Q routing method based on arc tangent learning rate factor
A learning rate and arctangent technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve the problems affecting the application performance of routing algorithms, unstable algorithm performance, slow algorithm convergence speed, etc., to improve parameter adjustment ability, improve performance and delivery delay stability, The effect of improving the convergence speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
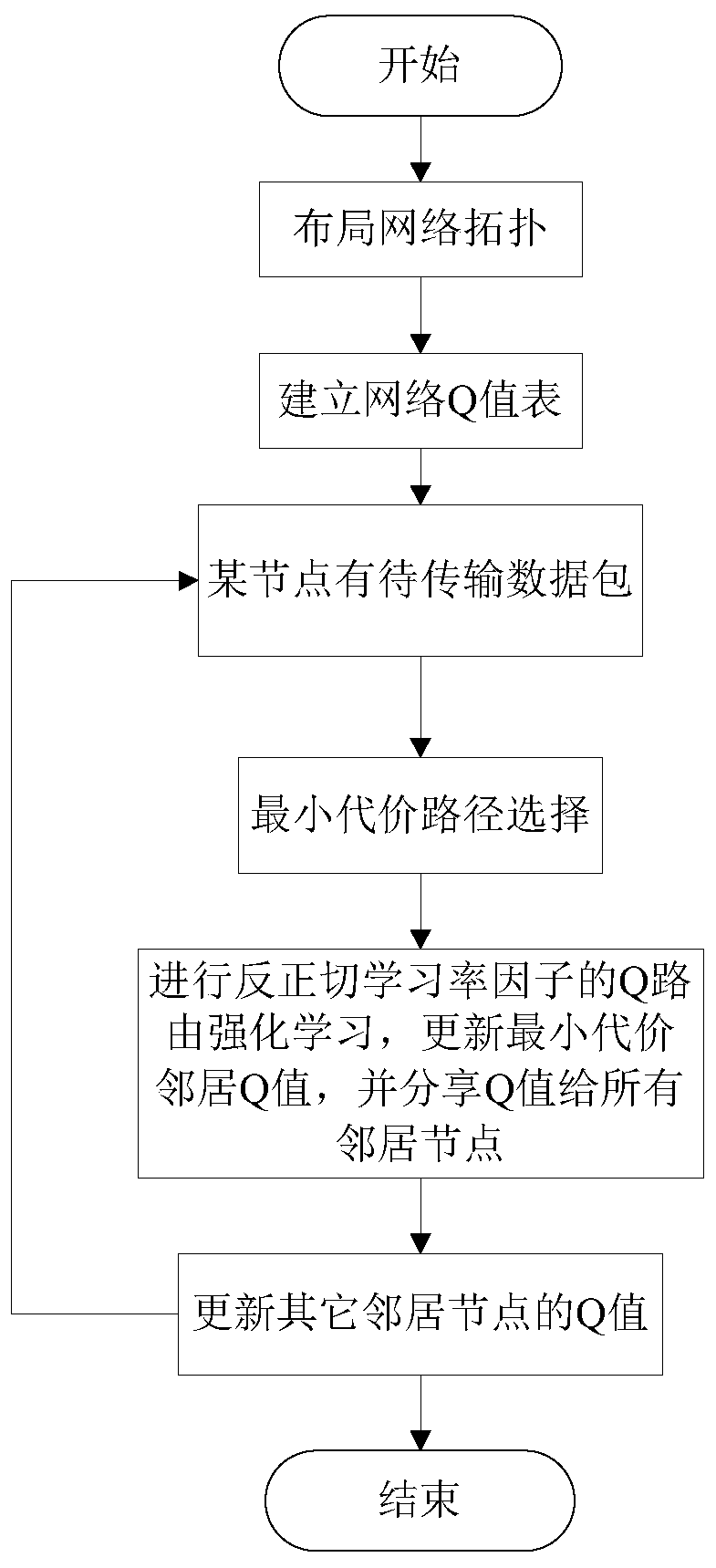
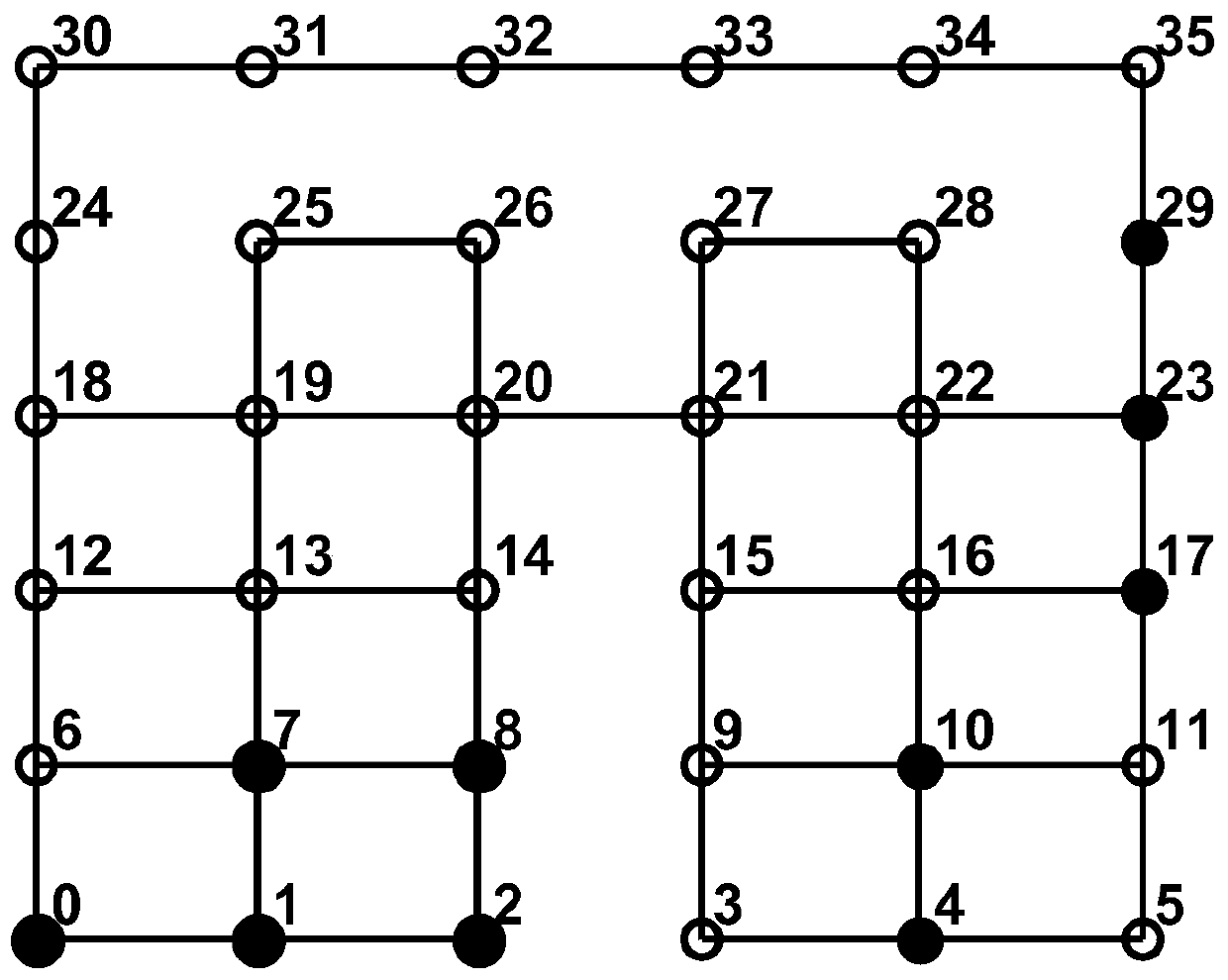
[0032]The network is inseparable from people's lives, and many nodes can be wirelessly connected into a network in practical applications such as hotels, airports, and earthquake relief environments. For many years, research on routing in wireless ad hoc networks has been a hot topic. Wireless ad hoc network is a multi-hop mobility network, especially suitable for network deployment in emergency environments. Nodes obtain information in the environment through ad hoc networking and exchange information. Due to poor flexibility and high computational complexity, traditional routing algorithms cannot adapt to highly variable networks. Reinforcement learning is an effective alternative to address real-world network situations. Some existing routing algorithms based on reinforcement learning have the advantages of less state and action space requirements, only use local node information, and self-adaptive adjustments, etc., but there are still inaccurate Q values in the early t...
Embodiment 2
[0057] The Q routing method based on the arctangent learning rate factor is the same as that in Embodiment 1, and the corresponding destination d and other neighbor nodes y in the Q value table for the current node x described in step 5 of the present invention 2For each Q value of , each update is performed using the arctangent learning rate factor η' one by one, and the calculation formula for updating the Q value of the neighbor with the minimum time cost is shown in the following formula:
[0058]
[0059] where y 2 is any other neighbor node of the current node x; η' is the arctangent adaptive learning rate factor, and the value of η' is in the range of (0,1); s 2 is the packet from x to node y 2 link transmission time; where is Q at time T x (d,y 2 ) value means, is Q updated at time T+1 x (d,y 2 ) value representation.
[0060] Only update the Q value of the next hop node determined in the network, and do not update the Q values of other neighbor nodes. A...
Embodiment 3
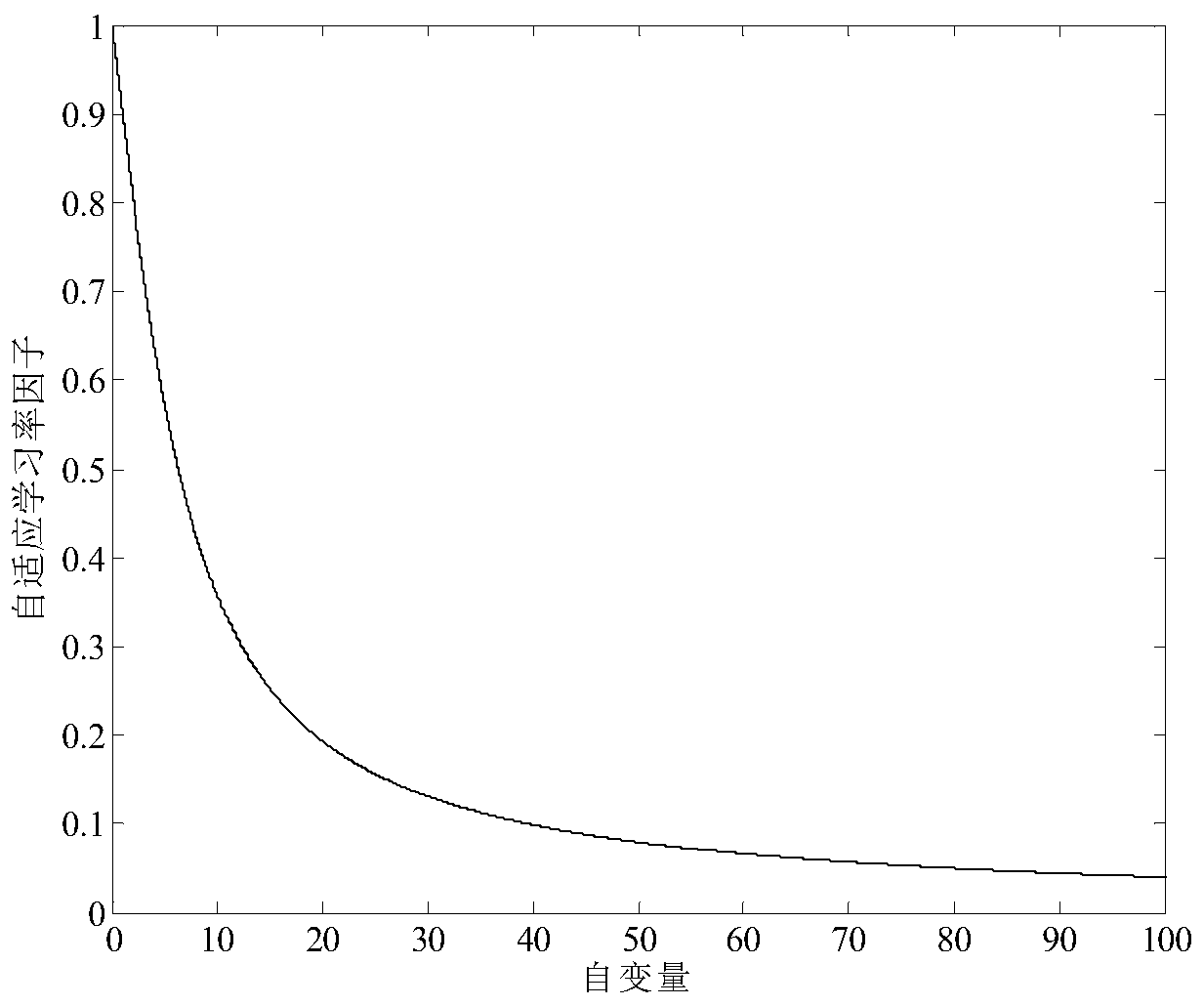
[0063] The Q routing method based on the arctangent learning rate factor is the same as embodiment 1-2, and the realization of the arctangent learning rate factor η' in step 5 of the present invention is as follows:
[0064] η'=1-(2atan((T max -T est ) / (2k 2 π)) / π)
[0065] where k 2 is a constant, the value range is (0,1]; by adjusting k 2 The arctangent learning rate factor η' can be adjusted to further adjust the routing strategy. Calculate the maximum delivery time T according to the Q value table of the current data packet transmission node x max and average delivery time T est difference, where T est is the arithmetic mean value of all neighbors’ Q values corresponding to sink d in the Q value table of the current node x, T max is the current node x so far, has obtained all T est The maximum of the values. If the difference between the maximum delivery time and the average delivery time of the current node x is T max -T est When η' is larger, the value of η...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com