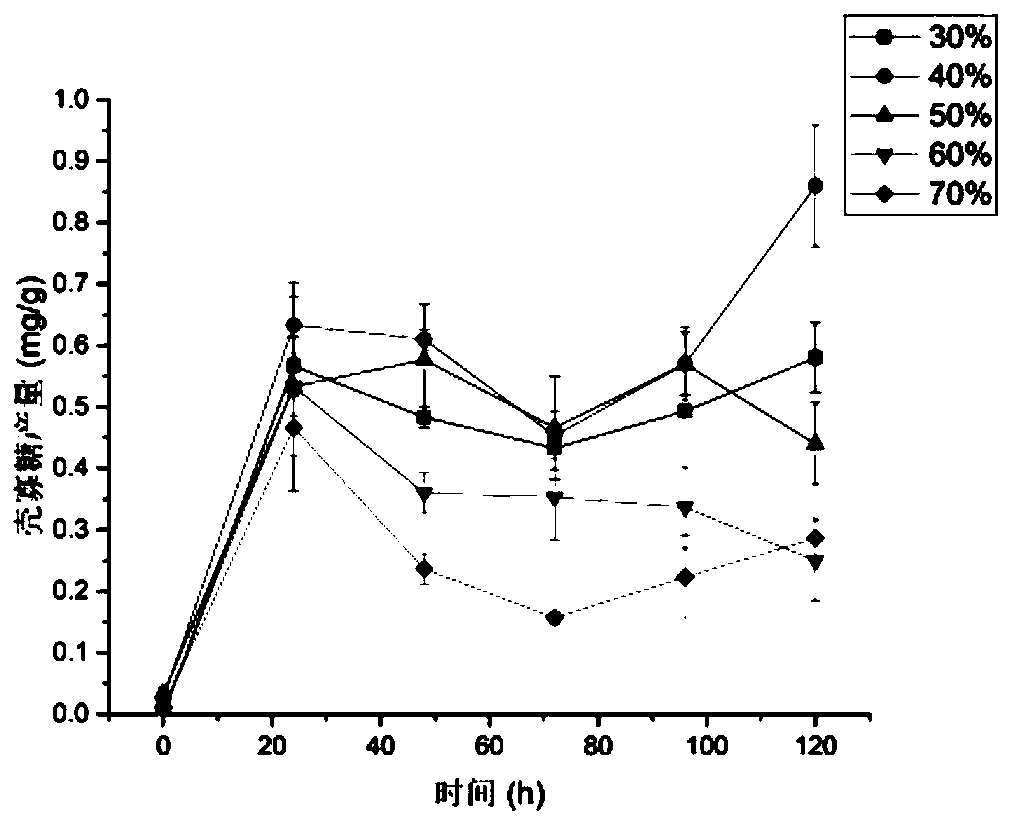
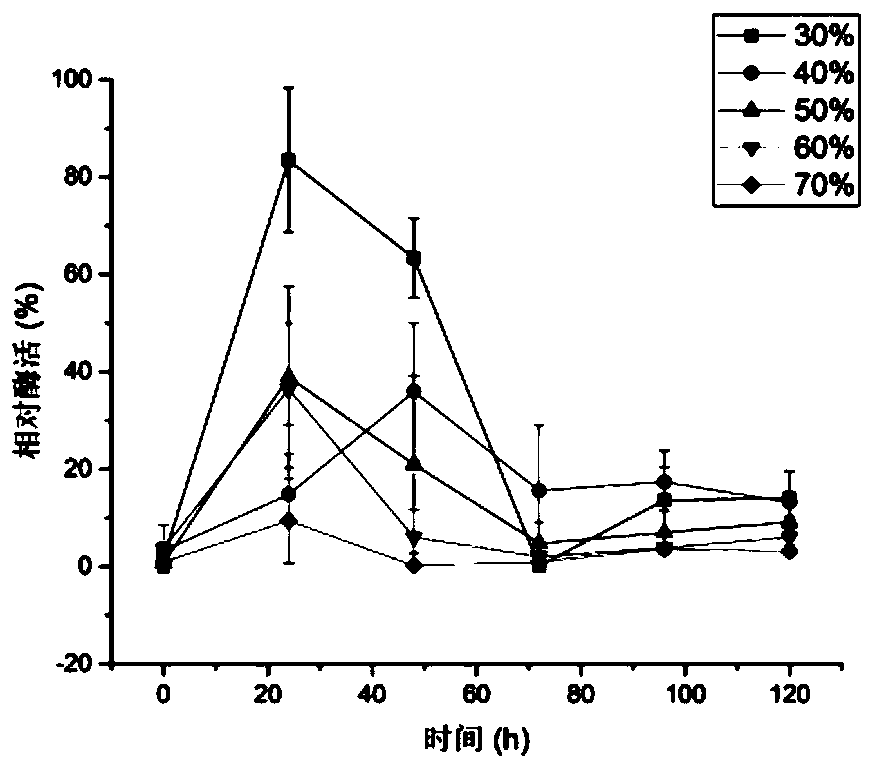
[0050] On the basis of the fermented solid medium, add distilled water to the medium according to the initial water content of 30%, 40%, 50%, 60%, and 70% respectively (the water content of bran is calculated as 12%), and the incubator at 30°C Cultured in medium for 120h, samples were taken every 24h. The content of glucosamine, the relative enzyme activity of chitosanase and the number of spores were determined respectively. The result is as Figure 1-2 Shown, followed by the content of chitosan oligosaccharides, chitosanase relative enzyme activity changes in the fermentation process.
[0051] Depend on Figure 1-2 It can be seen that the output of chitosan oligosaccharide fluctuates with the increase of time. Because when generating chitosan oligosaccharide, the Aspergillus oryzae thallus in the culture medium also consumes a part of chitosan oligosaccharide, so the output of chitosan oligosaccha...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Embodiment 2: inoculum size optimization
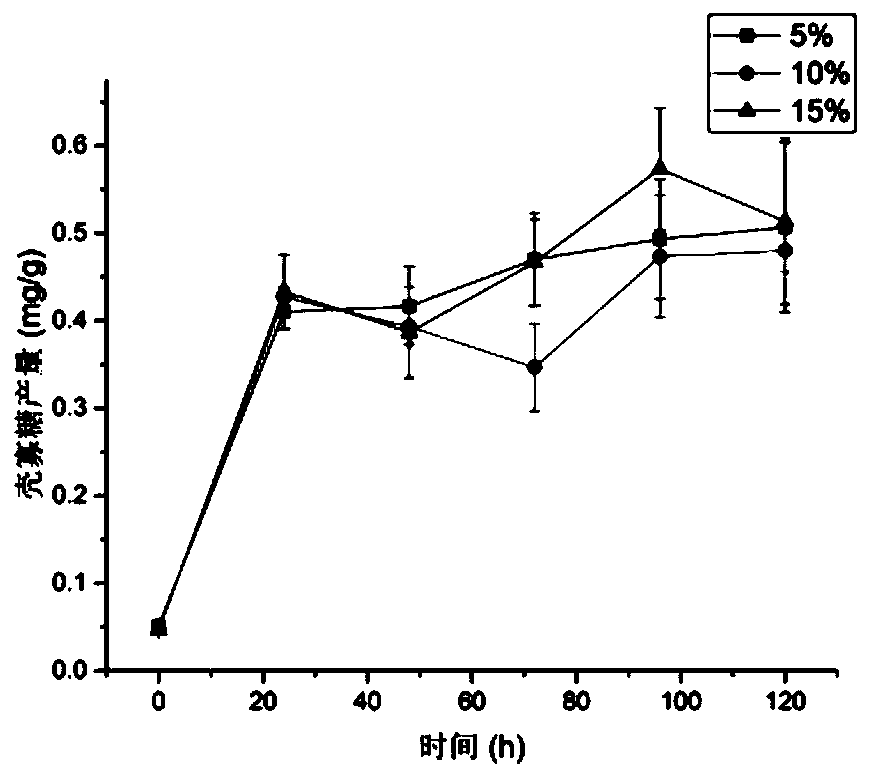
[0055] After confirming that the above-mentioned initial water content is 50%, on the basis of fermentation solid medium, inoculate according to the inoculation amount of 5%, 10%, and 15%, respectively, cultivate in a 30°C incubator for 120h, and take a sample every 24h. The content of glucosamine and the activity of chitosanase were determined respectively. The result is as Figure 3-4 Shown, followed by the content of chitosan oligosaccharides, chitosanase relative enzyme activity changes in the fermentation process.
[0056] Depend on Figure 3-4 It can be seen that the oligochitosan production in the 5% culture medium increases gradually with time, and the maximum value is 2.55 mg / ml for 120 h of fermentation; the 10% culture medium increases first Afterwards, the decline is increasing, and its maximum value is 2.36 mg / ml when it is fermented for 96 hours; the production of chitosan oligosaccharides in the 15% culture me...
Embodiment 3
[0059] Embodiment 3: Substrate addition amount optimization
[0060] After determining that the above-mentioned initial moisture content is 50%, and the inoculum size is 15%, on the basis of the fermentation solid medium, add chitosan according to the substrate addition amount of 2%, 5%, 8%, and 10%, respectively, at 30°C Cultured in the incubator for 120h, and samples were taken every 24h. The content of glucosamine and the activity of chitosanase were determined respectively. The result is as Figure 5-6 Shown, followed by the content of chitosan oligosaccharides, chitosanase relative enzyme activity changes in the fermentation process.
[0061] Depend on Figure 5-6 It can be seen that the production of chitosan oligosaccharides fluctuates with time in the medium with different additions of four kinds of substrates, and they all have a trend of first increasing, then decreasing, then increasing and then decreasing. The four different gradient media all reached the highe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com