Deep-buried loess tunnel deformation control construction structure based on cover arch and method
A loess tunnel and deformation control technology, applied in tunnels, tunnel linings, earthwork drilling, etc., can solve the problems of difficult control of tunnel deformation, large influence of water content on deformation, and excessive deformation of surrounding rock.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
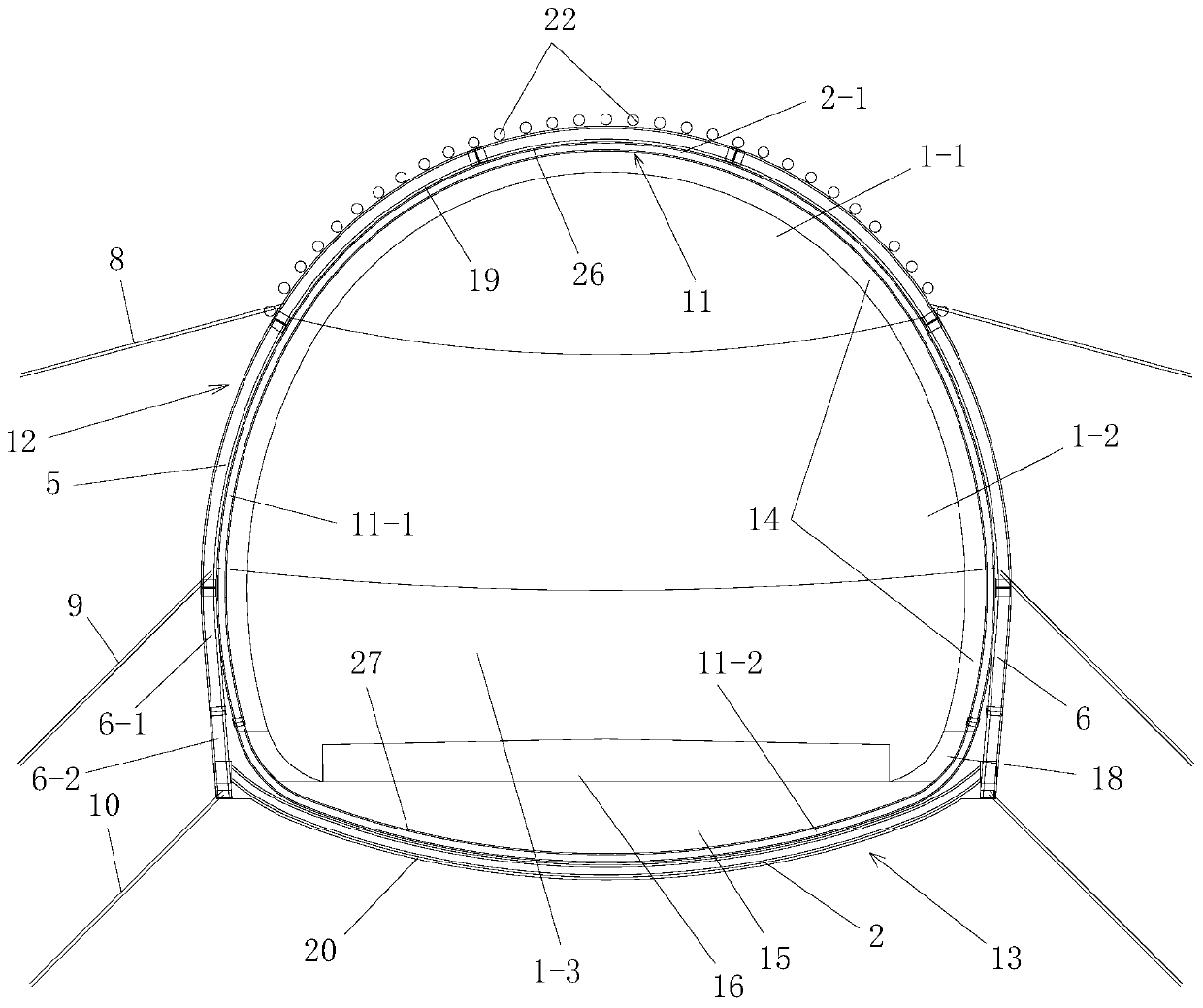
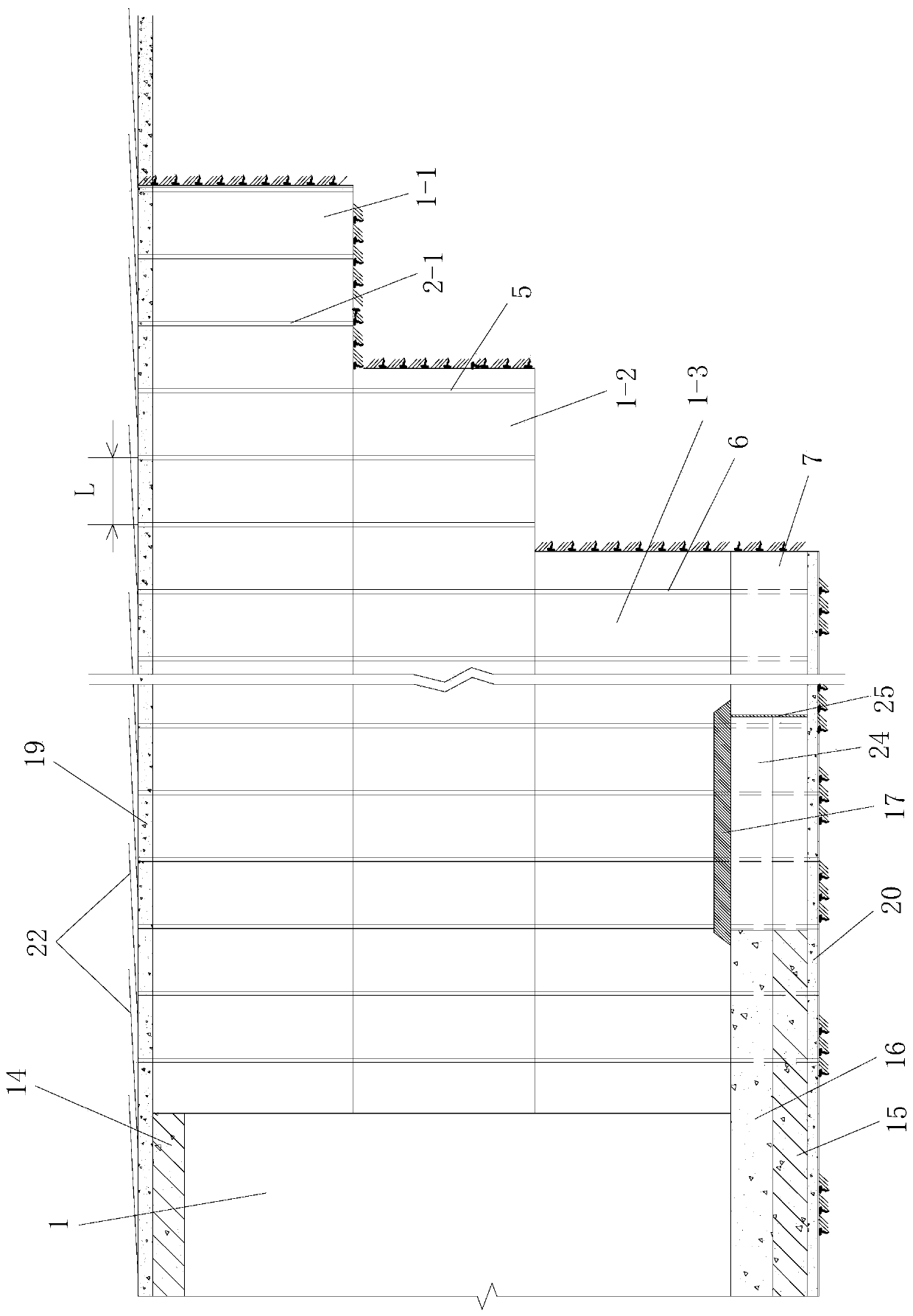
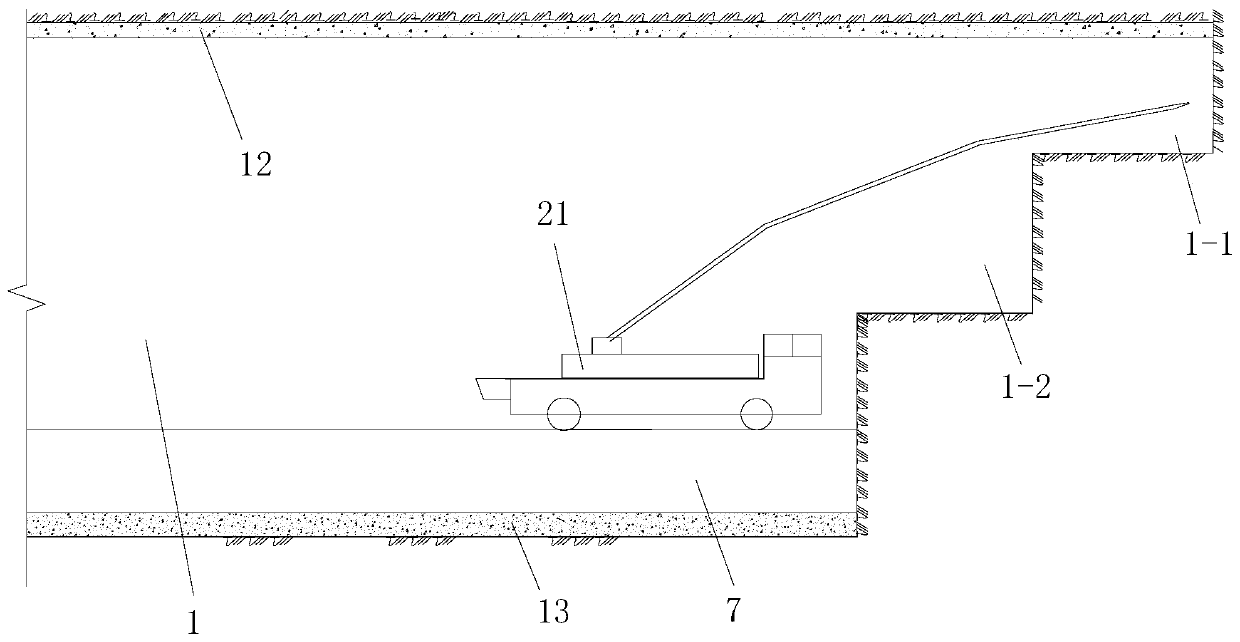
[0080] Such as figure 1 , figure 2 The deformation control construction structure of a deep-buried loess tunnel based on the set of arches shown includes a tunnel primary support structure for initial support of the tunnel hole 1 of the constructed loess tunnel and a tunnel primary support structure arranged inside the tunnel primary support structure and A reinforced arch for reinforcing the primary support structure of the tunnel, and both the initial support structure of the tunnel and the reinforced arch are full-section support structures for the full-section support of the tunnel hole 1; the tunnel hole 1 The cross-sectional area is greater than 100m 2 , the burial depth of the tunnel hole 1 is greater than 80m; the primary support structure of the tunnel and the reinforced arch located inside it form a reinforced primary support structure;
[0081] The reinforced arch set includes a plurality of set arch units, the structures of the plurality of set arch units are th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Layer thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com