Dynamic graph processing method based on FPGA
A processing method and technology for dynamic graphs, which are applied in electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, architecture with a single central processing unit, etc. It solves the problems of memory bandwidth utilization and high memory access delay, so as to reduce redundant computing, reduce memory access delay, and speed up incremental propagation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
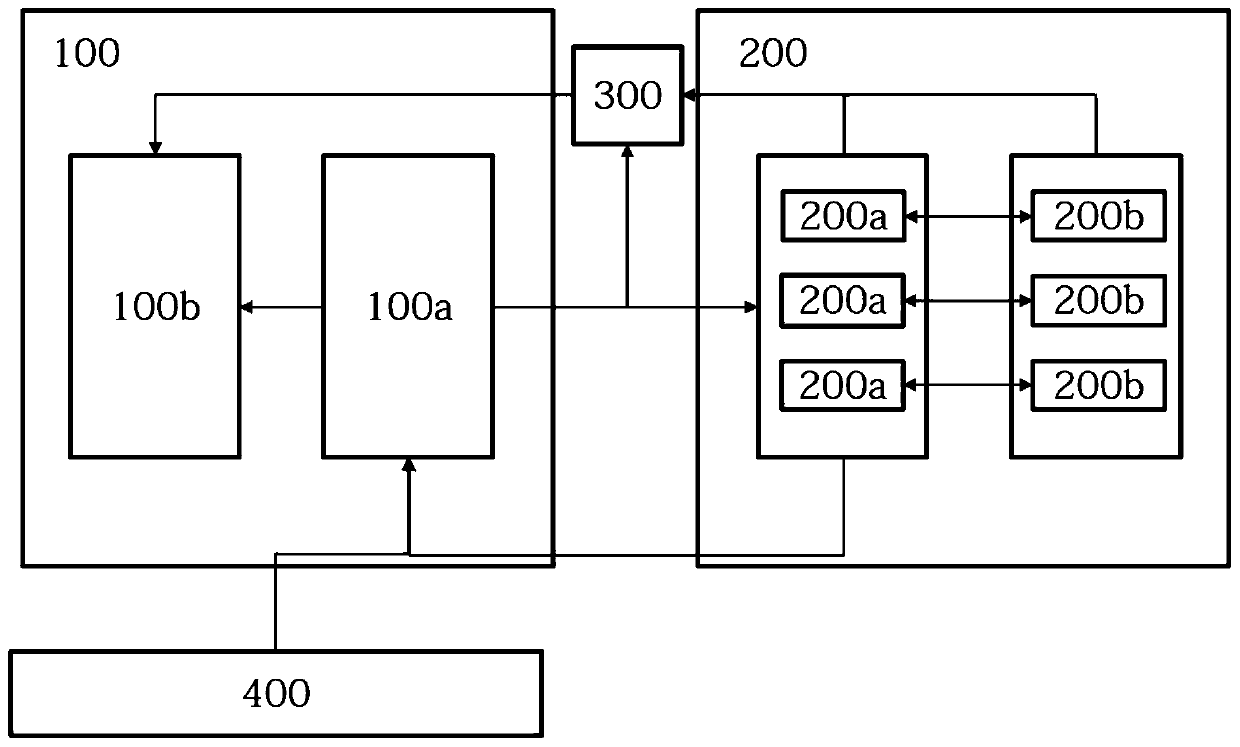
[0039] This embodiment discloses an FPGA-based dynamic image processing system. Such as figure 1 As shown, the system at least includes a preprocessing module 100a and an FPGA processing module 200 . The preprocessing module 100a divides the graph image into at least one path unit. Before dividing the graph image into path units, the preprocessing module 100a will determine whether there is an increment between graph images of adjacent time stamps. If there is an increment between the image images of adjacent time stamps, the preprocessing module 100a divides the image images of the next time stamp into at least one path unit. Preferably, in the path unit, the incremental calculation of any graph vertex only depends on the preceding graph vertex of the arbitrary graph vertex.
[0040] Preferably, the preprocessing module 100a is configured to divide the image image in the following sub-steps:
[0041] S1: Traverse the graph image of the dynamic graph corresponding to the n...
Embodiment 2
[0056] It should be understood that the specific embodiments described here are only used to explain the present invention, not to limit the present invention. In addition, the technical features involved in the various embodiments of the present invention described below may be combined with each other as long as they do not constitute a conflict with each other.
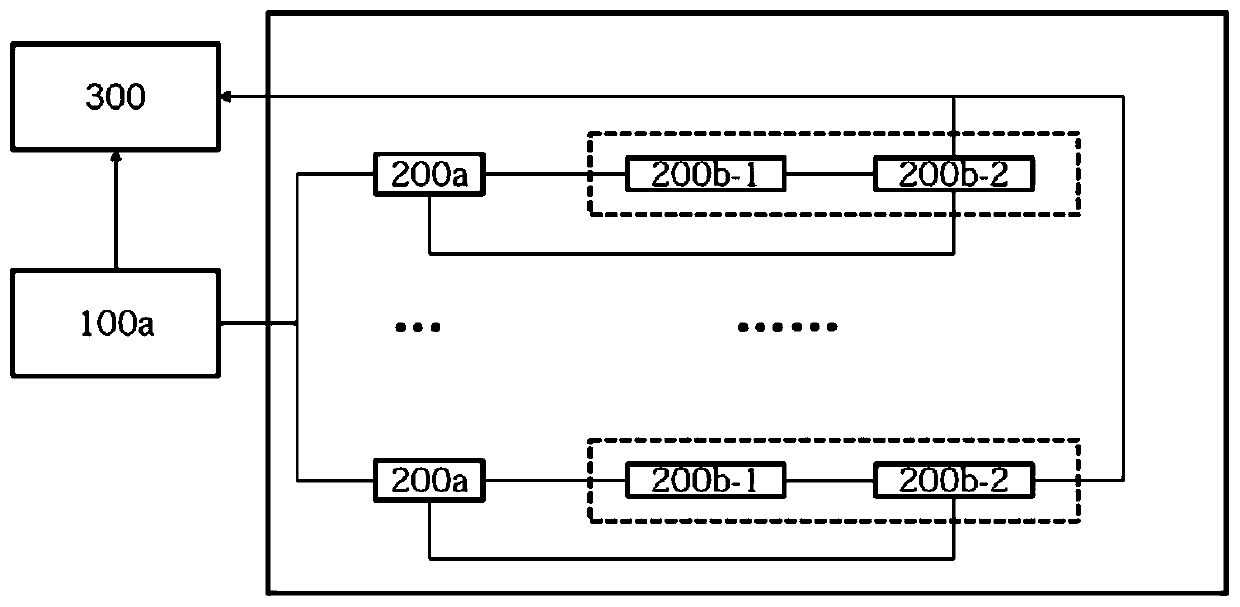
[0057] Preferably, the preprocessing module 100a can also be divided according to the following preprocessing sub-steps:
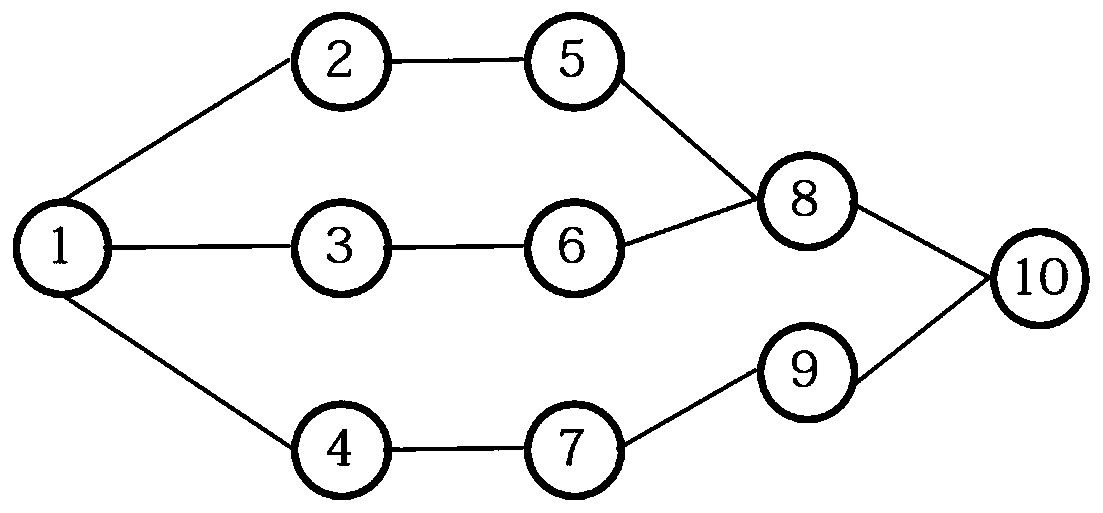
[0058]P1: The preprocessing module 100a can select at least one common node as the initial point for traversal, record the traversal path and mark the nodes with increments. For example the common nodes could be 1, 8, 10. When a common node traverses to another common node, the traversal ends. This method has the following advantages: 1. Simultaneous traversal can save the preprocessing time of the preprocessing module 100a; 2 path identification is faster, and common nodes generally have com...
Embodiment 3
[0062] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer and easier to understand, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments. The FPGA-based dynamic graph processing method provided by the present invention includes a preprocessing step and an incremental calculation step, specifically as follows:
[0063] (1) The effect of the preprocessing module 100 is to obtain the path set in the latest image image according to the increment between two adjacent image images of the dynamic graph, including the following sub-steps:
[0064] (1.1) If the dynamic graph is processed for the first time, then use the graph partition method to divide the graph image into a set of paths and store them in the memory; otherwise, enter step (1.2);
[0065] (1.2) Each edge in the increment is loaded into the on-chip memory, and the path position in the old graph image wher...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com