Short chain polypeptide EXP (Extracellular Vesicle Binding Peptide), medicine delivery system based on short chain polypeptide EXP and EVs (Extracellular Vesicles) recovery kit
A delivery system and drug delivery technology, applied in the direction of blood/immune system cells, animal cells, vertebrate cells, etc., can solve the problems of limited binding efficiency, exosome non-binding binding efficiency, etc., and achieve high stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experiment example 1
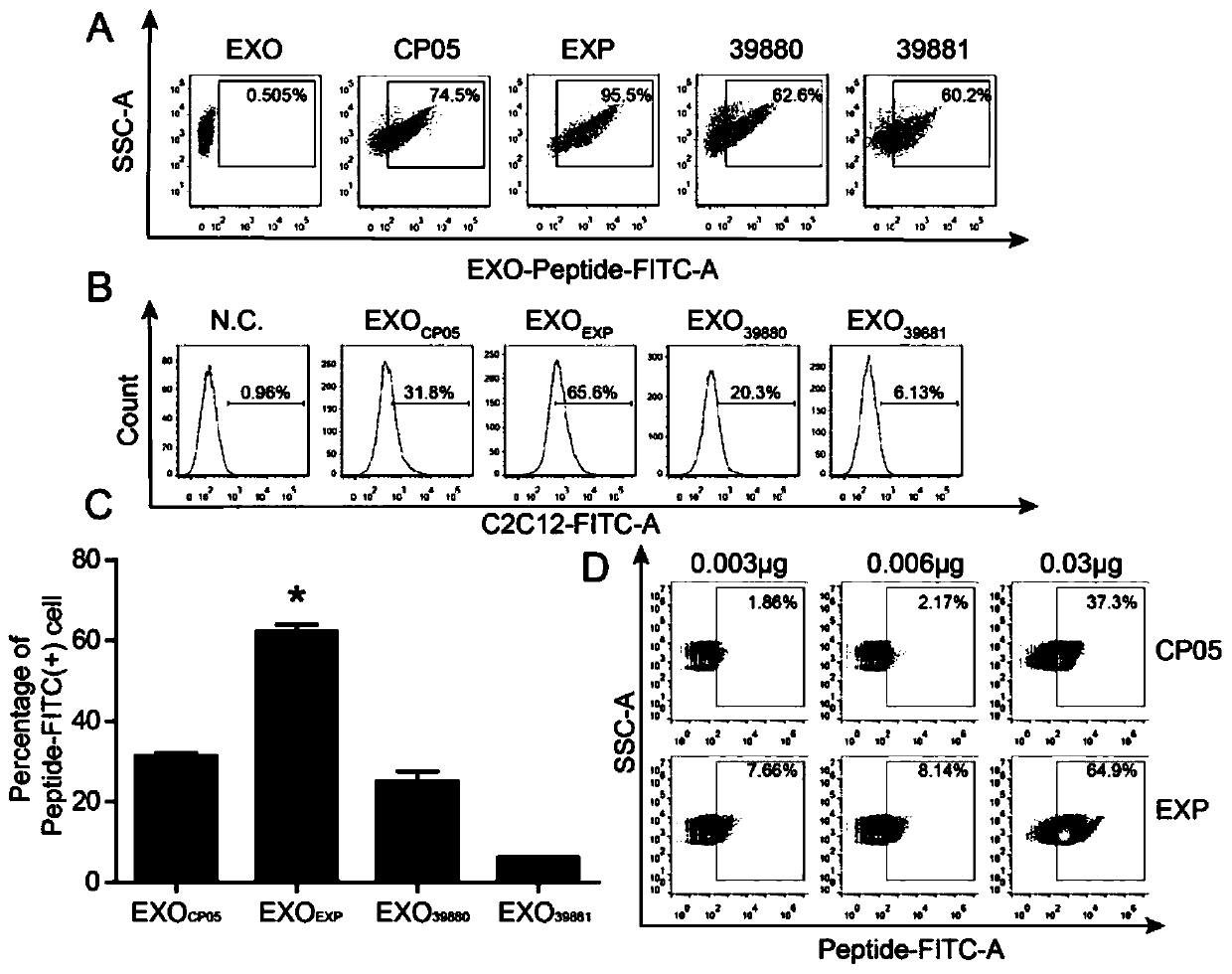
[0131] Experimental example 1. Detection of binding ability of CP05 and different short peptides to exosome.
[0132] 1.1 The binding ability of CP05 and different short peptides to exosome was detected by flow cytometry.
[0133] (1) Mix 0.06 μg of FAM-labeled CP05 and different short peptides with 10 μg of exosomes from different sources (dC2C12, CDC, serum), respectively, and make up DPBS to a volume of 200 μL.
[0134] (2) Rotate and incubate on a vertical shaker at 4°C for 2-4hrs.
[0135] (3) Detection of binding efficiency by flow cytometry.
[0136] The result is as figure 1 (A) shown.
[0137] 1.2 Detection of Exosome-mediated ability of CP05 and different short peptides to enter cells.
[0138] (1) C2C12 cells were digested and counted, planted in a 24-well plate, 4×10 4 / hole. 5%CO 2 , grow at 37°C for 12h.
[0139] (2) Incubate the FAM-labeled CP05 and different short peptides for 4hrs according to the method in 1.1 above.
[0140] (3) Put the incubated EX...
experiment example 2
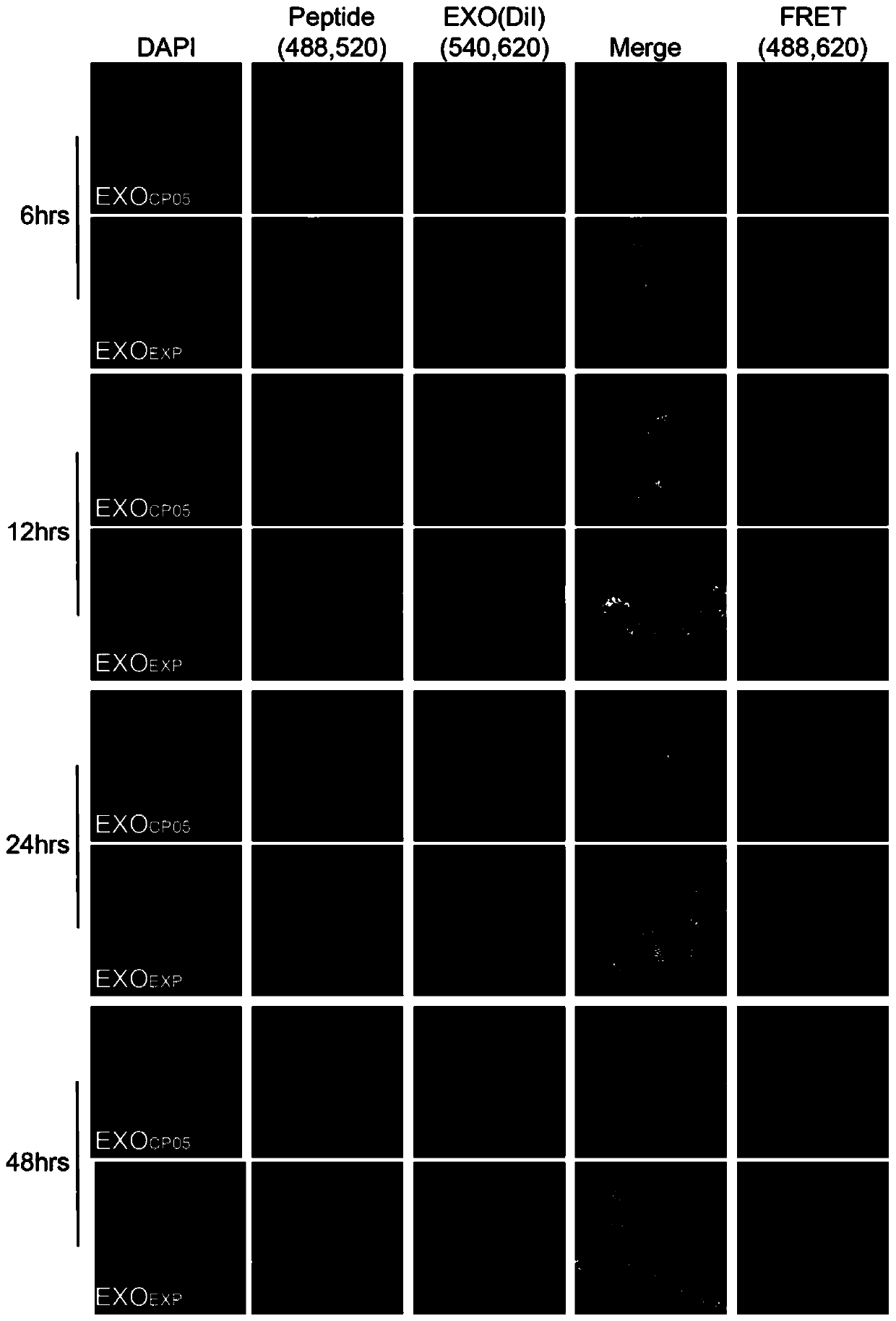
[0149] Experimental example 2, CP05 and EXP combined with exosom stability detection.
[0150] (1) C2C12 cells were digested and counted, planted in a 24-well plate, 4×10 4 / hole. 5%CO 2 , grow at 37°C for 12h.
[0151] (2) FAM-labeled CP05 and EXP (20 μg) were co-incubated with 10 μg DiI-labeled exosome respectively, and incubated at 4° C. for 4 hours with rotation.
[0152] (3) The above-incubated EXO CP05 and EXO EXP They were added to C2C12 cells respectively, and the culture medium was replaced with serum-free DMEM at 37°C to continue culturing.
[0153] (4) After culturing for different times (6hrs, 12hrs, 24hrs, 48hrs), the cells were washed with DPBS.
[0154] (5) 4% paraformaldehyde was fixed at room temperature for 30 min and then sealed.
[0155] (6) The colocalization efficiency and FRET fluorescence energy transfer of exosome (DiI) and short peptide (FAM) were observed under microscope at different time points.
[0156] The result is as figure 2 shown. ...
experiment example 3
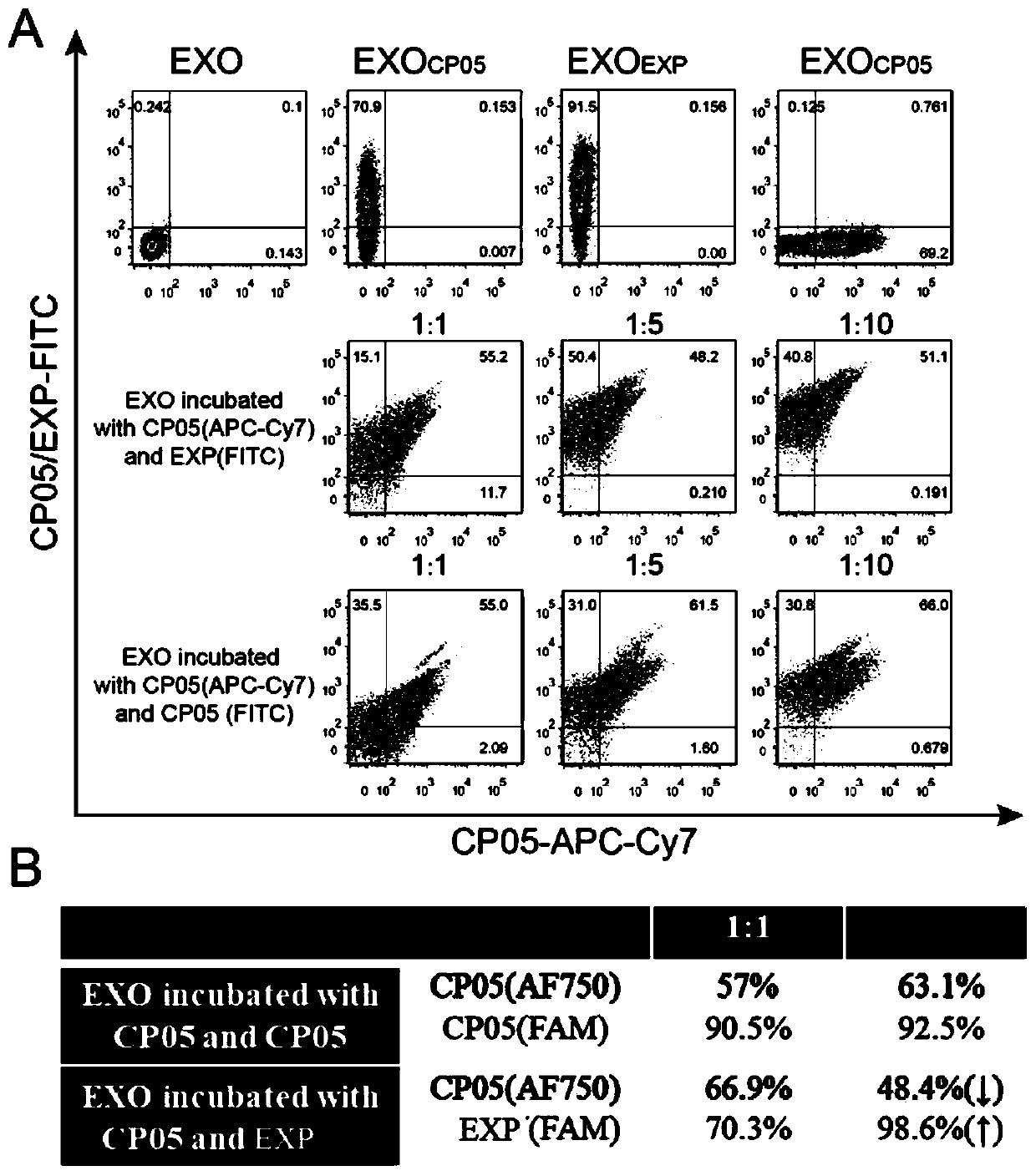
[0157] Experimental example 3, detection of competitive binding ability between CP05 and EXP and exosome.
[0158] (1) AF750-labeled CP05 (0.06 μg) was incubated with FAM-labeled CP05 (0.06 μg, 0.3 μg) or EXP (0.06 μg, 0.3 μg) and 10 μg exosome, and supplemented with DPBS to a volume of 200 μl.
[0159] (2) Incubate with rotation at 4°C for 4 hours.
[0160] (3) Exosome positive percentage of FITC and APC-Cy7 channels detected by flow cytometry.
[0161] The result is as image 3 shown
[0162] Experimental example 4, EXP target detection verification.
[0163] (1) Mix 100 μg EXP or CP05 with 30 μL activated Flag magnetic beads, and incubate overnight at 4°C.
[0164] (2) PBST washes away short peptides not bound to the magnetic beads, and recovers the magnetic beads.
[0165] (3) C2C12 cells were lysed with non-denaturing tissue lysate, lysed on ice for 30 min, and centrifuged at 12000 rpm to recover the supernatant.
[0166] (4) Add the C1C12 lysed supernatant to the r...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com