Electrochemical method for extracting rubidium and cesium from brine
An electrochemistry, rubidium-cesium technology, applied in the field of electrochemistry, can solve the problems of difficult mass production, limited surface area of conductive base layer, etc., and achieve the effects of less reagent consumption, high selective separation and utilization rate, and simple operation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0056] (1) Preparation of working electrode
[0057] Prussian blue (FeFe(CN) 6 ), carbon fiber and PVDF were mixed according to the mass ratio of 90:6:4 to obtain a mixture, 20g of the mixture was coated on a carbon fiber cloth with a size of 10×10cm, and after drying, a working electrode A with a coating thickness of 2.5mm was obtained.
[0058] A 10×10 cm graphite plate was used as working electrode B.
[0059] (2) Cesium intercalation process
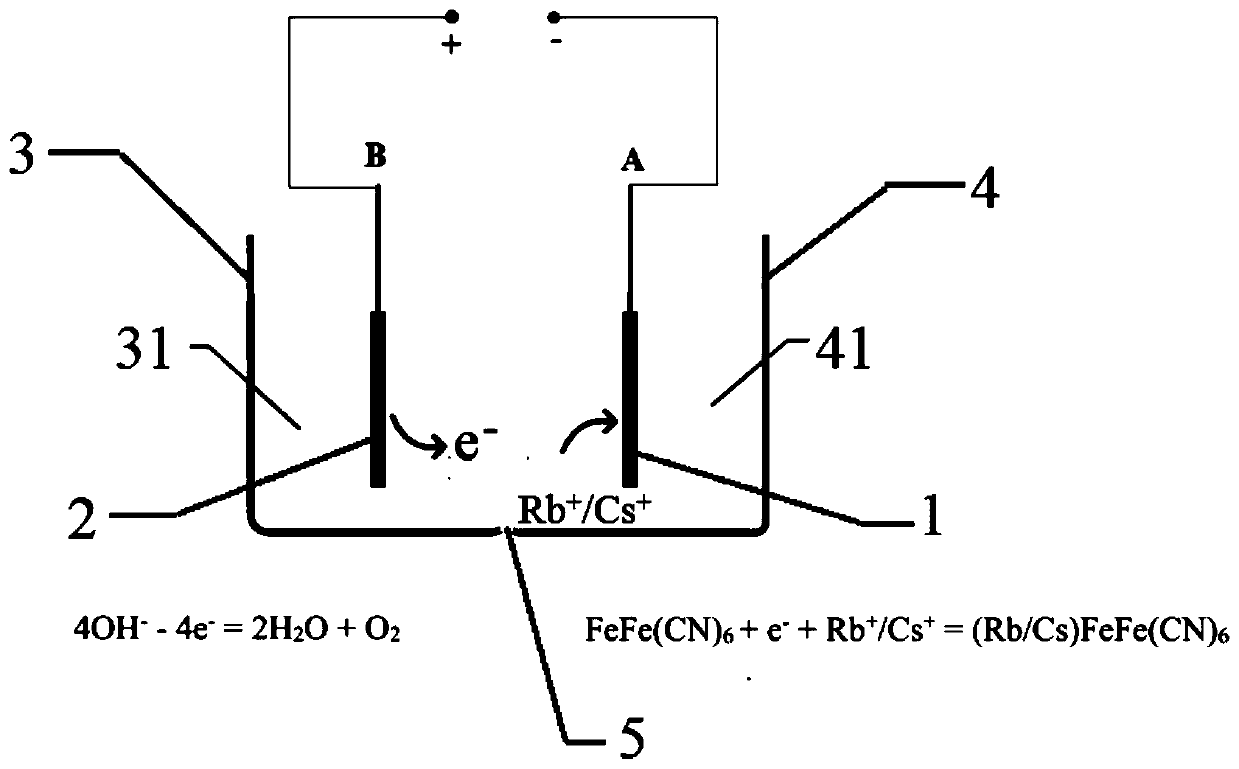
[0060] The total volume of the electrolytic cell is 10L, the cathode chamber and the anode chamber are 5L each, and the diaphragm is an anion exchange membrane containing basic active groups. Working electrode B is connected to the anode, and working electrode A is connected to the cathode. The working electrode B and the first anolyte are placed in the anode chamber, and the working electrode A and the first catholyte are placed in the cathode chamber for electrolytic reaction. Work process such as figure 1 As shown, the reacti...
Embodiment 2
[0071] (1) Preparation of working electrode
[0072] Prussian blue in working electrode A is FeNi(CN) 6 , other experimental materials are the same as in Example 1.
[0073] (2) Cesium intercalation process
[0074] The volume of the first catholyte is 10 L, which contains 250 mg / L of CsCl (calculated as Cs), 15 g / L of NaCl, and 10 g / L of KCl, and the pH value of the solution is 5.5. The cell voltage is 1.2V, and the control temperature is room temperature. After working for 4 hours, the concentration of cesium in the first catholyte is lower than 0.5mg / L, and the extraction rate of Cs is 99.8%.
[0075] (3) Cesium removal process
[0076] Replace electrolyzer, other operation process is with embodiment 1. The concentration of cesium in the cesium concentrate is 2400 mg / L, the desorption rate of Cs is 96.2%, and the method realizes the enrichment of Cs in brine by 9.6 times.
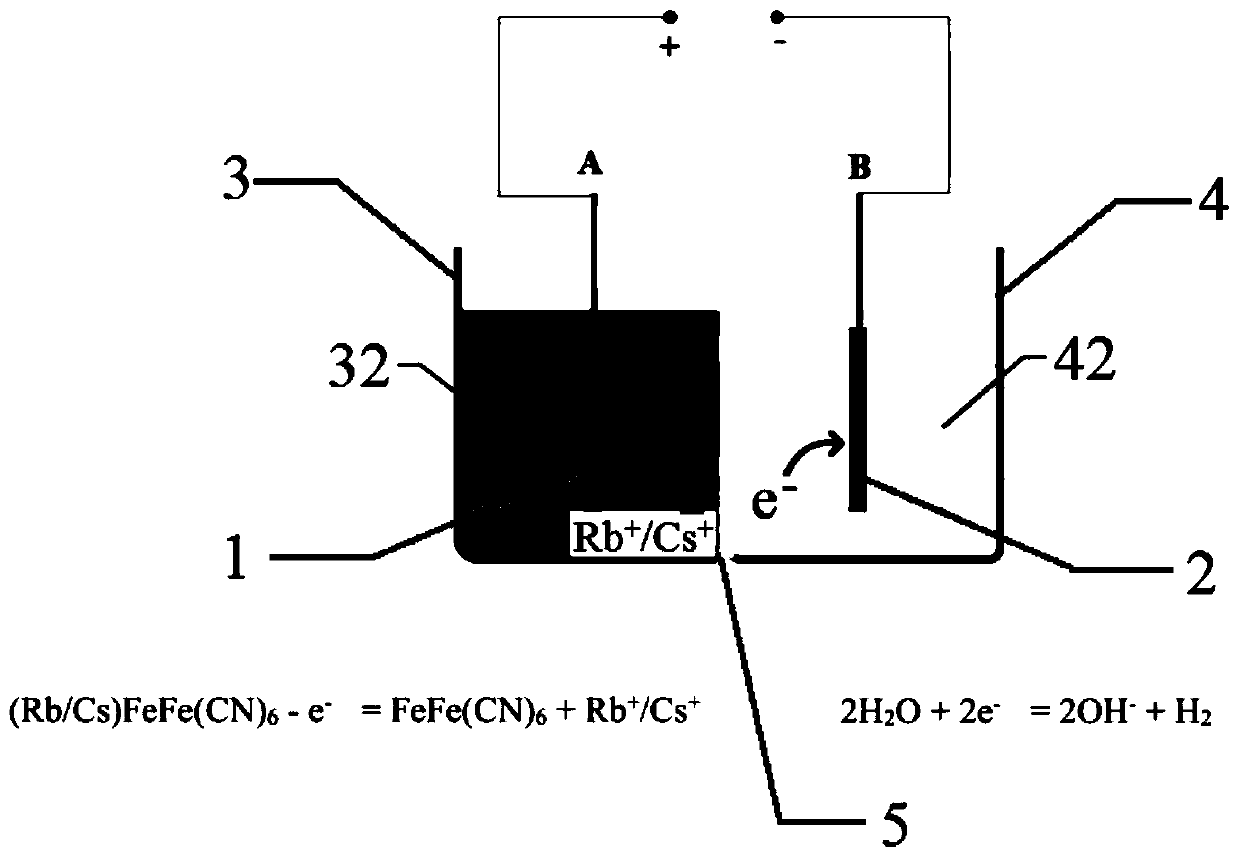
[0077] The working electrode A and the working electrode B after the electrolytic reaction in s...
Embodiment 3
[0079] (1) Preparation of working electrode
[0080] Prussian blue in working electrode A is FeMn(CN) 6 , other experimental materials are the same as in Example 1.
[0081] (2) Cesium intercalation process
[0082] The volume of the first catholyte is 100 L, which contains 20 mg / L of CsCl (calculated as Cs), 15 g / L of NaCl, and 10 g / L of KCl, and the pH value of the solution is 6. The cell voltage is 1.2V, and the control temperature is room temperature. After working for 4 hours, the concentration of cesium in the first catholyte is lower than 0.4mg / L, and the extraction rate of Cs is 98%.
[0083] (3) Cesium removal process
[0084] Replace electrolyzer, other operation process is with embodiment 1. The concentration of cesium in the concentrated cesium solution is 1880 mg / L, and the desorption rate of Cs is 95.9%. This method realizes the enrichment of Cs in the brine by 94 times.
[0085] The working electrode A and the working electrode B after the electrolytic rea...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com