User-defined data fragmentation method, device and equipment based on distributed database
A data sharding and database technology, applied in the database field, can solve the problems of inability to meet the requirements of data sharding with special rules and low efficiency of sharding processing, so as to achieve whether the data is updated clearly and orderly, prevent data sharding from confusion, The effect of improving efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
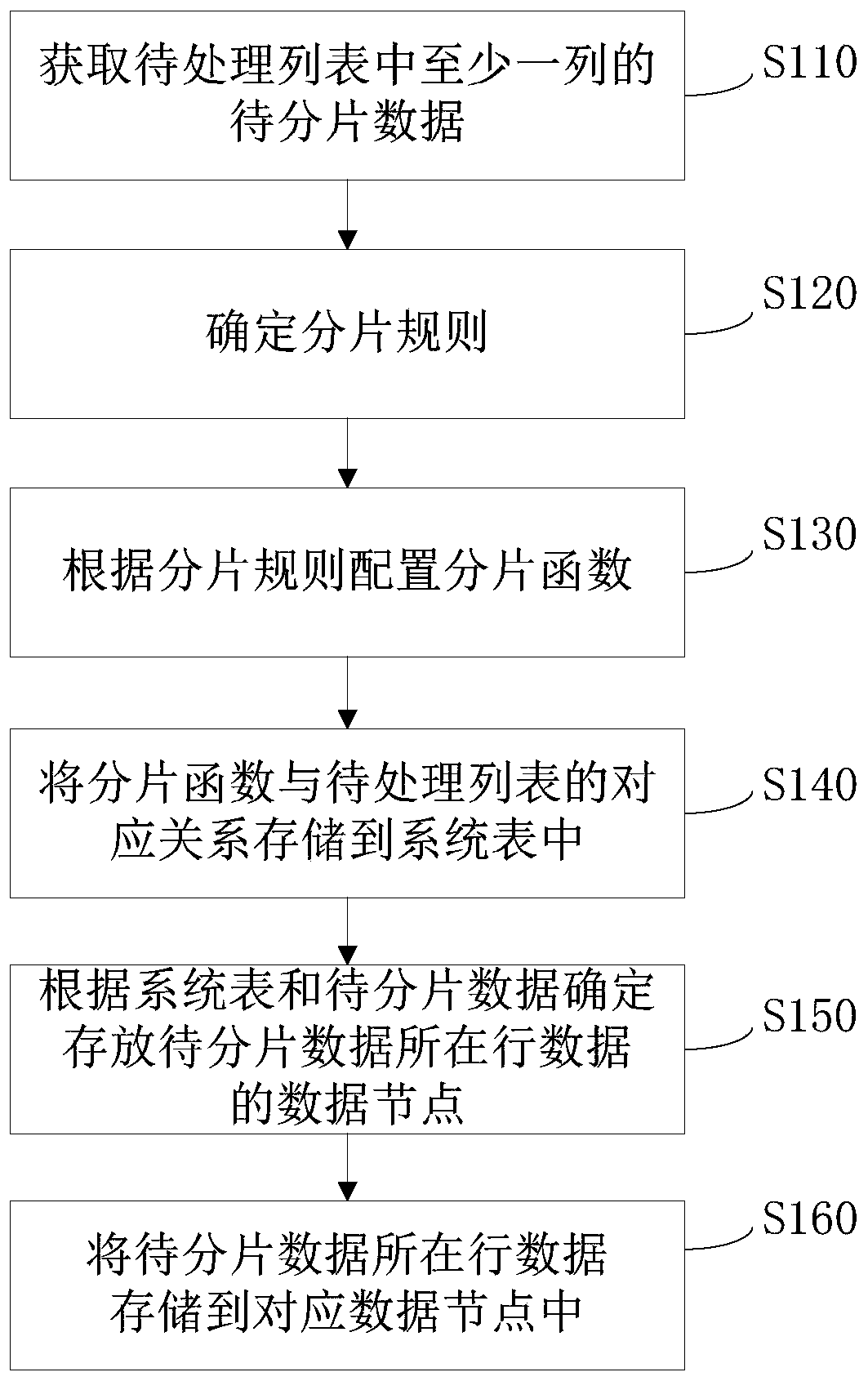
[0031] Data fragmentation is one of the characteristics of distributed databases. In a distributed database, each local database is obtained from a certain logical fragmentation of the global database, that is, the global database is divided into small data fragments according to a certain logic. In order to operate separately, data sharding is achieved through basic operations of algebra. For the data objects in the database, the user is the subject of the data object viewing operation, but for different users, their viewing rights to the data are not the same, for example, the data of the entire company is stored in a table, but a certain type The data can only be viewed by a certain department as the subject of the operation. In this case, the data needs to be fragmented. This embodiment provides a method for customizing data fragmentation based on a distributed database, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
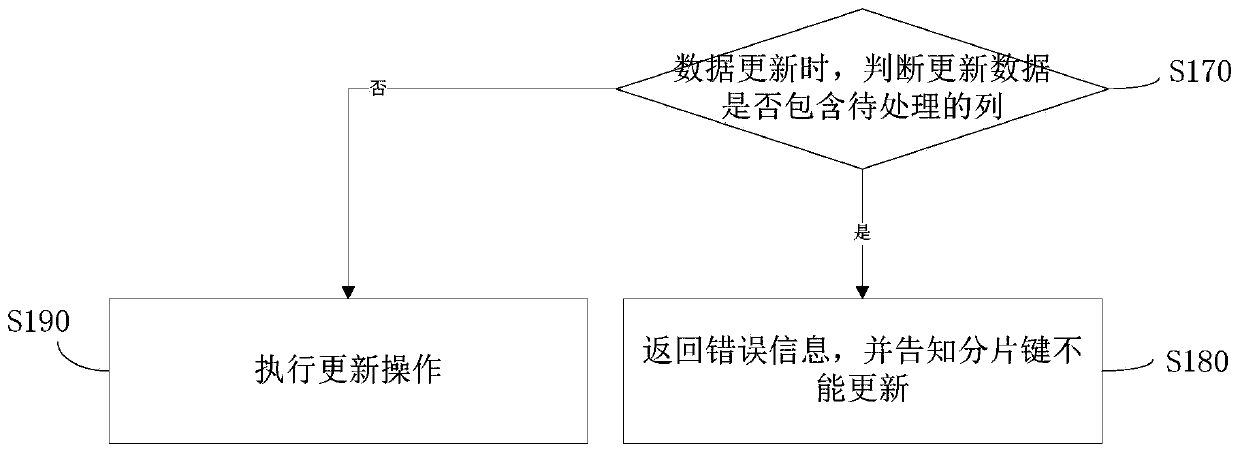
[0032] S110: Obtain at least one column of d...
Embodiment 2
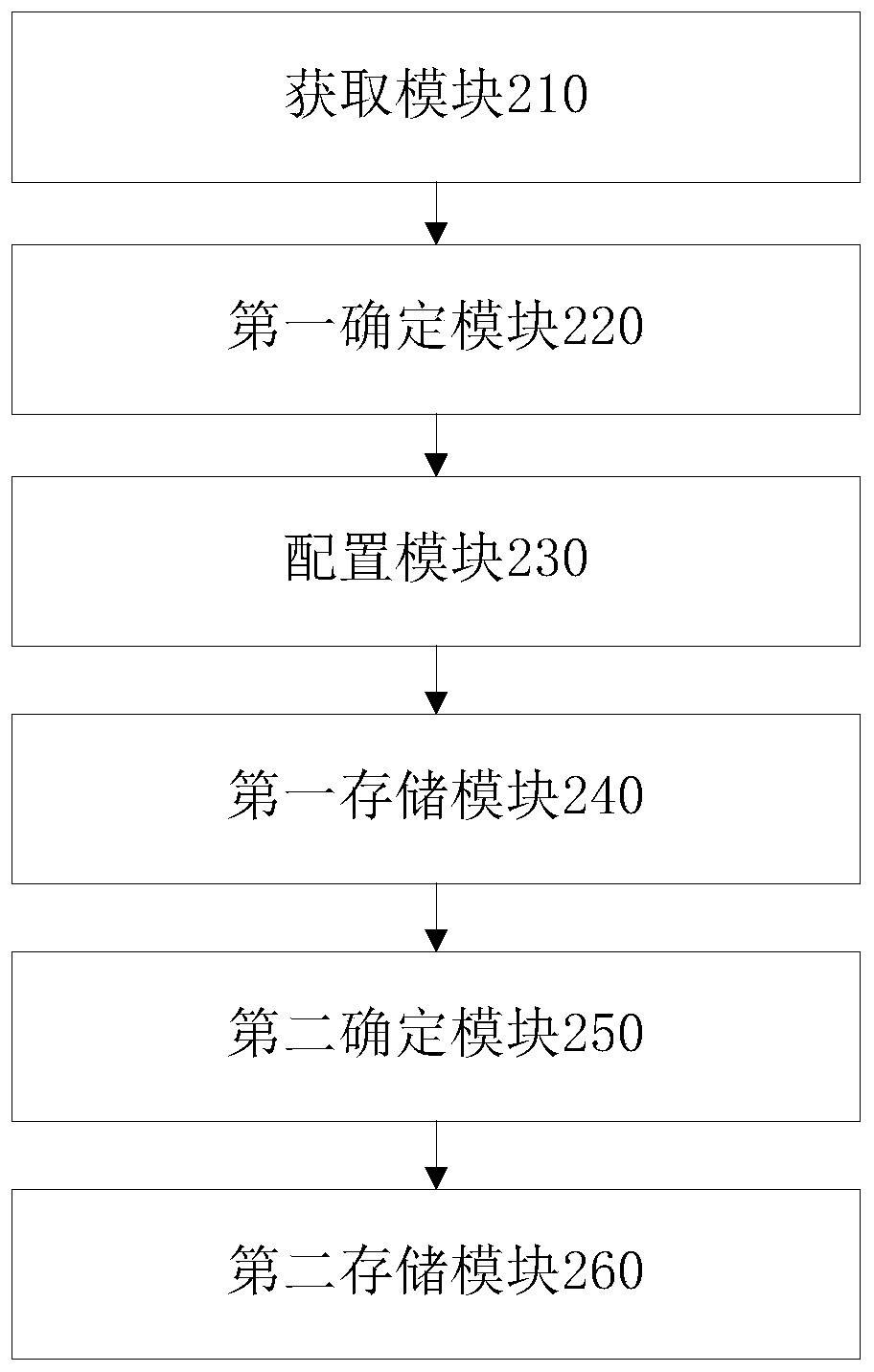
[0061] This embodiment provides a self-defined data fragmentation device based on a distributed database, such as image 3 shown, including:
[0062] The obtaining module 210 is configured to obtain at least one column of data to be fragmented in the list to be processed; for a specific implementation, refer to S110 in Embodiment 1, which will not be repeated here.
[0063] The first determination module 220 is configured to determine the sharding rule; see S120 in Embodiment 1 for the specific implementation manner, which will not be repeated here.
[0064] The configuration module 230 is configured to configure the fragmentation function according to the fragmentation rule; see S130 in Embodiment 1 for the specific implementation manner, which will not be repeated here.
[0065] The first storage module 240 is configured to store the corresponding relationship between the slice function and the list to be processed in a system table; see S140 in Embodiment 1 for a specific ...
Embodiment 3
[0081] The embodiment of the present application also provides a self-defined data fragmentation device based on a distributed database, such as Figure 5 As shown, a processor 510 and a memory 520, wherein the processor 510 and the memory 520 may be connected through a bus or in other ways.
[0082] The processor 510 may be a central processing unit (Central Processing Unit, CPU). The processor 510 may also be other general-purpose processors, digital signal processors (Digital Signal Processor, DSP), application-specific integrated circuits (Application Specific Integrated Circuit, ASIC), field-programmable gate array (Field-Programmable Gate Array, FPGA) or Other chips such as programmable logic devices, discrete gate or transistor logic devices, discrete hardware components, or combinations of the above-mentioned types of chips.
[0083] The memory 520, as a non-transitory computer-readable storage medium, can be used to store non-transitory software programs, non-transit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com