Application of tryptophan to enhancement of bactericidal effect on gram-negative bacteria
A Gram-negative bacteria, tryptophan technology, applied in antibacterial drugs, organic active ingredients, resistance to vector-borne diseases, etc. The emergence of drug-resistant bacteria, the effect of good therapeutic effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Example 1: Determination of the minimum inhibitory concentration of the sensitive strain MG1655 and the resistant strain EY1
[0036] Gentamicin and kanamycin were selected as the representative drugs of antibiotics in this experiment. The antibiotics were serially diluted by adding physiological saline, and the diluted antibacterial solution was added to a sterilized 96-well plate, and then added after freeze-drying. For the bacterial suspension cultured in broth, determine the smallest concentration MIC that inhibits the growth of the bacteria. The results are shown in the table below
[0037] Table 1. Minimum inhibitory concentration MIC determination (mg / L):
[0038] Strain Gentamicin Kanamycin MG165543.5 EY1 240220
Embodiment 2
[0039] Example 2: Sterilization effect experiment
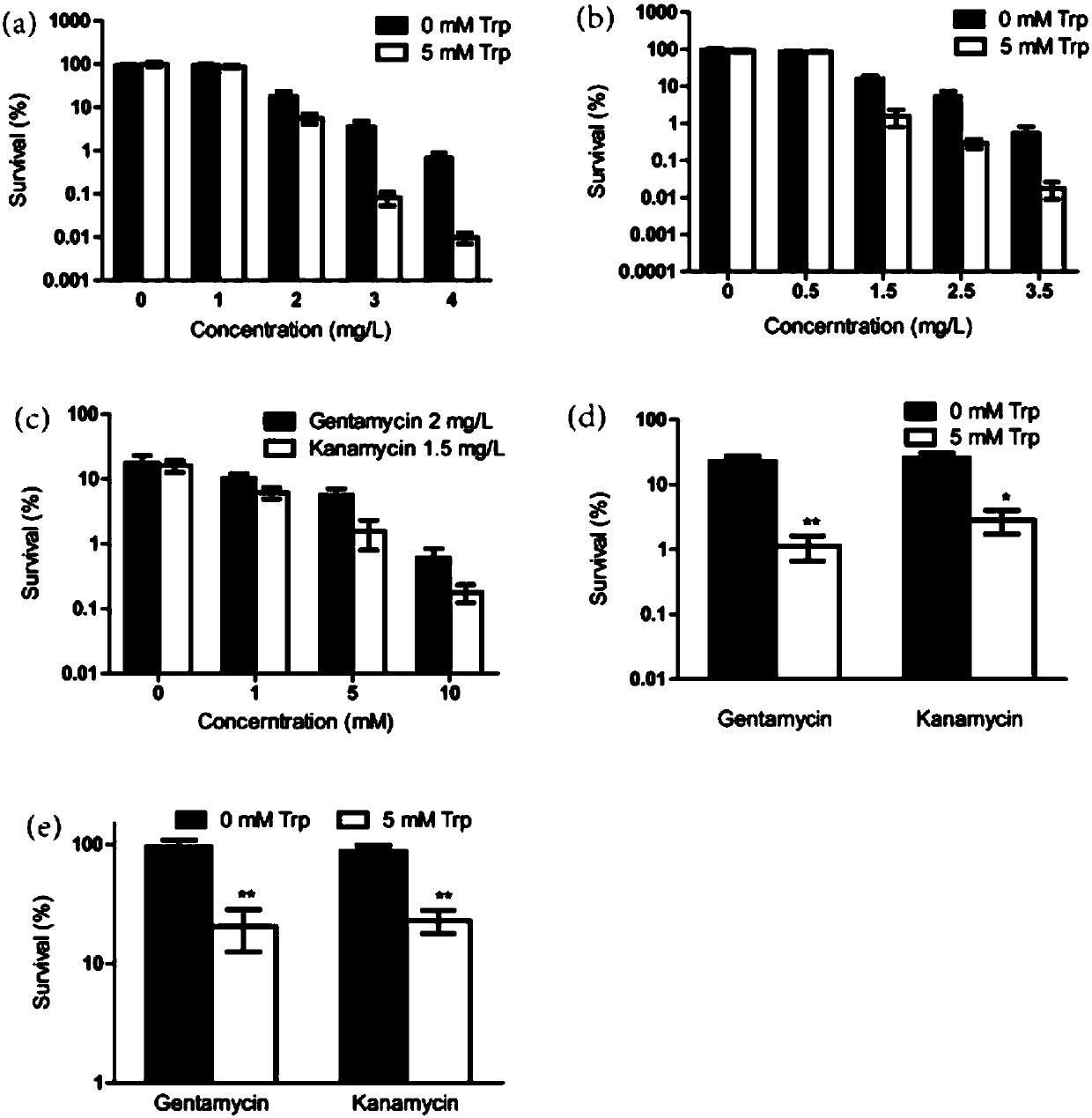
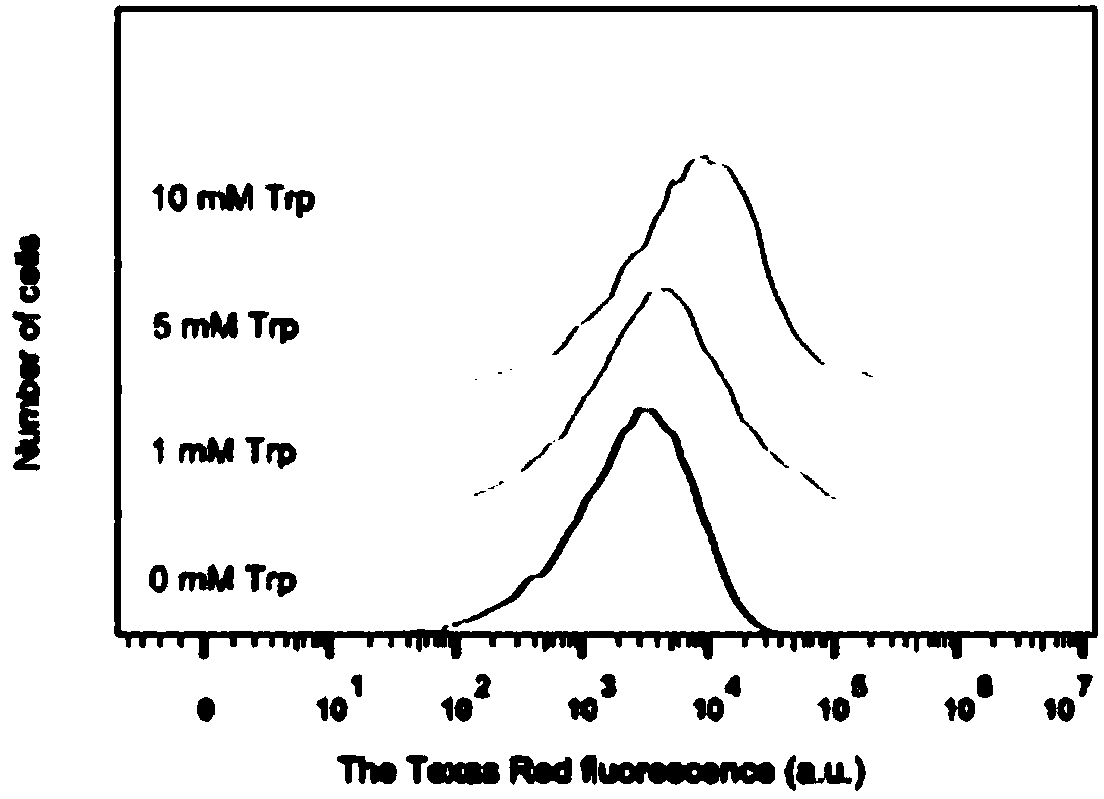
[0040] Select E. coli MG1655 in logarithmic growth phase and stable phase, and add the same concentration of gentamicin (0mg / L, 1mg / L, 2mg / L, 3mg / L, 4mg / L) and kanamycin to the medium (0mg / L, 1mg / L, 2mg / L, 3 mg / L, 4mg / L) and gentamicin and kanamycin after adding 5mM tryptophan for 24h, calculated by the method of viable bacteria count The number of surviving bacteria in each experimental group after treatment was used to determine the bactericidal effect of each group of drugs. The experimental results are as figure 1 As shown in (a)(b)(d): when combined with gentamicin, the bactericidal effect of tryptophan at 3mg / L and minimum inhibitory concentration of 4mg / L is higher than that of the experimental group without tryptophan 100 times, when combined with kanamycin, tryptophan at 1.5mg / L to the minimum inhibitory concentration of 3.5mg / L can increase the sterilization by 10-100 times. For stable MG1655, 5mM tryptophan and genta...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Example 3: Determination of the rate of production of resistant bacteria
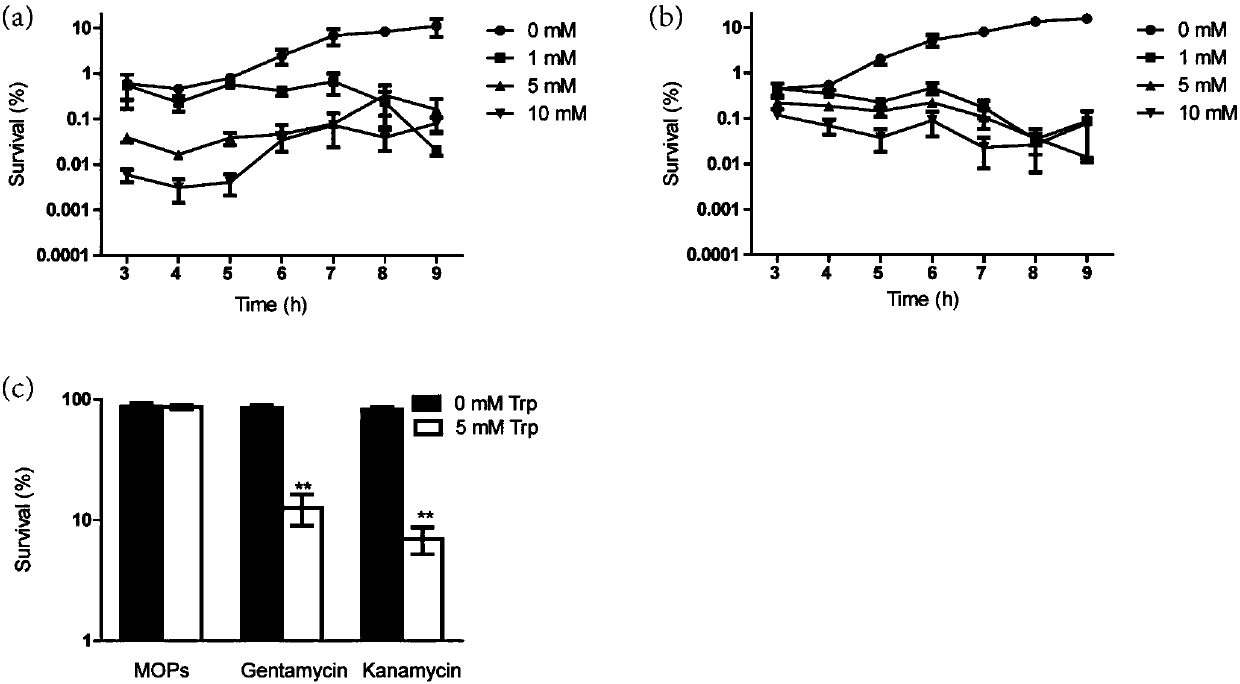
[0042] Transfer the overnight culture to fresh medium according to the transfer amount of 1%, and cultivate MG1655 for different time (from 3 hours to 9 hours) after 60mg / L gentamicin and 40mg / L calorie After 5 hours of natamycin treatment, different concentrations of tryptophan were added for 30 minutes, and the ratio of bacteria before and after treatment was compared by the method of viable bacteria count to determine the rate of drug-resistant bacteria. The experimental results are as figure 2 As shown in (a) and (b), tryptophan concentration-dependently reduces the production of resistant bacteria. The reduced efficiency can reach 10-1000 times.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com