Non-reducing peptide mapping method of protein
An analytical method and protein technology, applied in the field of biological proteins, can solve the problems of incomplete enzymatic hydrolysis, few peaks, and poor separation of chromatographic peaks, and achieve good separation, more peaks, and stable chromatographic baseline. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
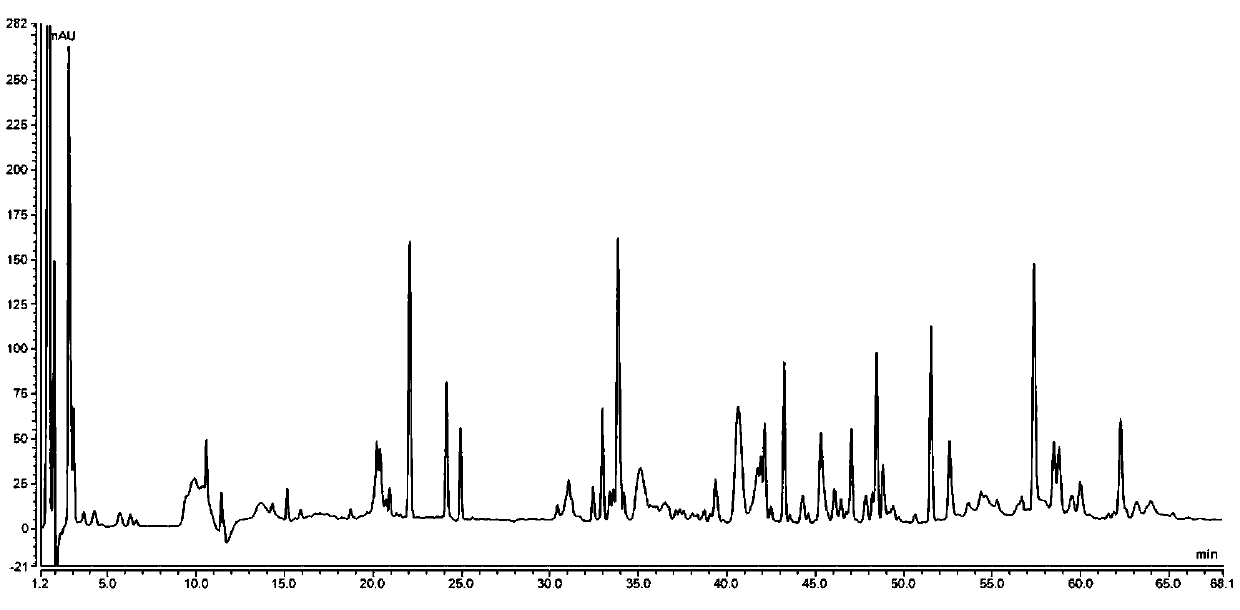
[0121] The protein sample treatment is as follows: take 0.2mg of the protein sample containing sequence 1, use 400μl of ultrapure water each time, 14000g, and change the liquid for 5min ultrafiltration three times, collect the protein solution after ultrafiltration with a pipette, if the solution volume is less than 50μl, use ultrapure water Make up with water, then add 50μl 0.2w / v% RapiGest SF and mix well, place the mixture in a boiling water bath for 10min, then take it out and cool to room temperature; add 20μl of 0.5M ammonium bicarbonate solution and 100μl 0.1mg / ml Promega Sequencing-grade trypsin, after mixing, take it out in a 37°C water bath for 16-18h, and occasionally take it out and shake gently; after the 37°C water bath, add 22 μl of 50% acetic acid solution, centrifuge at 10,000×g for 5 min, and take the supernatant for testing.
[0122] Negative samples are processed as follows: take 50 μl ultrapure water, 50 μl 0.2% RapiGest SF, mix well, place in a boiling wat...
Embodiment 2
[0137] Except that the mobile phase B is: 0.085% trifluoroacetic acid in acetonitrile solution, wherein the acetonitrile solution contains 10% water, other conditions are the same as in Example 1.
[0138] Test results:
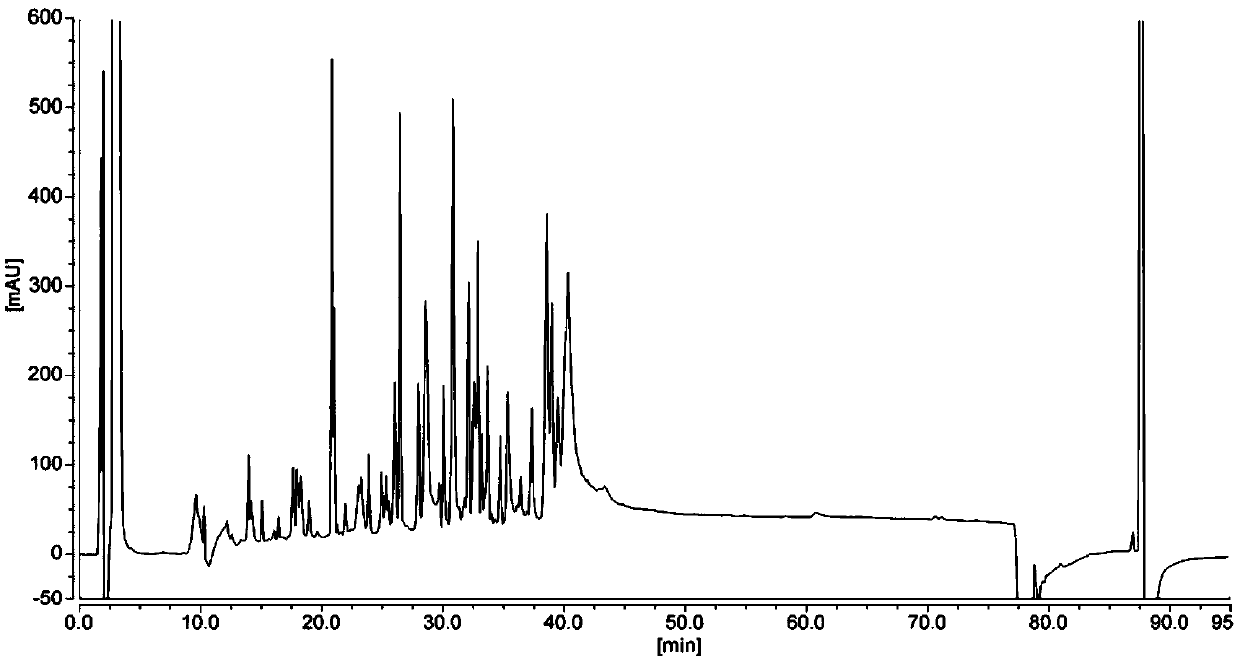
[0139] Test results such as Figure 6 and Table 6, from Figure 6 As can be seen from Table 6, when the water content in the mobile phase B is 10%, the number of peaks in the elution chromatogram is more (75 chromatographic peaks), the distribution of the chromatographic peaks of each peptide is relatively uniform, and the baseline is relatively stable.
[0140] Table 6 Protein peptide map detection results
[0141]
[0142]
Embodiment 3
[0144] Except that the mobile phase B is: 0.085% trifluoroacetic acid in acetonitrile solution, wherein the acetonitrile solution contains 30% water, other conditions are the same as in Example 1.
[0145] Test results:
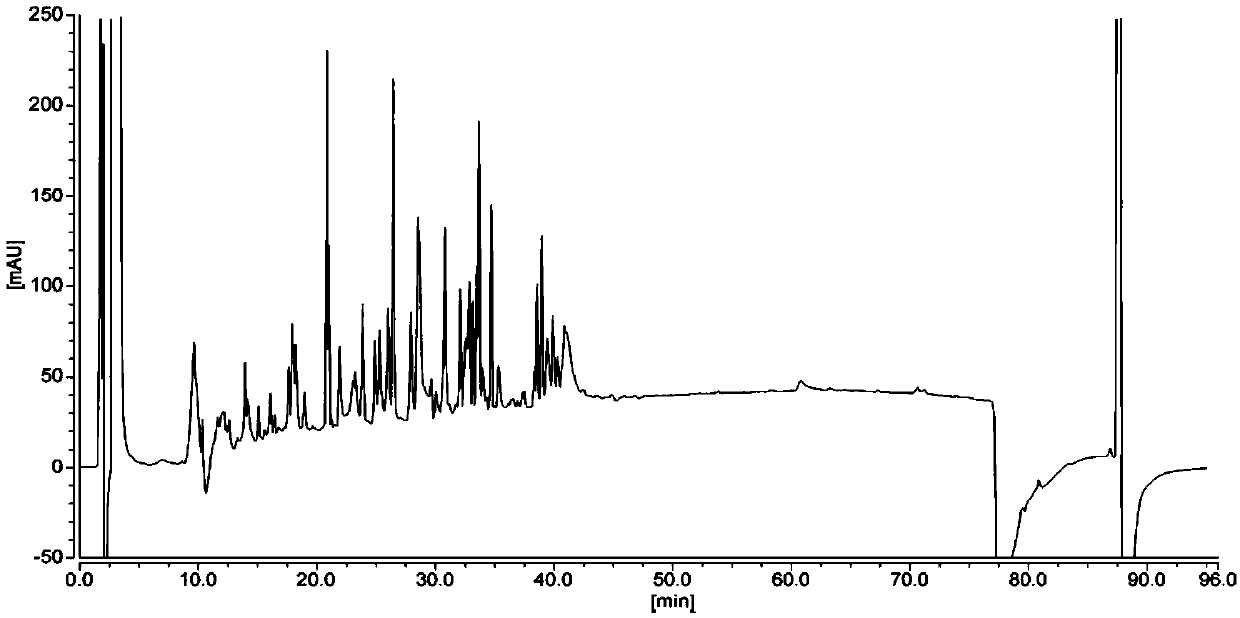
[0146] The protein sample test results are as follows: Figure 7 and Table 7, from Figure 7 As can be seen from Table 7, the number of peaks in the elution chromatogram is large (56 chromatographic peaks), the distribution of the chromatographic peaks of each peptide is relatively uniform, and can be separated better, and the baseline is relatively stable.
[0147] Table 7 Protein peptide map detection results
[0148]
[0149]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com