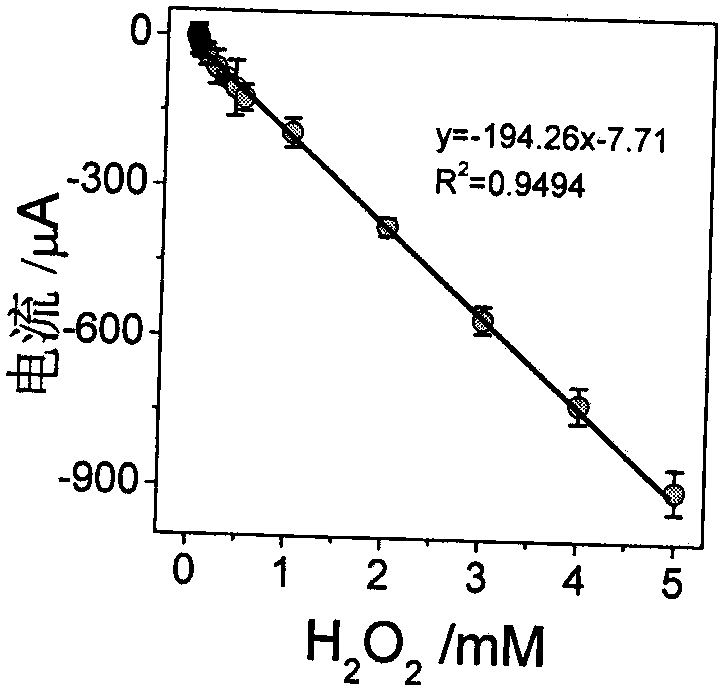
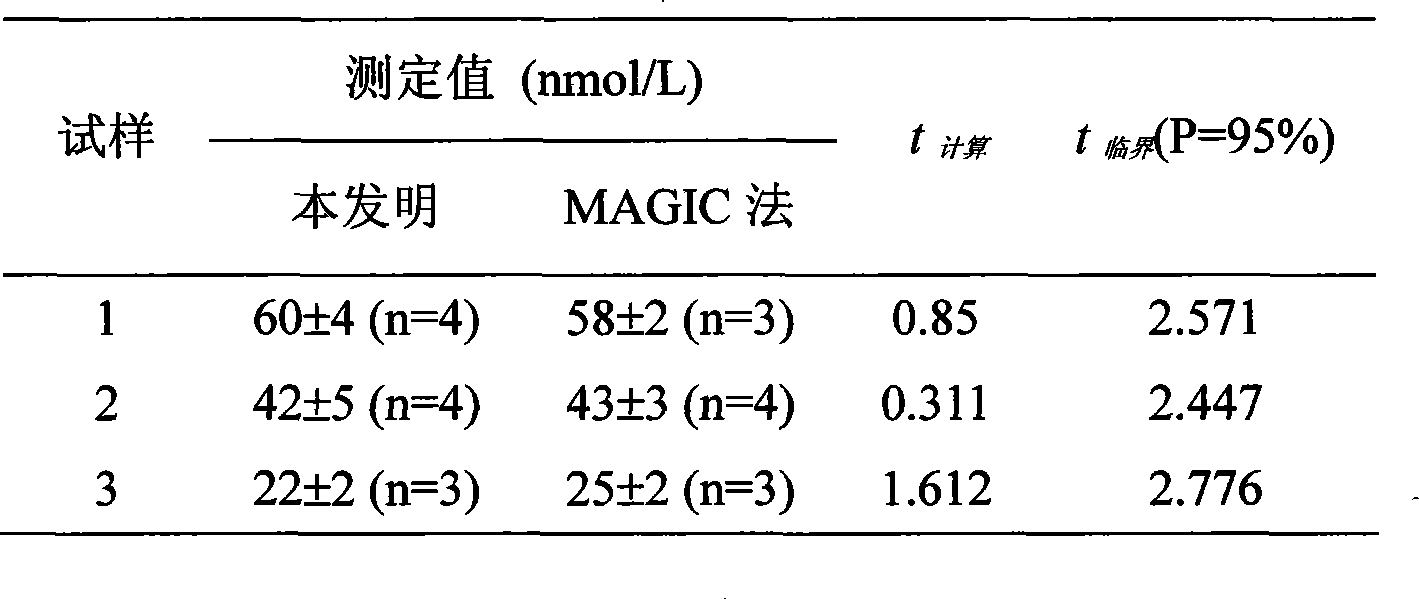
Patents
Literature
68results about How to "Less reagent consumption" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
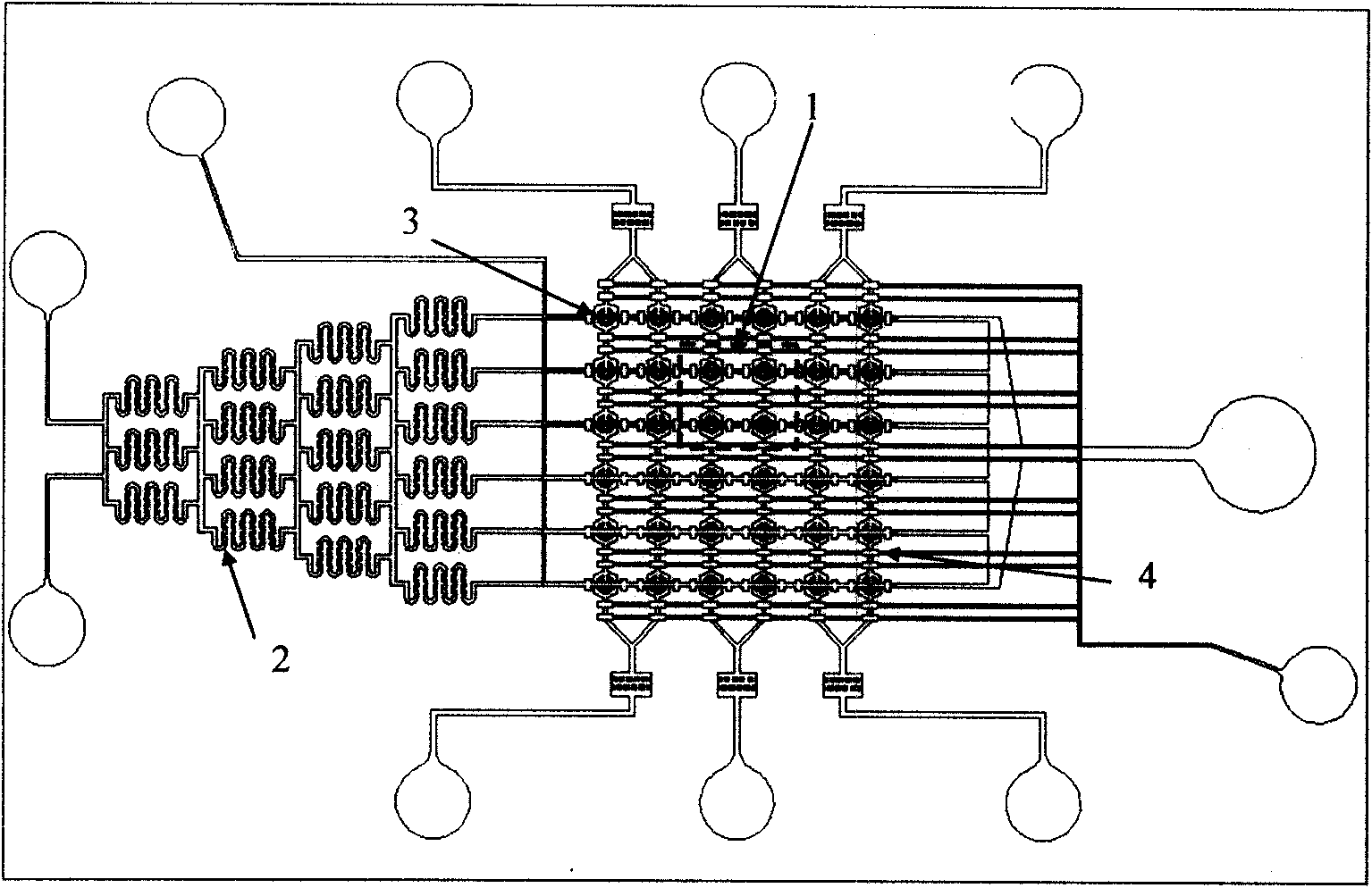
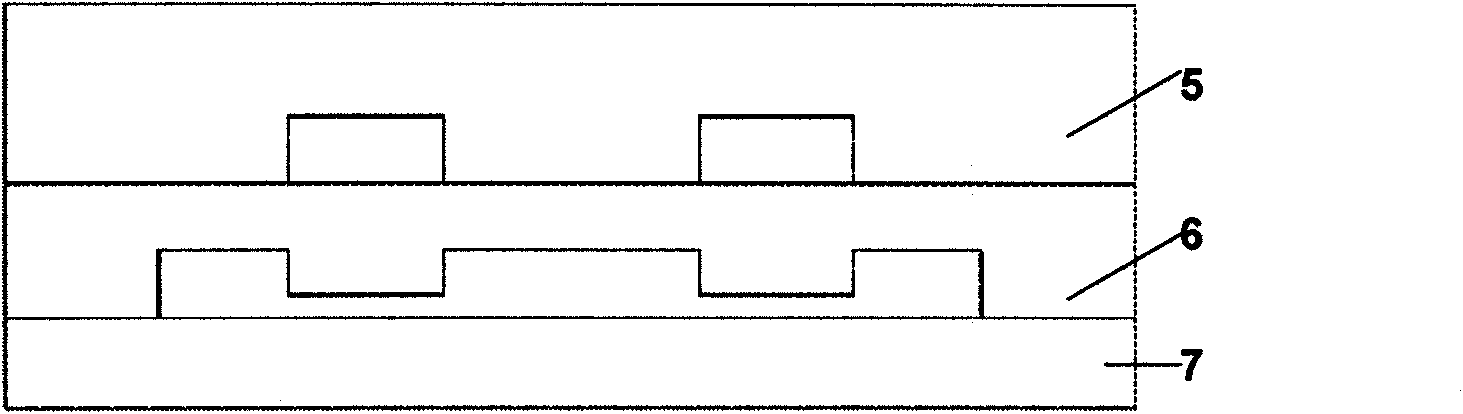
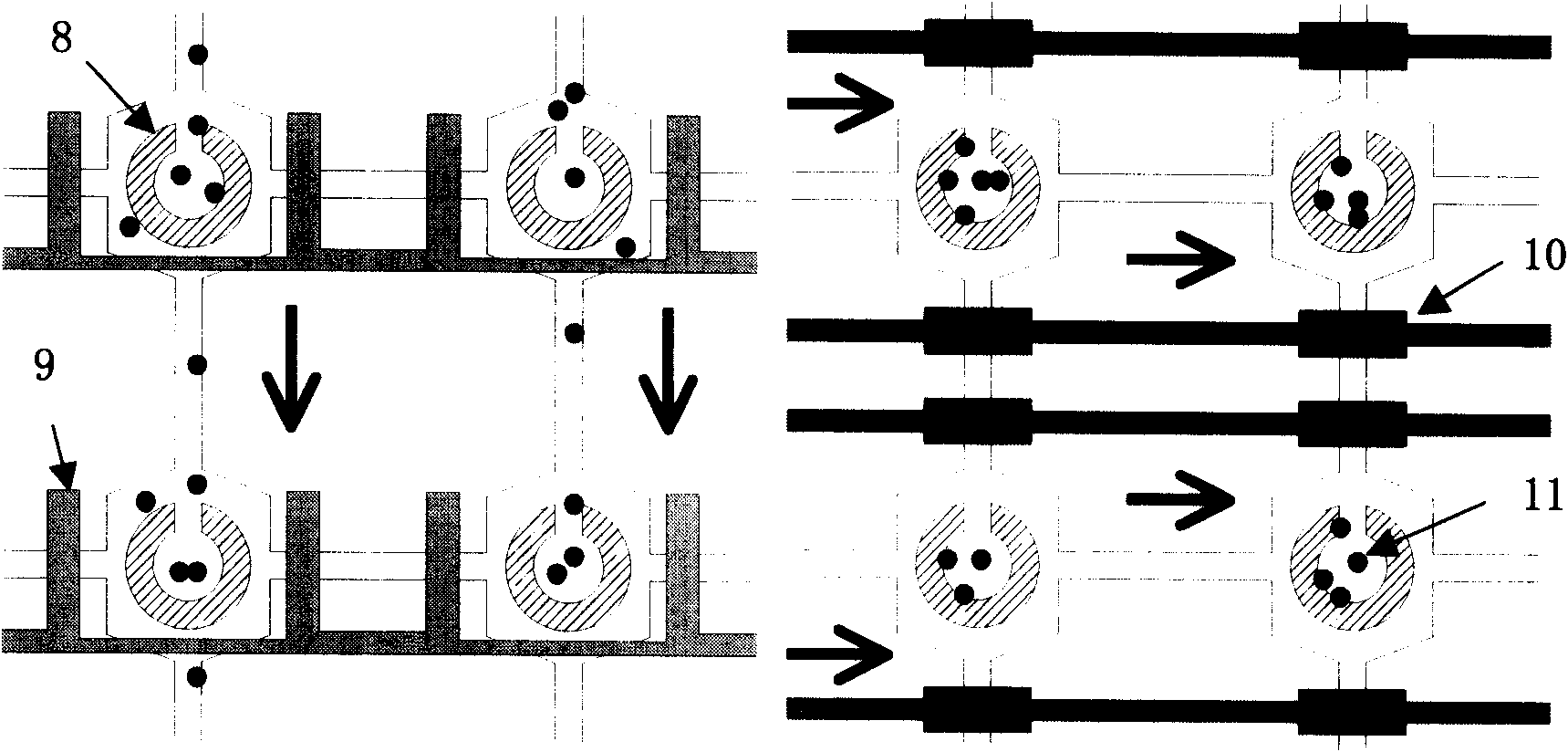
Microfluidic cell array chip for high-throughput medicament screening, method and use
InactiveCN101629143AResolving disordered cell distributionLess reagent consumptionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPhotoresistWidth ratio
The invention relates to a microfluidic cell array chip for high-throughput medicament screening, a preparation method thereof and use thereof. The microfluidic cell array chip for high-throughput medicament screening is characterized by sequentially comprising a valve-controlled channel layer, a fluid channel layer and a glass layer suitable for the anchorage growth of cells from top down. The chip can be used in high-throughput medicament screening by the parallel action of different medicament concentrations on various cells. The chip is manufactured by a multixposure one-development Su-8 negative photoresist process and multilayer PDMS bonding and has a structure with a high depth-to-width ratio. The microfluidic cell array chip provided by the invention can realize low reagent consumption and high-throughput co-culture of various cells, parallel analysis of the stimulation effect of different medicament concentrations on different cells and the real-time observation and detection of a slide of the cells and provide a fire-new technical platform and a method for high-throughput medicament screening and cell-medicament researches.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing low molecular weight seaweed polysaccharide sulfate
The present invention relates to the preparation process of low molecular weight seaweed polysaccharide sulfate. The preparation process includes adding ascorbic acid and hydrogen peroxide into the solution of natural seaweed polysaccharide sulfate as material, with the added amount being 0.1-50 mmol / L and 0.1-100 mmol / L and the ratio being 1 to 0.1-10, constant degradation under controlled temperature for 0.5-3 hr, dialysis or ultrafiltering, decompression concentration and freeze drying to obtain low molecular weight seaweed polysaccharide sulfate product of molecular weight 4-100 KDa. The present invention has the advantages of fast degradation speed, low reagent consumption, simple process, concentrated molecular weight distribution and other advantages. The low molecular weight seaweed polysaccharide sulfate product has controllable molecular weight, greatly raised dissolubility and bioactivity.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
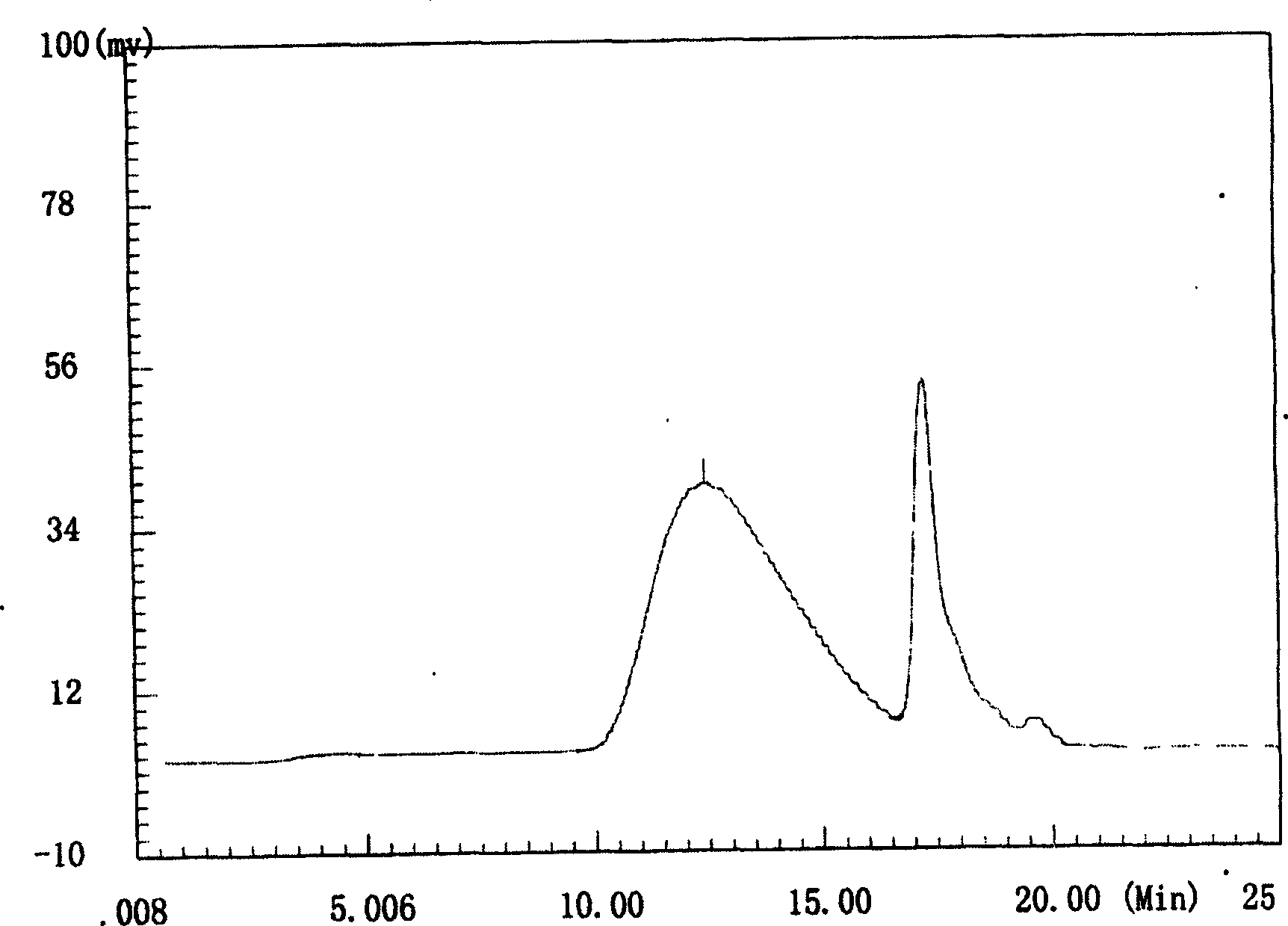
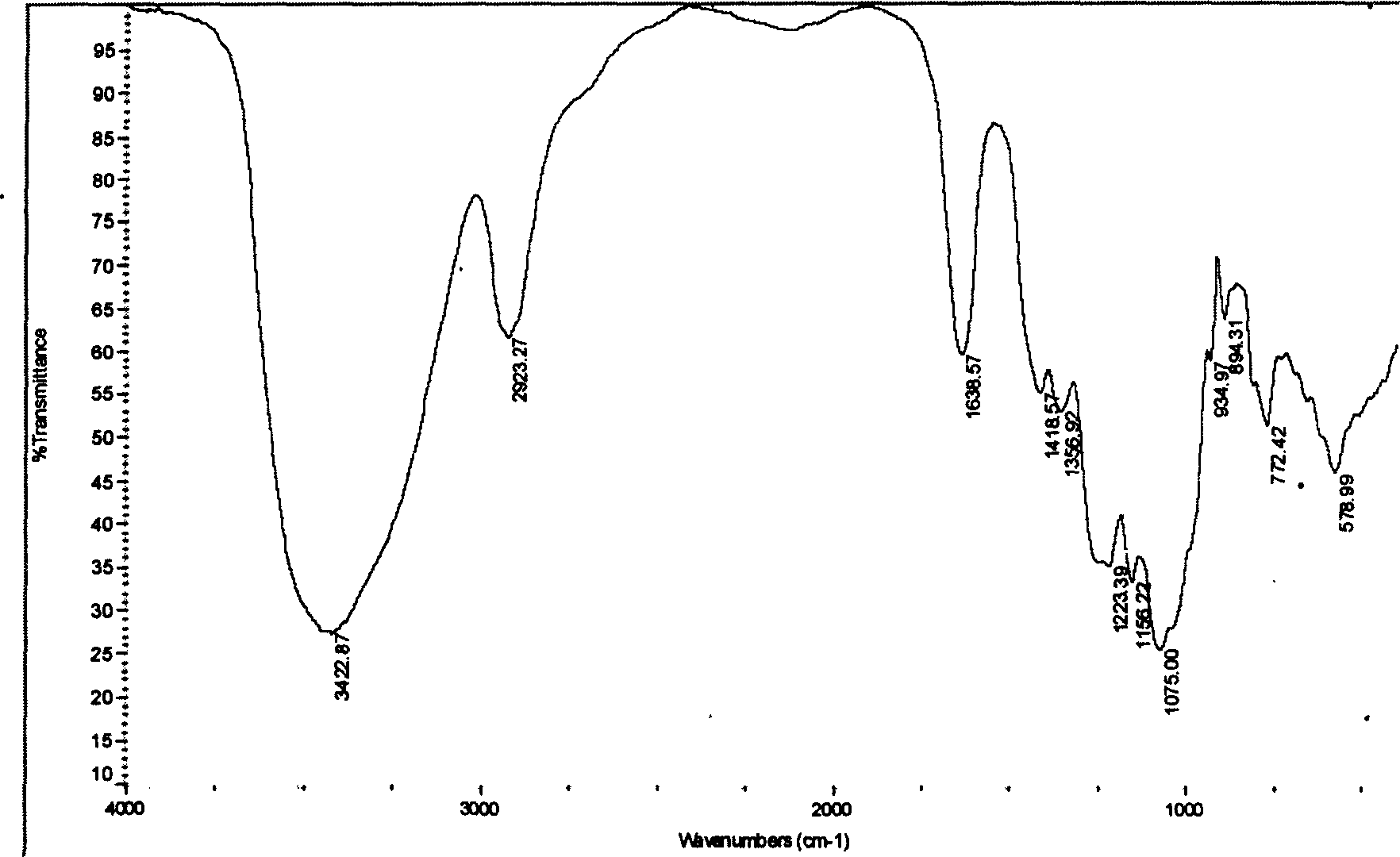
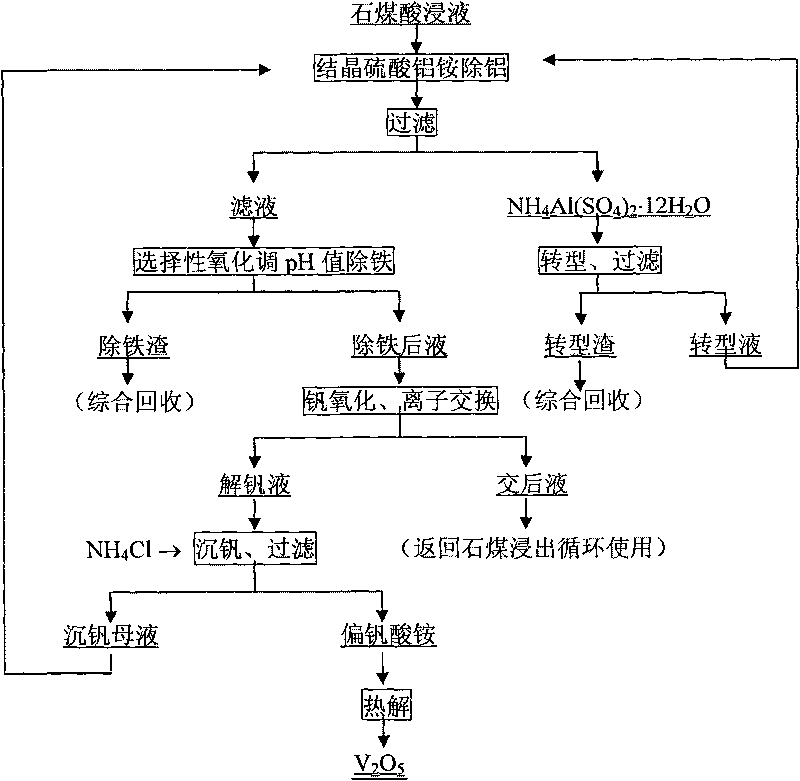
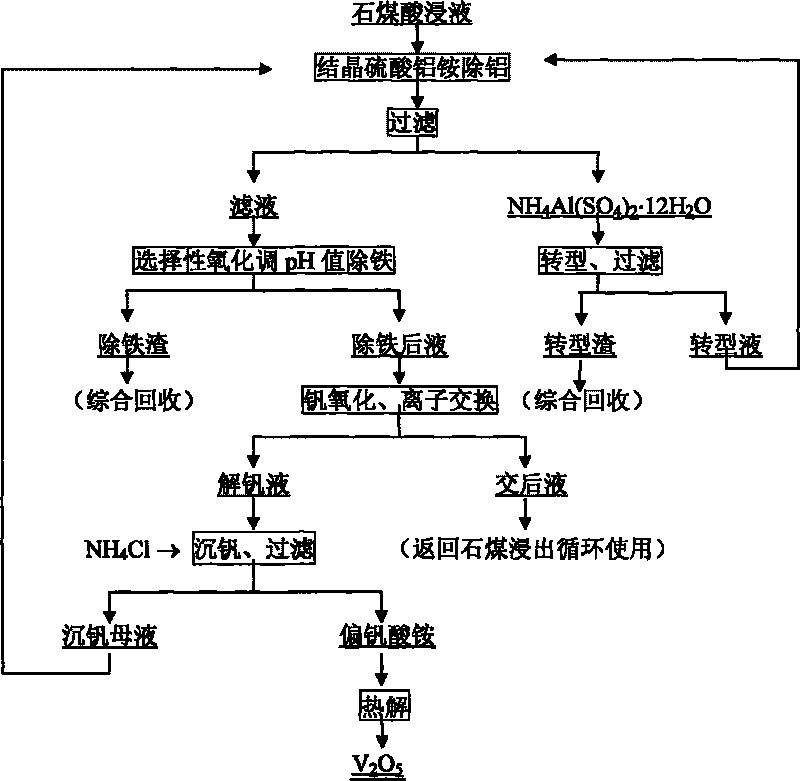
Process for extracting vanadium by acid leaching of stone coal
InactiveCN101760651AShort processLess reagent consumptionProcess efficiency improvementAluminium saltsCoal
The invention provides a process for extracting vanadium by acid leaching of stone coal. The process mainly comprises the following steps of: removing aluminum from crystal aluminum sulfate ammonium vanadium obtained from acid leaching solution of stone coal, performing selective oxidation and adjustment of a pH value of the solution obtained after the aluminum removal to remove iron, performing oxidizing transformation of vanadium in the solution obtained after the iron removal, adsorbing the vanadium in the transformed solution by anion exchange resin, desorbing and regenerating the vanadium-loaded resin, performing ammonium salt precipitation of the vanadium-desorbing solution, performing pyrolysis of ammonium metavanadate, transforming the aluminum sulfate ammonium vanadium and the like. The process has the advantages of short flow, little consumption of reagent, high vanadium recovery rate, low production cost, good product quality and the like.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for extracting vanadium from stone coal pickle liquor
InactiveCN103789560AShort processLess reagent consumptionProcess efficiency improvementSolventAluminium
The invention discloses a method for extracting vanadium from stone coal pickle liquor. The technical process mainly comprises the steps of extracting the stone coal pickle liquor subjected to aluminum removal through an acidic phosphate ester extracting agent solvent to remove ferric iron, enriching the vanadium through the acidic phosphate ester extracting agent solvent after the iron is removed and the pH of the liquor is adjusted, neutralizing precipitates with the vanadium-enriched liquor to obtain vanadium dioxide hydrate, refining the vanadium dioxide hydrate, calcining the refined vanadium dioxide hydrate to obtain a vanadium oxide product and the like. The method for extracting the vanadium from stone coal pickle liquor has the advantages of short technical flow, low consumption of reagents, low production cost, high product quality, environment friendliness and the like.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Process for extracting sesamin
InactiveCN1535970AImprove extraction yield and purityLess reagent consumptionOrganic chemistryLiquid solutions solvent extractionSolventChemistry
The present invention discloses an extraction process of sesamin. Said process includes: firstly, purification process of sesamin: making sesame oil pass through the cylindrical body container whose interior is filled up with chromatographic adsorbent, at the same time making fat-soluble eluent, pass through the cylindrical body container to elute oily impurity, eluting until the bottom layer colour band of the cylindrical body container is removed; them making extraction process of sesamin: collecting adsorbent color band layer positioned in middle portion of the cylindrical body container, and utilizing solvent capable of dissolving sesamin to extract extract of sesamin containing in the color band layer. Said invention has the advantages of high extraction rate and high purity.
Owner:朱萧俊
Determination method for trace impurity elements such as sodium, magnesium, calcium, iron and lead in high-purity boric acid
InactiveCN102928364ALess reagent consumptionReduce reagent blankPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationInductively coupled plasma emission spectroscopyMagnesium
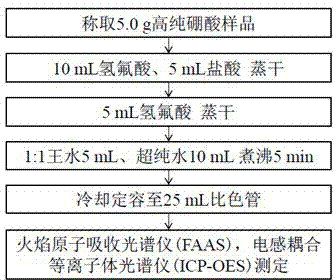
The invention discloses a determination method for trace impurity elements such as sodium, magnesium, calcium, iron and lead in high-purity boric acid. The determination method comprises the following specific steps of: heating hydrofluoric acid and hydrochloric acid to remove boron; extracting soluble salts by using aqua regia; setting constant volume by using ultrapure water; determining by an atomic absorption spectrometer and an inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometer; and performing quantitative enriching and assay determination on the trace impurity elements in a high-purity boric acid sample. According to the determination method, the boron is removed by the hydrofluoric acid; the using amount of reagents is small; the sample blank rate is low; sample computer analysis is facilitated by removing boric acid matrixes; and a single element and multiple elements can be simultaneously determined by means of atomic spectrums comprising the atomic absorption spectrometer and the inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometer. The determination method is suitable for the assay determination of the trace impurity elements in the high-purity boric acid sample and has the advantages of low detection limit, high sensitivity, wide linear range and the like. The average processing time of a single high-purity boric acid sample is not more than 2 hours.
Owner:INST OF MULTIPURPOSE UTILIZATION OF MINERAL RESOURCES CHINESE ACAD OF GEOLOGICAL SCI
Process for extracting vanadium from stone coal by acid method by using leaching agent
InactiveCN101845560AImprove overall recoveryOvercome the disadvantage of low recovery rateProcess efficiency improvementGrain treatmentsCoalLeaching rate
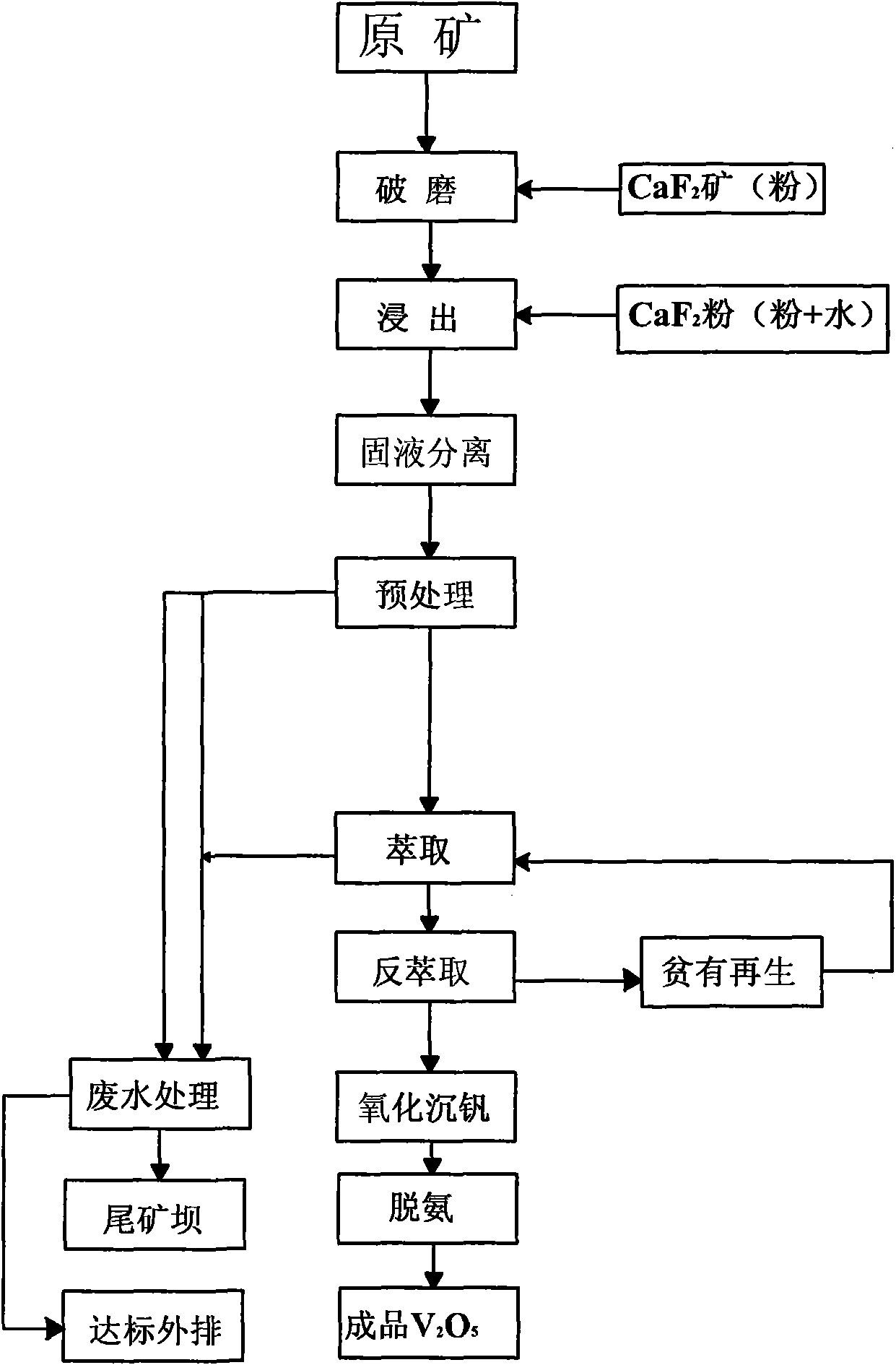
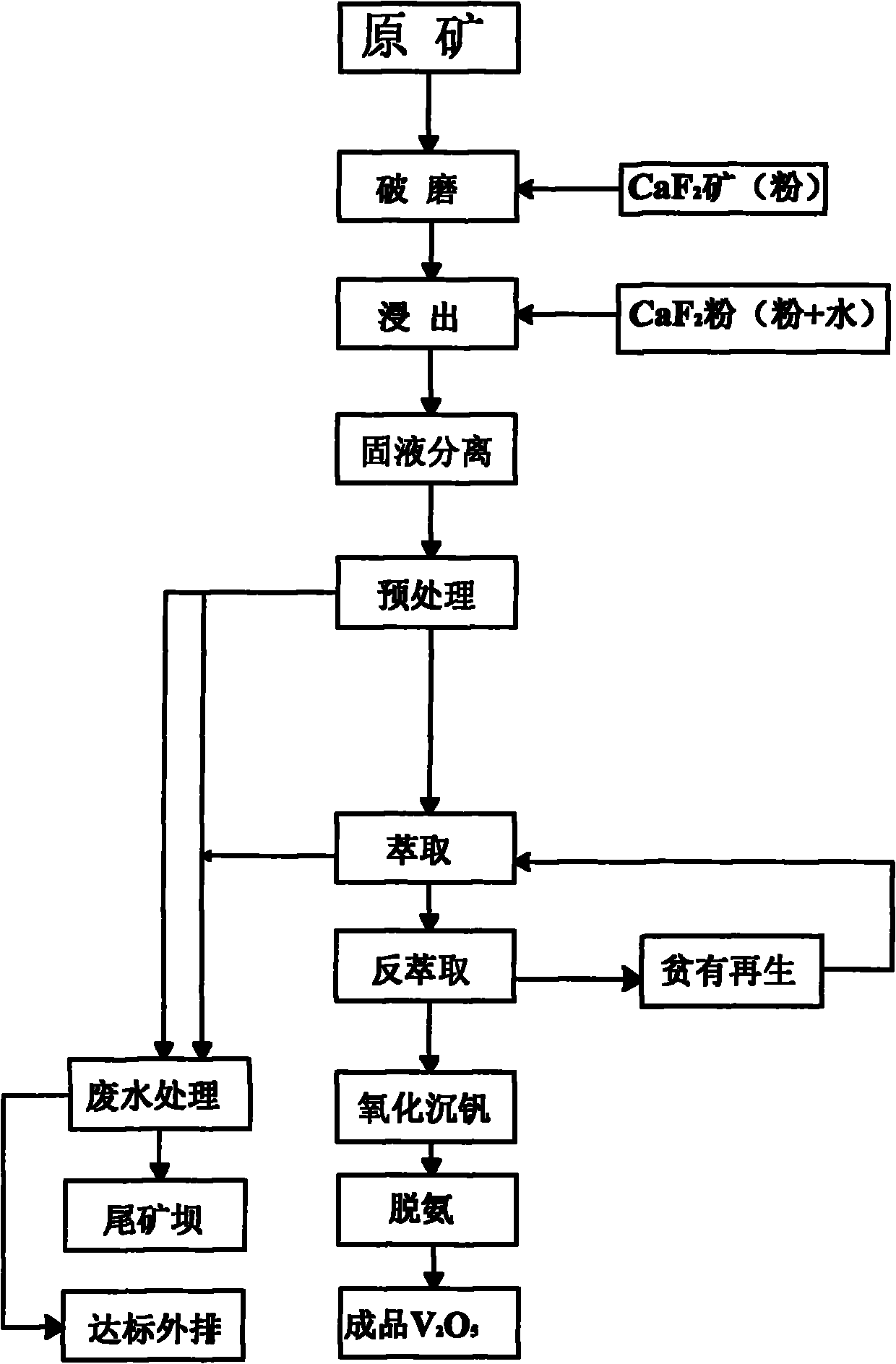
The invention discloses a process for extracting vanadium from stone coal by an acid method by using a leaching agent. The process comprises the following steps of: rude ore crushing, acid leaching, liquid-solid separation, solution pretreatment, extraction and back-extraction, oxidization of the vanadium precipitation, and red vanadium deamination, wherein a CaF2-containing leaching agent is added in the step of rude ore crushing or / and acid leaching and pulping; and the weight ratio of rude ore to CaF2 is 100:1-8. Due to the adoption of the process, the technical problem that the leaching rate of vanadium-containing stone coal is low is solved; the leaching rate is high; specific yield is improved; and unit cost is saved.
Owner:SHANYANG YINHUA MINING
Microfluidic chip used for cell co-culture and cell culture method thereof
ActiveCN106544270ASimple processingReduce shear forceCell culture supports/coatingTissue/virus culture apparatusMicrofluidic chipCulture mediums
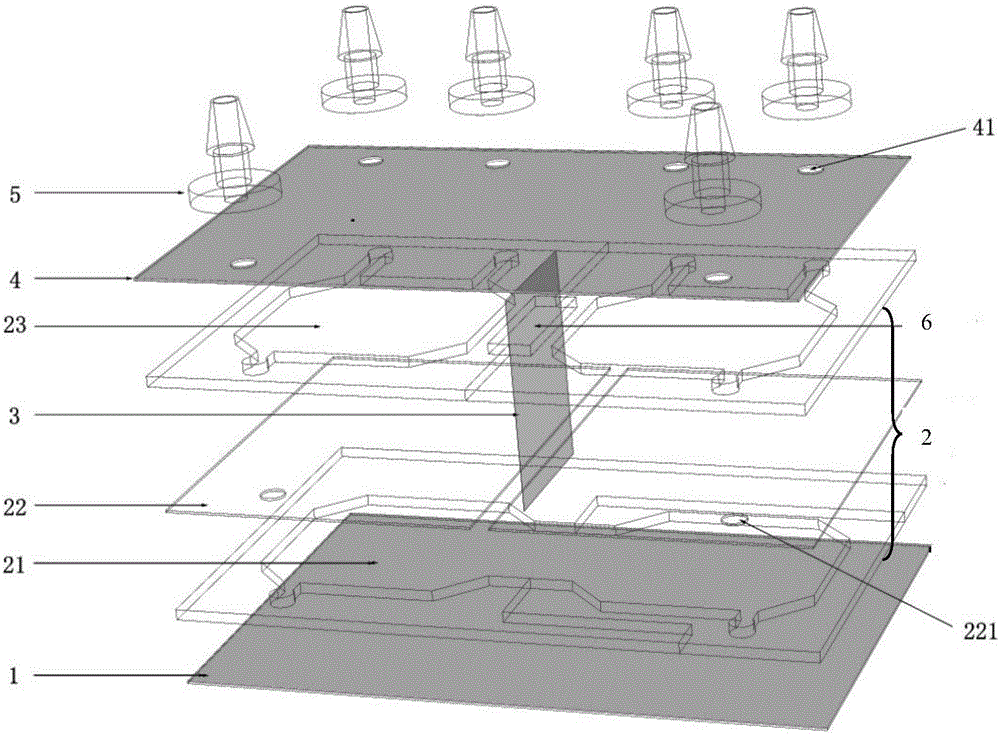
Disclosed is a microfluidic chip used for cell co-culture and a cell culture method thereof. The microfluidic chip comprises successively from bottom to top: a basal layer, a cell culture chamber layer and an upper cover plate layer. A bolting cloth is arranged in the cell culture chamber layer to divide cell culture chambers into two layers, the upper layer is a culture medium exchanging layer, and the lower layer is a cell culture layer. A microfiltration membrane is arranged between the adjacent cell culture chambers. One or more upper cover plate through holes, corresponding to each cell culture chamber, are formed in the upper cover plate layer, and the through holes mutually correspond to bolting cloth through holes in position. Connectors are arranged in the positions corresponding to the upper cover plate through holes. A pipeline used for culture medium exchanging and cell inoculating or cell detecting is arranged in each connector. The microfluidic chip used for cell co-culture can intercept and retain suspension cells effectively, so that microfluidic cell co-culture of adherent cells and suspension cells or suspension cells and adherent cells is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Determination method for chloride ions of foods
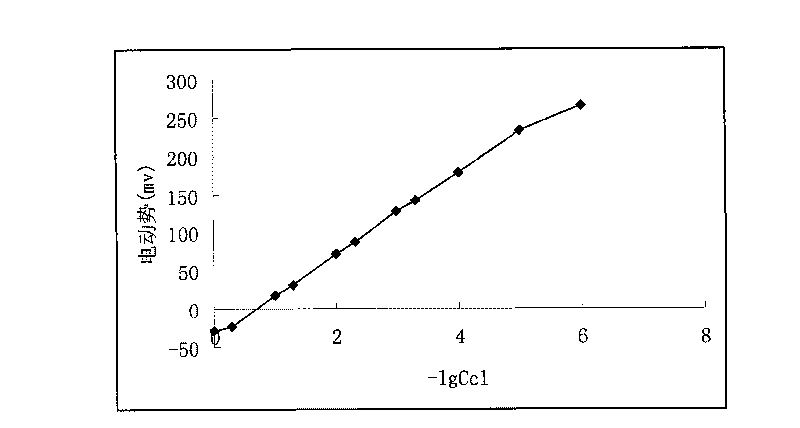
InactiveCN101750445AFast extractionLess reagent consumptionMaterial electrochemical variablesDirect readingMegasonic cleaning
The invention relates to a determination method for chloride ions of foods, which belongs to the technical field of food analysis. The method takes a chloride ion selective electrode as an indicator electrode and a two-liquid junction saturated calomel electrode as a reference electrode which are inserted in a sample solution to form a working battery, and when the concentration of chloride ions is in a range of 1 to 10-5g / L, the battery electromotive force is linear with the logarithm of chloride ion activity, and the concentration of the chloride ions of the foods is determined by a digital ion meter. The method of the invention adopts ultrasonic extraction and direct reading concentration method coupling techniques to determine the chlorine content in samples, and the used ultrasonic cleaning device greatly improves extraction speed; and the method has the obvious advantages of difficult sample contamination, low reagent consumption, simpleness and rapidity, accurate and reliable result.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Complex tracer agent for oil field high-temperature hypersalinity block interwell monitoring and application thereof
ActiveCN103343684ALess reagent consumptionGood separation and enrichment effectConstructionsGadolinium chlorideDysprosium
The invention provides a complex tracer agent for oil field high-temperature hypersalinity block interwell monitoring and the application thereof. The tracer agent comprises one or more of chlorinated hydroxylamine erbium, hydroxylamine gadolinium chloride, chlorinated hydroxylamine dysprosium, chlorinated hydroxylamine ytterbium and chlorinated hydroxylamine holmium, and the tracer agent is formed by a tracer element and a complexing agent in a complexing mode. The tracer element is selected from one or more of erbium, gadolinium, dysprosium, ytterbium and holmium, the complexing agent is hydroxylammonium chloride, and the molar ratio between the tracer element and the complexing agent is 1:8-1:9 and preferably is 1:8. The tracer agent can resist high temperature (250 DEGC-300 DEG C) and hypersalinity (5000mg / L-20000mg / L). The invention further provides a tracer method for conducting the oil field high-temperature hypersalinity block interwell monitoring by means of the tracer agent, and the method comprises the process of conducting separation and enrichment on the tracer agent in a taken sample.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Living spore content high throughput detection method based on spectrophotometry method
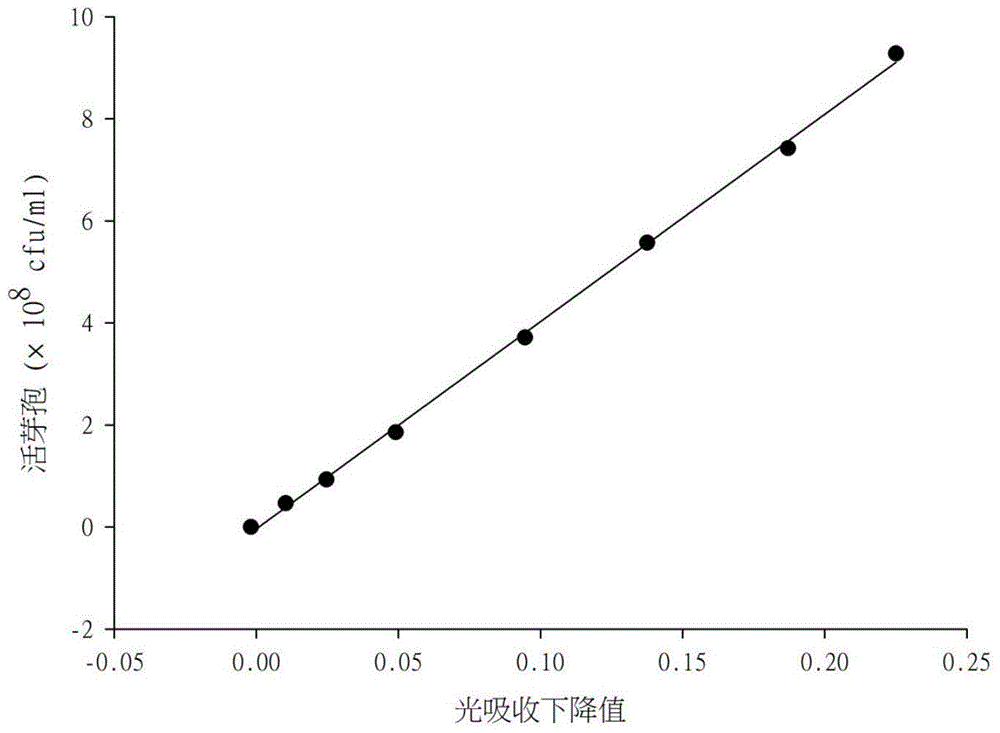
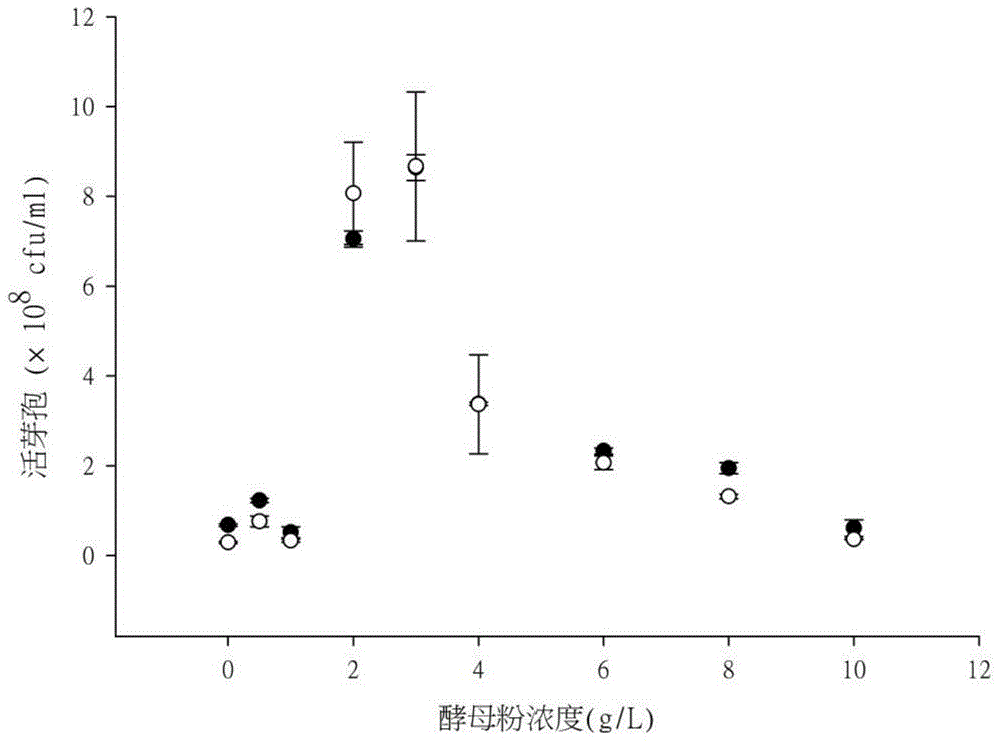
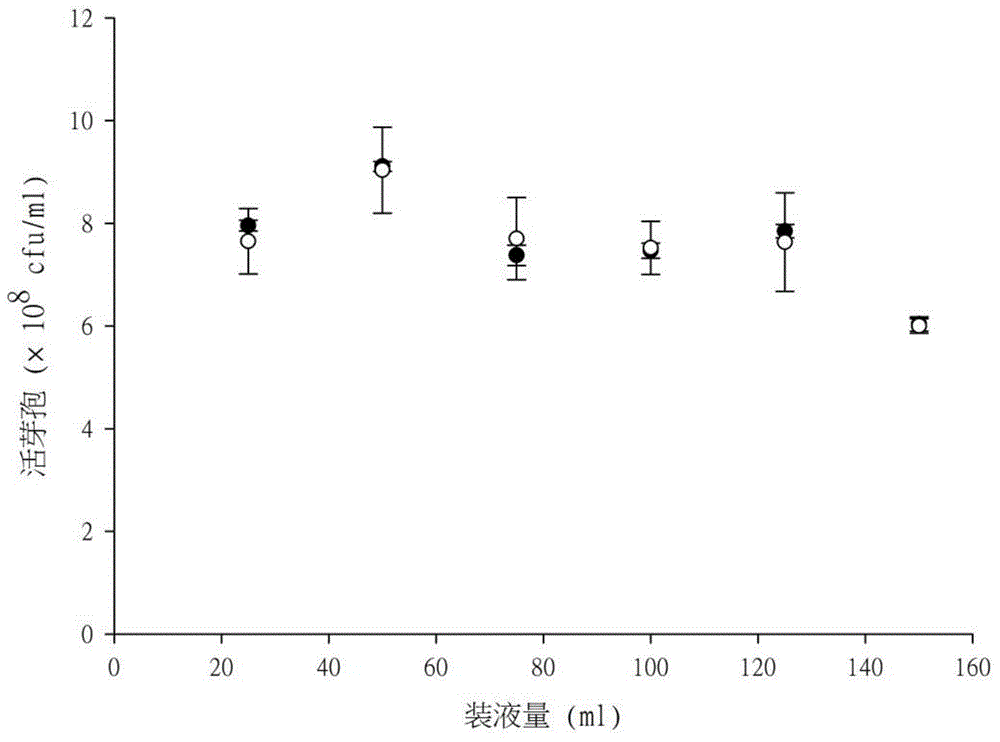
ActiveCN104316475AImprove efficiencyHigh speedPreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsSpore germinationWorkload
The invention discloses a living spore content high throughput detection method based on spectrophotometry method, once spore encounters a suitable environment, the spore may germinate rapidly, light refraction property of the spore converted from a dormant state into a vegetative growth state is very strong, and in the process of germination, light absorption decrease is caused by water absorption swelling and light refraction property disappearance of the multilayer structure. The light absorption decrease as the characterization of spore germination activity is used to evaluate the spore reproduction vitality, can greatly simplify the detection process of living spore content, and overcomes the problems of detection workload and long cycle and high cost of a traditional method.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Thiosulfate gold extraction method taking Fe (III) cyanide salts as oxidants
InactiveCN102534204ALess reagent consumptionFast leachingProcess efficiency improvementLeaching rateThiosulfate
The invention provides a thiosulfate gold extraction method taking Fe (III) cyanide salts as oxidants. The method comprises the following steps: crushing and wet milling golden placer or mineral; adding solutions of Fe (III) cyanide salts, thiosulfate, and thiocarbamide into the ore pulp so as to ensure that in the whole system, the concentration of the thiosulfate is 0.01 to 2 mol / dm<3>, the concentration of the Fe (III) cyanide salts is 0.1 to 1.0 mmol / dm<3>, and the concentration of the thiocarbamide is 0.001 to 10.0 mmol / dm<3>; adjusting the pH value of the system to be 8 to 13; stirring and leaching for 9 to 24 hours; and recycling gold in the leachate according to a conventional method. The method has the advantages that the leaching rate is high; the process operation is simple and easy to control; the consumption of thiosulfate is low; the ingredients of the golden leachate are simple, so as to facilitate the recycling of gold; the application range is wide; and the purpose of environmental protection is realized.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for measuring nanomolar reactive phosphate in sea water
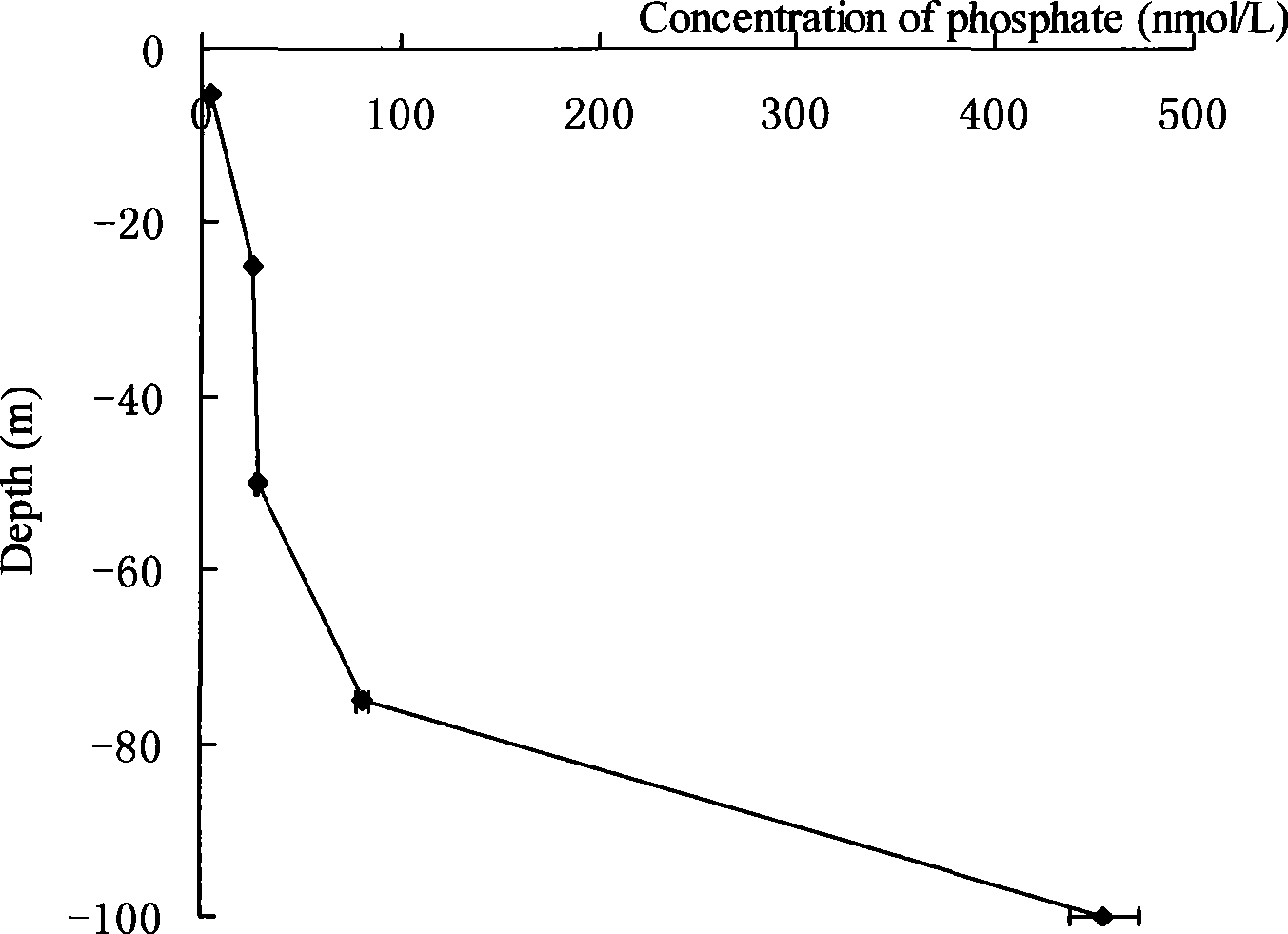
InactiveCN101477039AImprove developmentLess reagent consumptionComponent separationColor/spectral properties measurementsPhosphateField analysis
The invention discloses a method for determining nanomolar active phosphate in seawater, and relates to a method for determining active phosphate with the concentration as nanomolar grade in the seawater. The invention provides the method for determining the nanomolar active phosphate in the seawater which is sensitive, accurate and quick, and is easy for field analysis on ships. The seawater with phosphate is added with a standard solution and is mixed with a reagent; water and a pre-washing solution are used to wash an enriching column after extraction and enrichment; then an extracted substance is eluted; a detector is used to detect at a position between 650 and 850nm; a corresponding signal is recorded; a working curve of the concentration of the phosphate and the corresponding signal is worked out; an actual seawater sample is mixed with the reagent, the water and the pre-washing solution are used to wash the enriching column after the extraction and the enrichment; then the extracted substance is eluted; the detector is used to detect at the position between 650 and 850nm; the corresponding signal is recorded; the standard working curve is used to work out the concentration of the phosphate in the seawater; and the determined concentration of the phosphate is the concentration of the active phosphate according to a definition of the active phosphate.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Method for detecting sulfonamide and beta-lactam antibiotics in livestock and poultry breeding wastewater
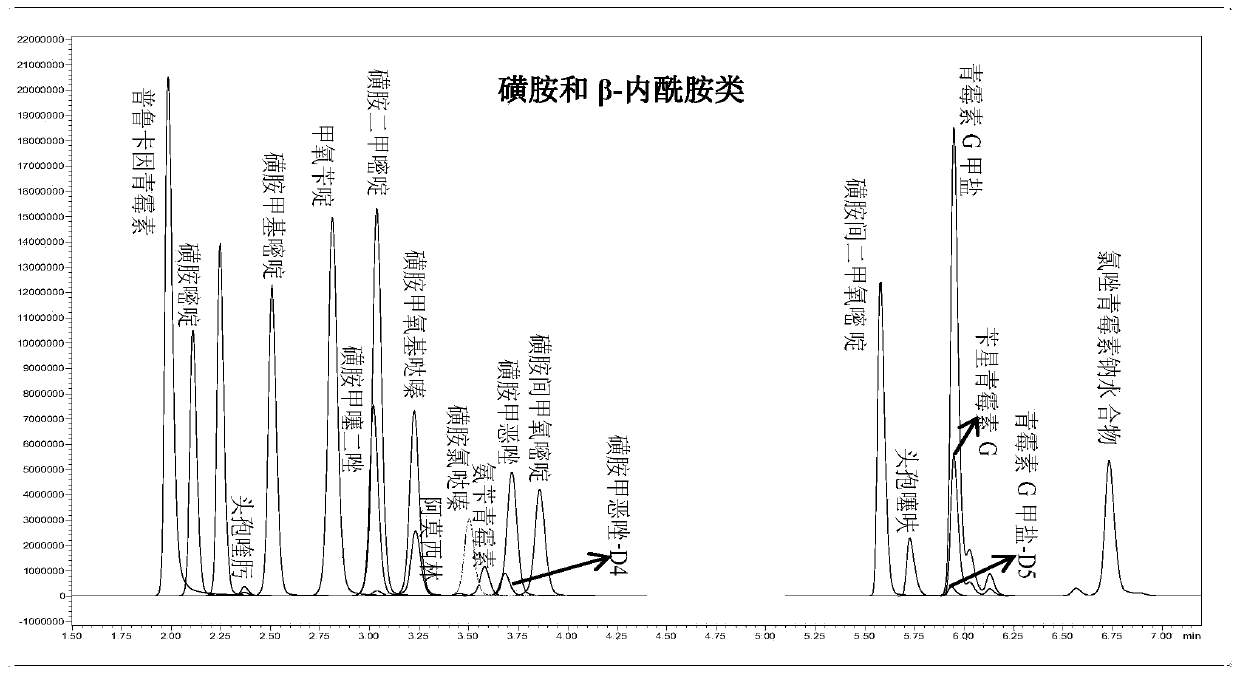
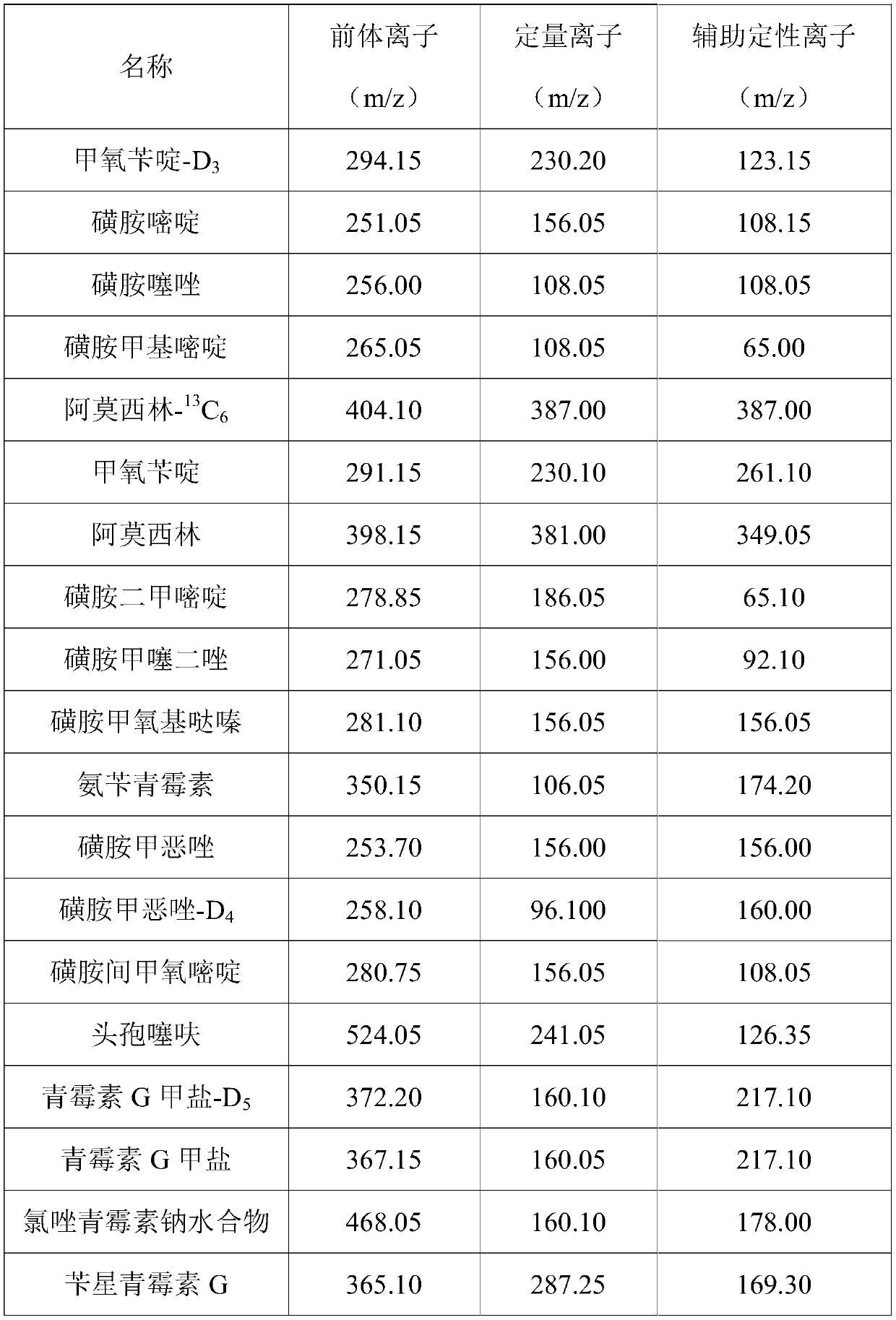
PendingCN111505149AQuick checkDetection time is shortComponent separationBiotechnologyTreated water sample
The invention discloses a method for detecting sulfonamide and beta-lactam antibiotics in livestock and poultry breeding wastewater. The method comprises the following steps: sequentially centrifugingand filtering a to-be-detected water sample; adding deionized water into the obtained filtrate for dilution; adding Na2EDTA, adjusting the pH, carrying out solid-phase extraction treatment on the obtained pre-treated water sample, carrying out negative-pressure leaching treatment and normal-pressure elution treatment on a solid-phase extraction column subjected to the solid-phase extraction treatment, collecting eluent, and then carrying out nitrogen blowing and constant volume treatment to obtain an antibiotic solution to be detected; and carrying out antibiotic content detection on the antibiotic solution to be detected by adopting a high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method. According to the detection method disclosed by the invention, a solid phase extraction-liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry method is adopted, and various process conditions and parameters are selected and determined, so that the detection method can be used for rapidly and accurately detecting antibiotics in water and detecting sulfonamide and beta-lactam antibiotics in the livestock and poultry breeding wastewater at the same time.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for analyzing trace phosphorus in ferromanganese
InactiveCN101929949ASolve the cumbersome operationLess reagent consumptionColor/spectral properties measurementsChemistryAmount of substance
The invention relates to a method for analyzing trace phosphorus in ferromanganese, in particular to a method for quickly measuring phosphorus content in steelmaking raw material ferromanganese, which belongs to the technical field of chemical analysis test. The technical scheme comprises the following steps: taking a standard sample closing to an analysis sample as a working curve; after the sample is completely dissolved, analyzing by directly using an inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometer; and dissolving the ferromanganese sample by using hydrochloric acid, nitric acid and perchloric acid. The invention has the beneficial effects of effectively solving the problems of complicated operation and slow analysis, reducing the reagent amount, reducing the environmental pollution and improving the analysis accuracy due to the adoption of high-precision analysis instrument. As the standard sample closing to the analysis sample is taken as the working curve, the influence caused by a matrix effect is eliminated. The result indicates that the error and precision completely conform to the technical requirements of the state standard. The result of analyzing a standard substance by using the invention is consistent with the determined value, and the invention can be used for measuring the trace phosphorus in high, middle and low-carbon ferromanganese.
Owner:TANGSHAN JIANLONG IND CO LTD
Method for detecting NO (nitric oxide) content in exhaled gas of human body
InactiveCN102507720AQuick monitoringImprove stabilityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansESI mass spectrometryMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
The invention discloses a method for detecting NO (nitric oxide) content in exhaled gas of a human body, wherein PTIO (3-oxo-2-phenyl-4,4,5,5-tetramethyl imidazoline-1-oxygen) is utilized as an oxidizing agent of the NO, and the content of the NO in the exhaled gas of the human body can be directly and quickly detected by adopting an electrospray ionization extraction mass spectrometry method. The method disclosed by the invention has strong specificity and high sensitivity without pre-treatment on a sample; the PTIO has better stability and reaction sensitivity, and can selectively react with the NO. In addition, the method is integrated with sample collection and treatment, so that the consumed dose is small, the operation is convenient and simple and the detection can be finished in a short time. The method has the advantages of high mass spectrum sensitivity and good stability, breaks through the disadvantage of a traditional method, and realizes fast and sensitive monitoring of the NO in the exhaled gas of the human body.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for isolating magnesium and lithium from solution containing magnesium and lithium
ActiveCN106629790ALess reagent consumptionReduce manufacturing costLithium carbonates/bicarbonatesLithium carbonateMagnesium salt
The invention relates to a method for isolating magnesium and lithium from solution containing magnesium and lithium; the method comprises: adjusting pH of the solution containing magnesium and lithium, adding soluble phytate into the solution containing magnesium and lithium, so that Mg<2+> in the solution containing magnesium and lithium forms water-insoluble complex precipitate while Li<+> remains in the solution; after solid-liquid separation, concentrating the solution containing Li<+>, precipitating to obtain lithium carbonate, dissolving the magnesium-containing precipitate with hydrochloric acid, adsorbing phytate ions therein through weak alkalinity anions in weak acidity environment, and using the obtained solution containing Mg<2+> to prepare a magnesium salt; using NaOH solution to desorb the resin that loads phytate ions for the purpose of regeneration, and using the desorbed solution to precipitate Mg<2+> in solution containing magnesium and lithium in next cycle. The method has a short process, is simple to perform, and is efficient for isolating magnesium and lithium from the solution containing magnesium and lithium, the phytate is recyclable, the production cost is low, and the method is easily industrially applicable.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
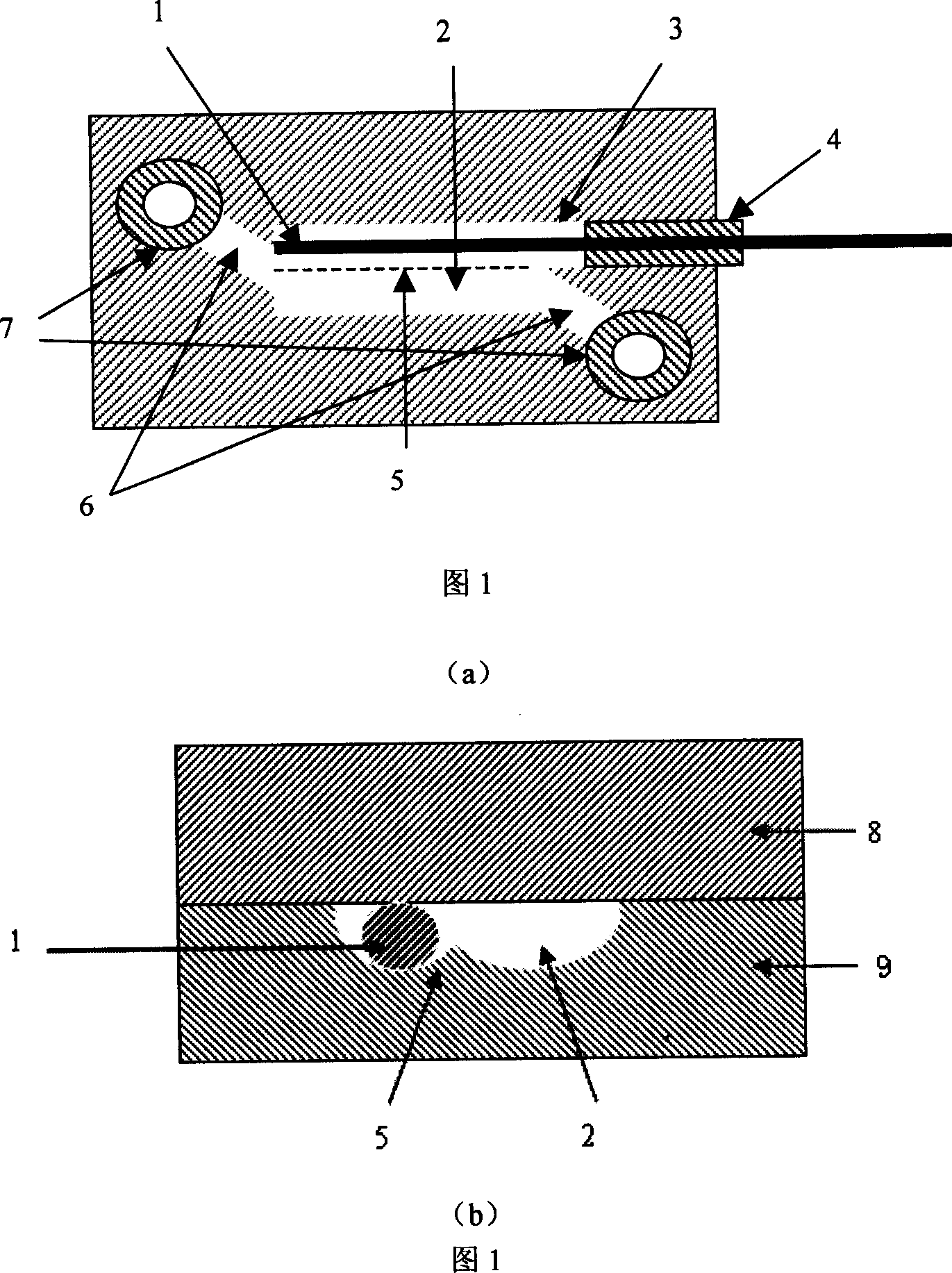
Glass-chip flowing minisize electrolyzer and manufacturing method
InactiveCN1936561AFacilitate mass transferLess reagent consumptionTelevision system detailsImpedence networksPhotolithographyEngineering
A glass chip mobile micro electrolytic cell includes the electrode, micro-electrolytic cell channel, solution channel, solution inlet and outlet, cover piece and substrate, electrode channel, electrode positioning ridge, electrode doors. On the substrate or on the substrate and the cover are synchronously etched with a micro electrolytic cell channel and electrode channel, the connection part of the two channels forms the electrode positioning ridge. Use glass lithography method and the heat integration to make chip usually. Electrodes are lead in from the side of the chip and positioned in the electrode channel. The volume of the micro mobile cell is Nano litre grade so the reagent consumption is low. The electrodes are separated without film because of lamina flow action of the channel. Advantages: dismounting and changing electrode is convenient, chip can be repeatedly used and electrode configuration is agility.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
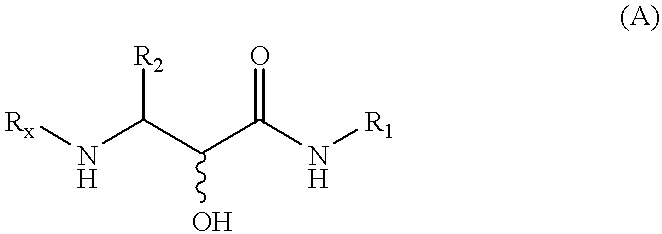
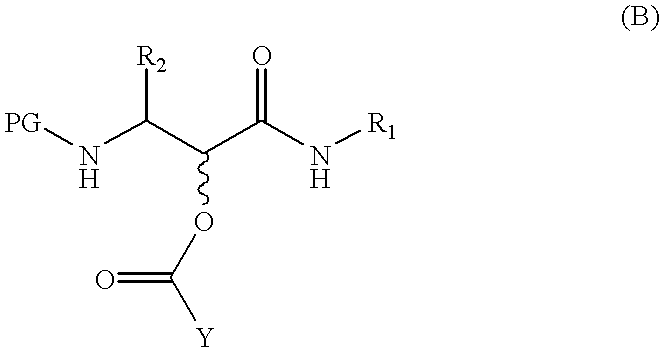
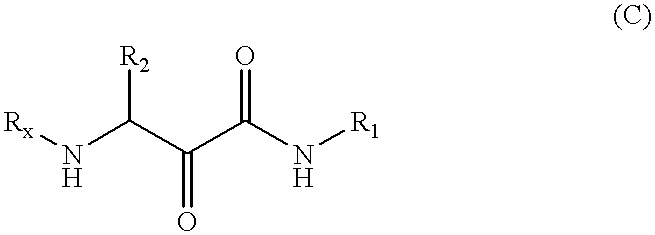
Methods for the synthesis of alpha- hydroxy-beta-amino acid and amide derivatives
InactiveUS6376649B1Few stepsIncrease productionPeptide/protein ingredientsOrganic compound preparationPineapple ProteaseEnzyme inhibitor
Methods for the synthesis of alpha-hydroxy-beta-amino acid and amide derivatives and alpha-ketoamide derivatives and novel derivatives made by these methods are provided. These methods involve reacting a N-terminally blocked (protected) aminoaldehyde with an isonitrile and a carboxylic acid to give an amino-alpha-acyloxy carboxamide. The acyloxy group may be removed to give the derivative. Alternatively the protecting group is removed and acyl shift occurs to give the derivative. These derivatives are useful in the synthesis of compounds such as peptidyl alpha-ketoamides and alpha-hydroxy-beta-carboxylic acid and amide derivatives. Certain of these compounds have been reported to have activity as inhibitors of proteases, such as serine proteases and cysteine proteases.
Owner:CORVAS INT INC
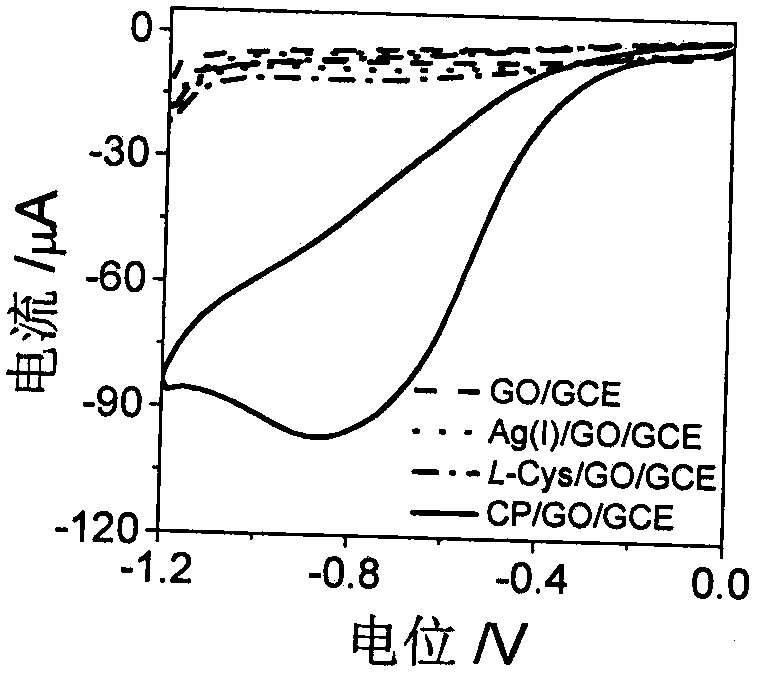
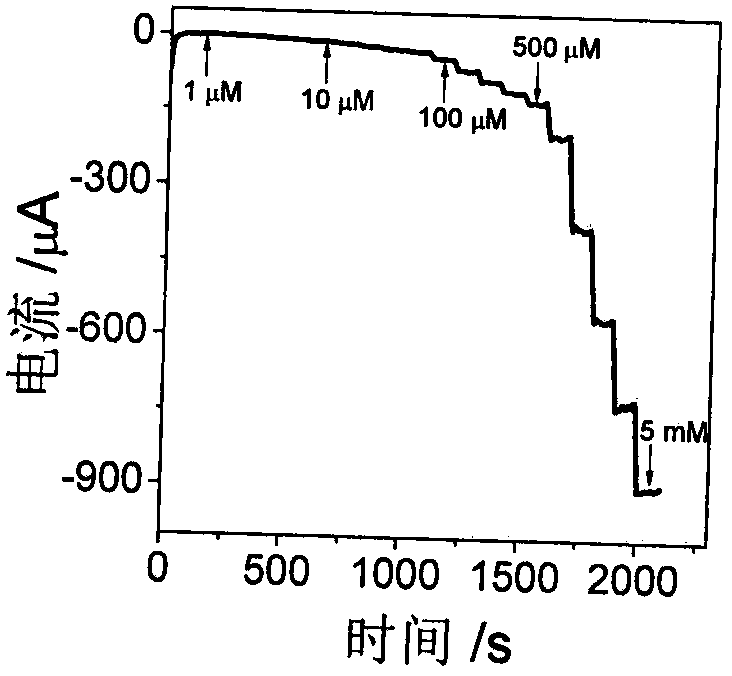
Electrochemical biosensor based on polypeptide analog with electrocatalytic activity for acetylcholin esterase detection
ActiveCN108120761AThe result is accurateLess reagent consumptionPreparing sample for investigationMaterial electrochemical variablesNafionGraphene
The invention discloses an electrochemical biosensor based on polypeptide analog with the electrocatalytic activity for acetylcholin esterase detection. The biosensor for acetylcholin esterase detection is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) intensively stirring and uniformly mixing silver nitrate, L-cysteine and secondary distilled water on a stirrer, and incubating in an oscillator; (2) electrodepositing graphene onto a bare glassy carbon electrode by utilizing an electrochemical method, mixing 0.05 weight percent of a Nafion solution with the solution obtained in the step (1), and dropwise coating GO / GCE to obtain an electrochemical biosensor based on the polypeptide analog with electrocatalytic activity (CP / GO / GCE); (3) performing acetylcholin esterase activity detection, namely catalyzing acetylcholine in one step to generate H2O2, uniformly mixing acetylcholine, AchE and choline oxidase, and incubating to generate H2O2, and detecting the solution with the sensorprepared in the step (2) with good specificity, high sensitivity, high detection speed, accurate and reliable result; and (4) performing AChE inhibitor malathion detection, namely uniformly mixing acetylcholine, AChE, malathion and choline oxidase, incubating, and detecting the solution with the sensor prepared in the step (2). The biosensor has the advantages of good specificity, high sensitivity, high detection speed and accurate and reliable result.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Chemical luminescence detection method for ultra-trace reactive phosphate in sea water
InactiveCN101477057ANo distractionLess reagent consumptionTesting eggsChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceChemical reactionMOPS
The invention provides a chemiluminescent detection method for an ultra trace amount of active phosphate in seawater. Under acid conditions, phosphate and a molybdate solution generate MoP; an MoP-CTAB ion-pair compound generated by a reaction between the MoP and CTAB can be enriched by a C18 column, and is eluted by an ethanol sulfate solution with certain concentration; an eluent and a luminol solution perform a chemical reaction under alkaline conditions; and a chemiluminescent instrument is utilized for detection. The ultra trace amount of the active phosphate in the seawater is determined through a MoP-CTAB ion pair-solid phase extraction-luminol chemoluminescence method. The method has the advantages that the method consumes few reagent and water sample, has short determination time, is sensitive, has low detectability, improves the sensitivity by 150 times compared with a phosphomolybdate-blue spectrophotometry, has simple and convenient steps, ensures that the whole process is easy to realize the automation, is easy to develop a ship loading type field analytical instrument, and has no interference of a seawater substrate relative to other chemoluminescence methods.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Pretreatment method for detecting metal elements in kapok powder
ActiveCN105241741ASolve the problem of interference detectionShort timePreparing sample for investigationPretreatment methodDecomposition
The invention discloses a pretreatment method for detecting metal elements in kapok powder. The pretreatment method comprises the steps that 1, kapok is crushed and then put into a digestion tank, and nitric acid and hydrogen peroxide are added into the digestion tank; 2, the digestion tank is put into a digestion instrument for microwave digestion; 3, digestion sample liquid in the digestion tank is transferred into a polytetrafluoroethylene crucible, the digestion tank is washed with ultrapure water, all washing liquid is gathered into the polytetrafluoroethylene crucible, and heating is performed for removing the acid; 4, when the polytetrafluoroethylene crucible is cooled to room temperature, the liquid in the polytetrafluoroethylene crucible is all transferred into a volumetric flask, the polytetrafluoroethylene crucible is washed with the ultrapure water, and all the washing liquid is gathered into the volumetric flask, and constant volume is performed with nitric acid with the mass fraction of 2%. Compared with traditional open type methods such as an ashing method and an acid heating digestion method, the pretreatment method has the advantages of being short in time consumption, little in pollution and reagent amount consumption, thorough in digestion and good in reproducibility, and the problem that organic substances left in sample decomposition disturb detection can be effectively solved.
Owner:GUANGXI BOTANICAL GARDEN OF MEDICINAL PLANTS
Droplet chip nucleic acid analysis system and analysis method thereof
ActiveCN108823092AFlexible applicationLess reagent consumptionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBioinformaticsSignal acquisition
The invention relates to a droplet chip nucleic acid analysis system. The droplet chip nucleic acid analysis system comprises a mounting platform as a base mounting plane, a sample carrying bench forcarrying a nucleic acid analysis sample, a reagent carrying bench for carrying a nucleic acid analysis reagent, chip carrier carrying benches for carrying an open chip, a sampling needle that translates between the chip carrying benches, a temperature control module that controls the temperature of a chip, a magnetic control module that performs magnetic bead transferring on the contents of the chip, an optical detection module for performing nucleic acid analysis on the contents in the chip, and a signal acquisition module for performing signal acquisition on the optical detection module, Theoptical detection module is used to detect optical signals in the droplets of the nucleic acid analysis chip. The invention also relates to an analysis method of the droplet chip nucleic acid analysis system. The system has the advantages of small volume, low reagent consumption, flexible operation and fast analysis speed, and belongs to a medical device for biological detection.
Owner:广州市第一人民医院
Rapid aflatoxin B1 detecting method based on smartphone detecting system
ActiveCN105784706ALow costLess reagent consumptionPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansPrint-throughRapid detection
The invention discloses a rapid aflatoxin B1 detecting method based on a smartphone detecting system.The rapid aflatoxin B1 detecting method includes the steps that aflatoxin B1 microchannels are prepared, detection reagents are added into the microchannels to prepare silver-stained PC sheet, aflatoxin-B1-detection optical hardware is designed through 3DMax software and printed through a 3D printer, the silver-stained PC sheet and a mobile phone are arranged into an optical hardware device, an aflatoxin B1 reaction area is photographed through a camera of the mobile phone, and the detection result of aflatoxin B1 is processed and displayed through a smartphone detection program.According to the rapid aflatoxin B1 detecting method, aflatoxin B1 is rapidly detected based on a smartphone, and the rapid aflatoxin B1 detecting method has the advantages of being convenient to carry, easy and convenient to operate, low in cost, high in flexibility and the like, and is suitable for rapid site detection.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for detecting endotoxin
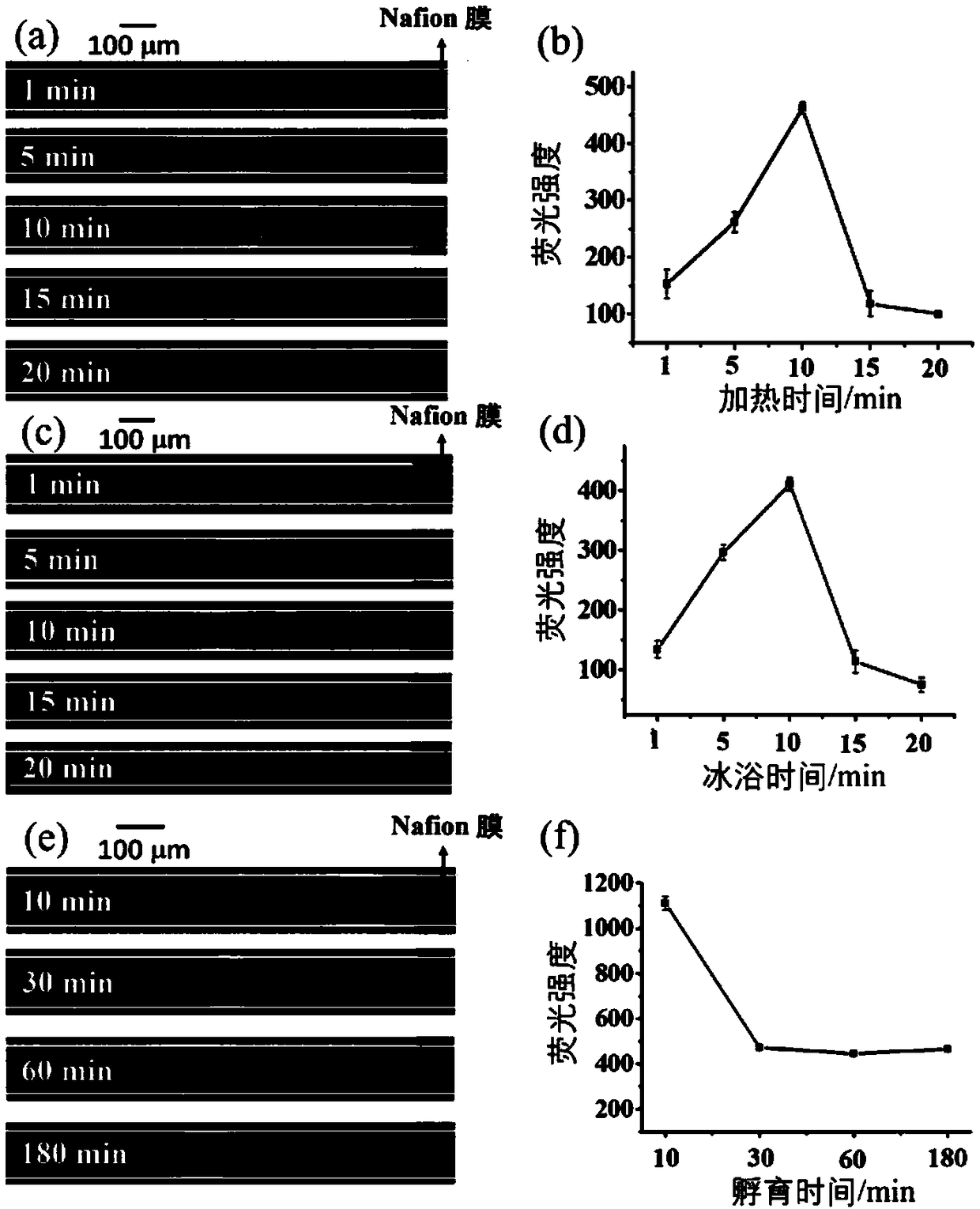
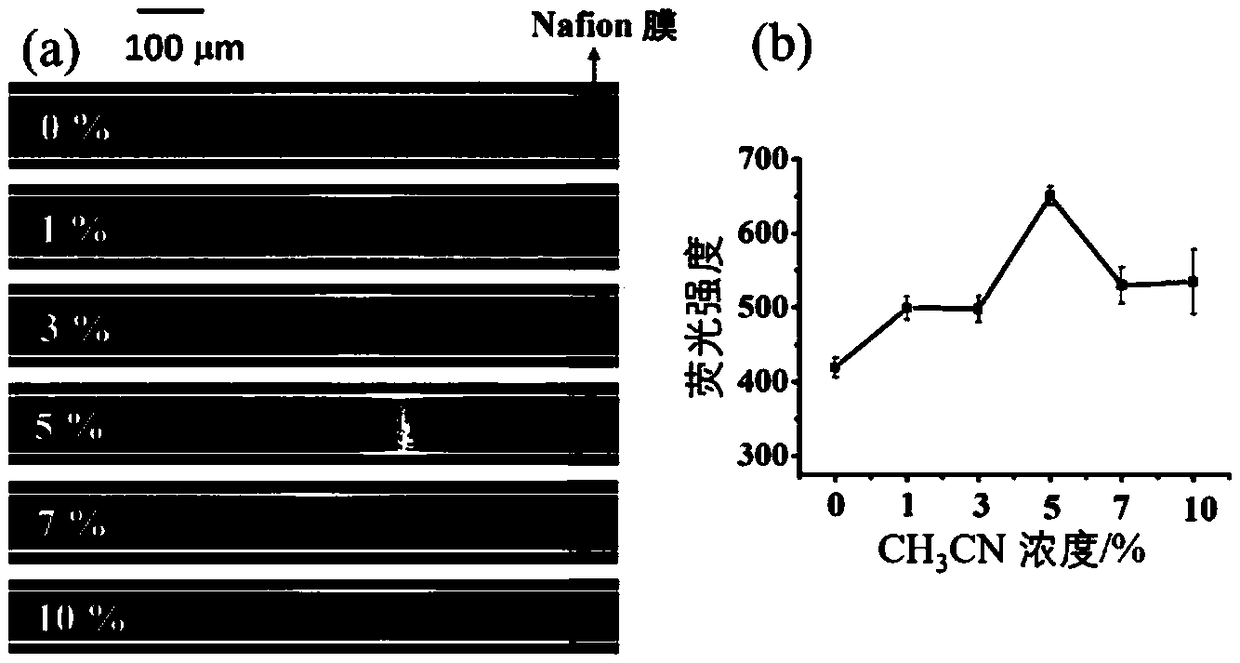
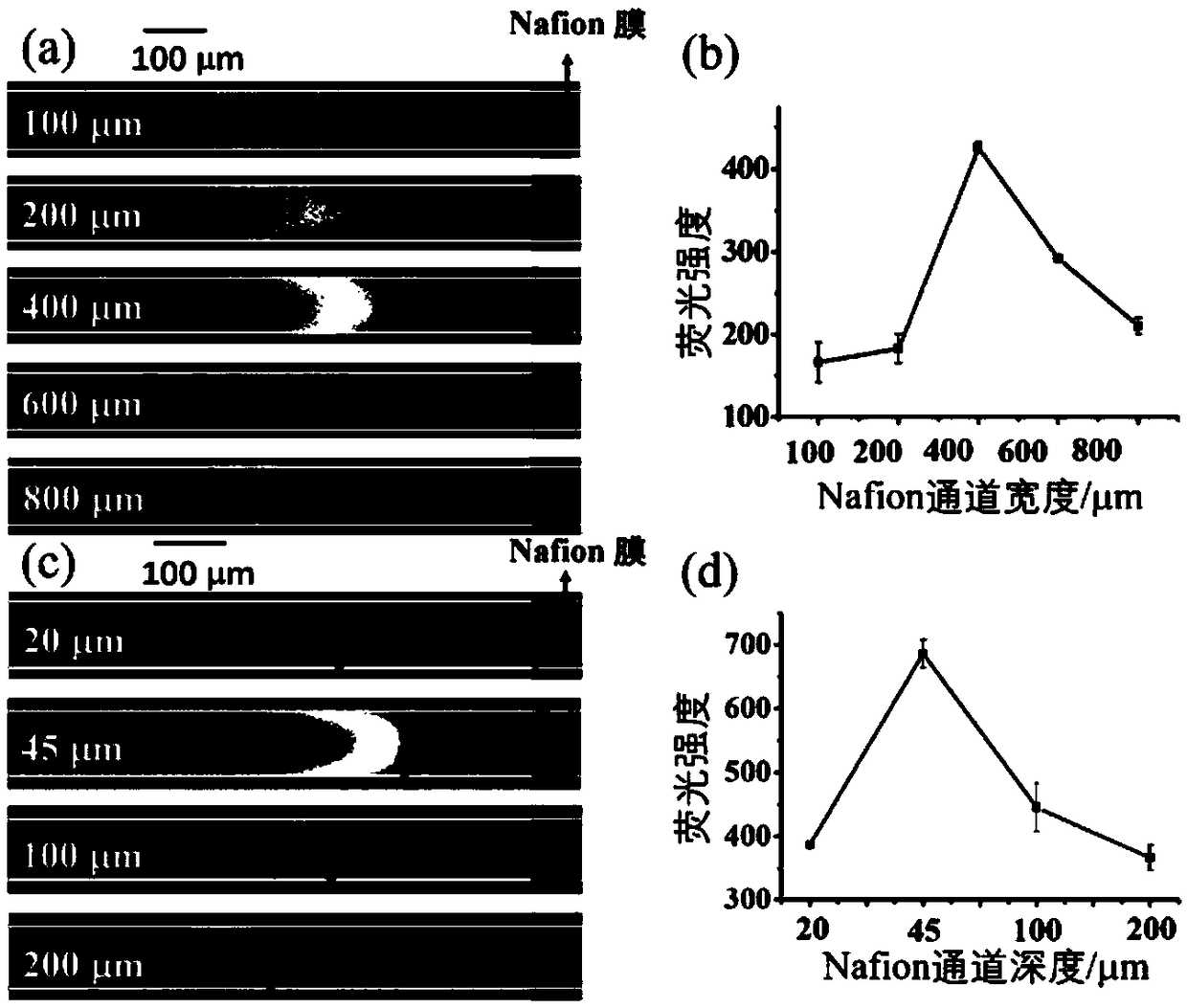
The invention discloses a method for detecting endotoxin. The method comprises the following steps of performing incubation on a to-be-detected sample and a fluorescently-labeled LPS aptamer; then adding reduced graphene oxide and a TBE buffer solution, and performing incubation; adding the incubated sample into a sample inlet of a micro-fluidic chip, applying a voltage between the sample inlet and a sample outlet of the micro-fluidic chip to perform processing, arranging an anode at the sample inlet, and detecting the fluorescence intensity between a Nafion membrane channel and the anode after the voltage processing; and determining the content of LPS in the to-be-detected sample according to the fluorescence intensity and a standard curve. The method has a lowest detection limit of 8 fM,is wide in linear range, high in sensitivity, good in selectivity and relatively strong in anti-interference capability, and can rapidly distinguish gram-positive bacteria, gram-negative bacteria andfungi.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
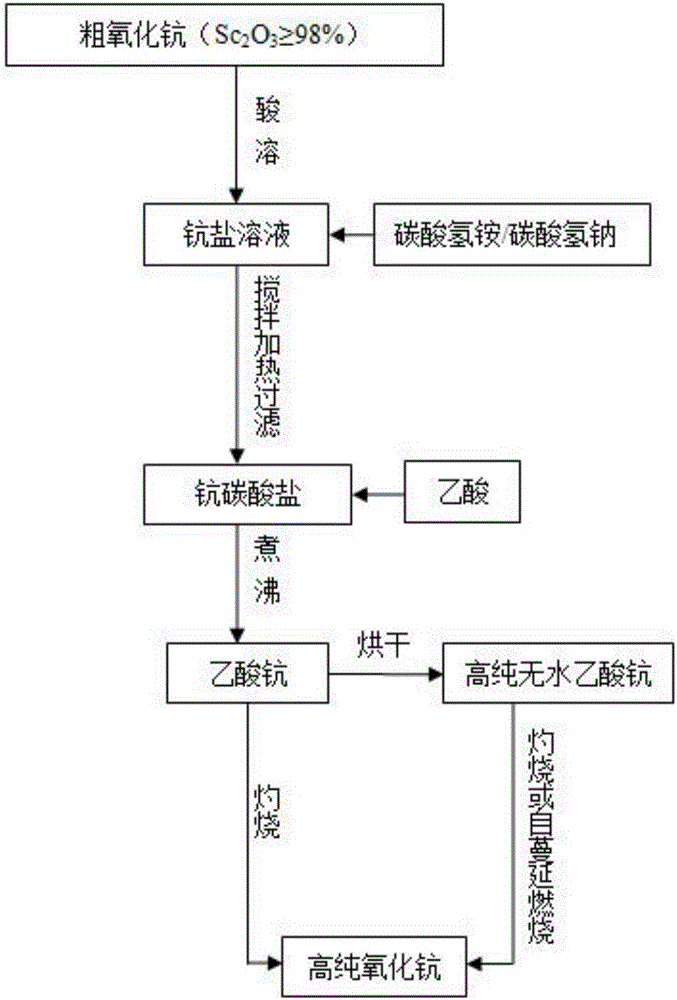
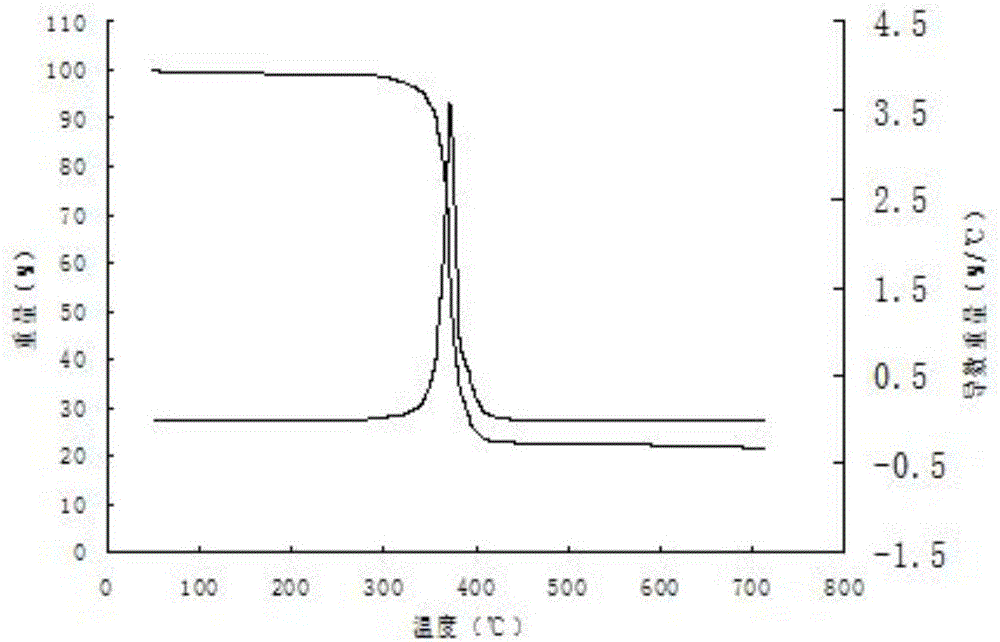
Method for preparing high-purity anhydrous scandium acetate and high-purity scandium oxide
ActiveCN106430278ALarge particlesLoose structureRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesOrganic compound preparationSodium bicarbonateAcetic acid
The invention relates to a method for preparing high-purity anhydrous scandium acetate and high-purity scandium oxide. The method comprises the following steps: (a) adding strong acid into rough scandium oxide, heating to dissolve, and filtering to obtain filtrate I; (2) adding ammonium bicarbonate or sodium bicarbonate into the filtrate I under a stirring condition at a temperature maintained at 0-100 DEG C, stopping the adding when the pH value is 5-8, washing precipitates, and filtering, so as to obtain scandium carbonate precipitates; (c) adding acetic acid into the precipitates for dissolving, and filtering, so as to obtain filtrate II; (d) heating the filtrate II to a constant temperature of 70-100 DEG C, adding glacial acetic acid after crystals are separated, carrying out constant temperature treatment for 5-30 minutes, immediately filtering the crystals, collecting the crystals, and washing with absolute ethanol; (e) drying, so as to obtain high-purity anhydrous scandium acetate, and firing to obtain high-purity scandium oxide; and (f) firing high-purity anhydrous scandium acetate, or carrying out self-propagating combustion in an oxygen introduction condition, so as to obtain high-purity scandium oxide. The method has the advantages that the operation is simple and convenient, the environmental pollution is low, and the like.
Owner:YIYANG HONGYUAN RARE EARTH
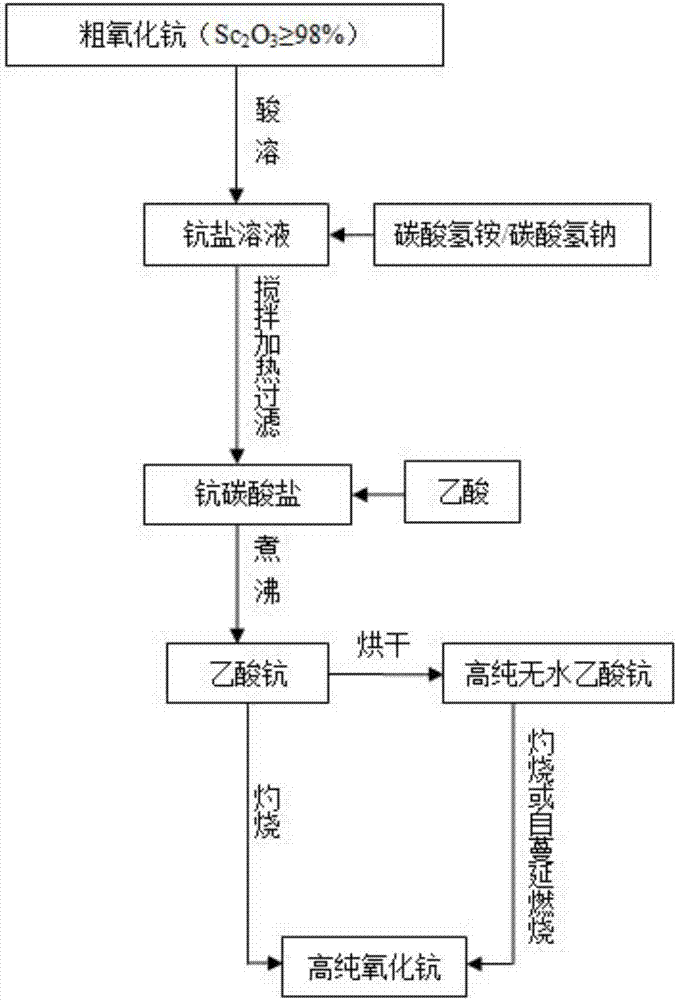
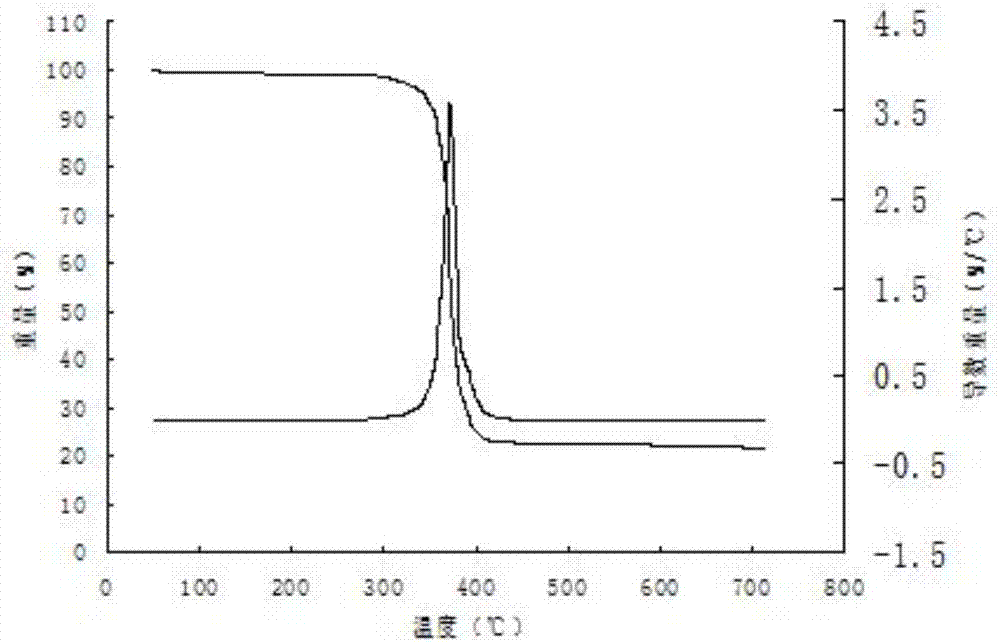
A kind of preparation method of high-purity anhydrous scandium acetate and high-purity scandium oxide
ActiveCN106430278BLarge particlesLoose structureRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesOrganic compound preparationSodium bicarbonateAcetic acid
Owner:YIYANG HONGYUAN RARE EARTH
Method for preparing electronic cigarette liquid through microwave-assisted extraction
InactiveCN105341998ALess reagent consumptionReduce pollutionGas treatmentTobacco treatmentSolventTobacco leaf extract
The invention discloses a method for preparing an electronic cigarette liquid through microwave-assisted extraction. An extraction liquid and mixed tobacco leaves are mixed and irradiated by microwaves, organic phases are merged after filtering and washing operation, an organic solvent is finally removed, and a tobacco leaf extract is obtained, wherein the extraction liquid and the mixed tobacco leaves are mixed in the weight ratio being (1:1)-(5:1); the adopted power is 400-800 W during microwave irradiation; the faint-scent tobacco leaf extract is prepared from Yunnan Yuxi faint-scent tobacco leaves, Yunnan Dali faint-scent tobacco leaves and Yunnan Qujing faint-scent tobacco leaves. By comparison with conventional extraction methods such as a room-temperature extraction method and a heating reflux method, the extraction time is greatly shortened, the use quantity of solvents is reduced, and the extraction efficiency is remarkably improved. Besides, the extract is prepared from mixed tobacco leaf extracts, and different tobacco leaf extracts complement each other in scent, so that the scent and the taste of the electronic cigarette liquid are more close to those of conventional cigarettes.
Owner:立场电子科技发展(上海)有限公司
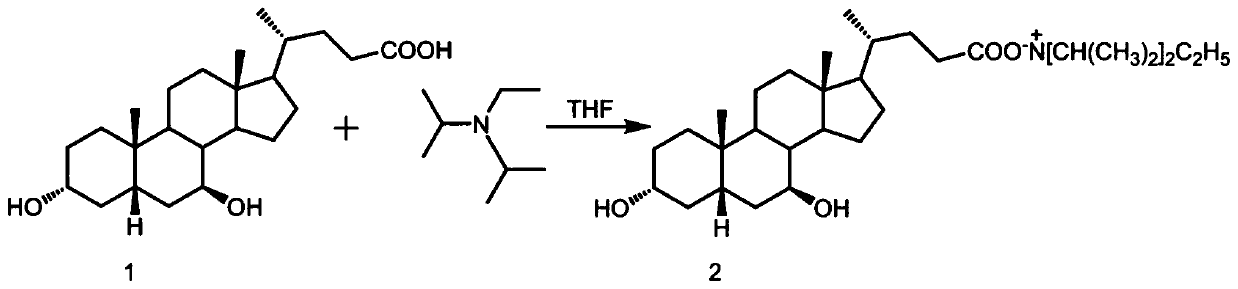
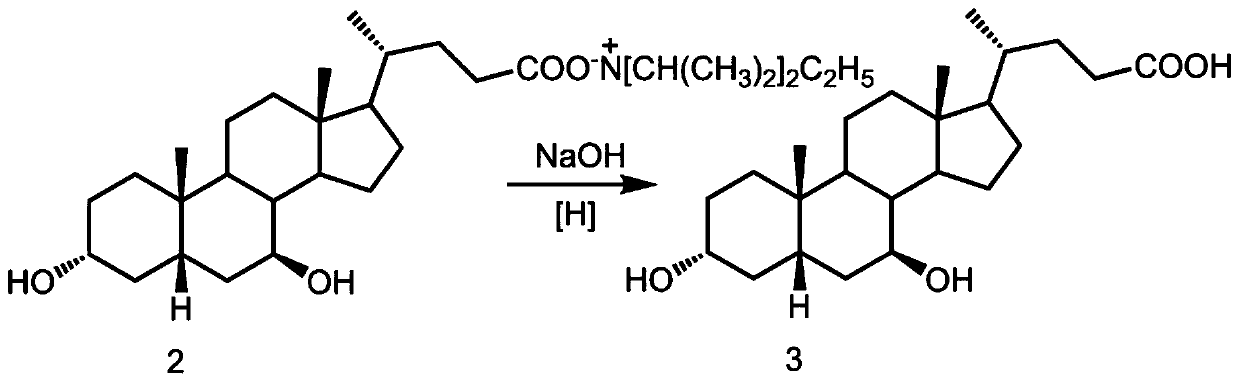
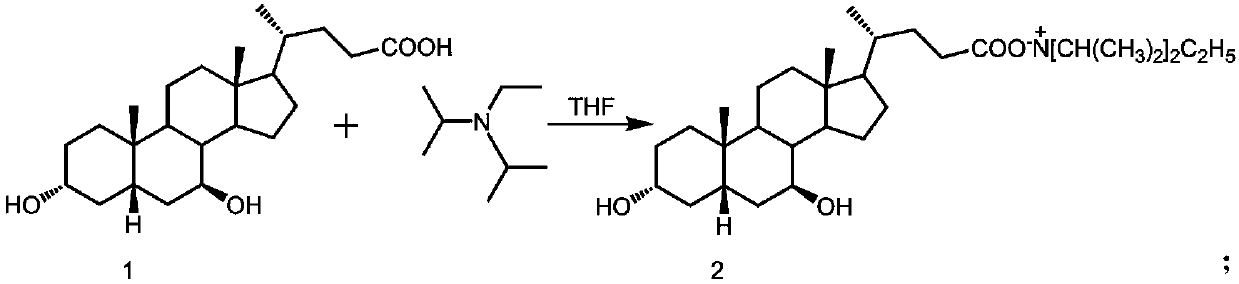
Method for purifying ursodeoxycholic acid
The invention discloses a method for purifying ursodeoxycholic acid. The method comprises: 1) dissolving a ursodeoxycholic acid-containing mixture in tetrahydrofuran, adding diisopropylethylamine, andcarrying out a reaction to prepare a ursodeoxycholic acid diisopropylethylammonium salt-containing solution; 2) cooling the ursodeoxycholic acid diisopropylethylammonium salt-containing solution at 0-5 DEG C to crystallize the solution, and then performing separation to obtain ursodeoxycholic acid diisopropylethyl ammonium salt; and 3) hydrolyzing the ursodeoxycholic acid diisopropylethyl ammonium salt. The method has the advantages of simplicity in operation, low reagent consumption, high selectivity, and high purity of the obtained ursodeoxycholic acid.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Method and device for fixing and assembling DNA and markers
InactiveCN101225446ASimple methodEasy to operateBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsA-DNAElectrochemistry
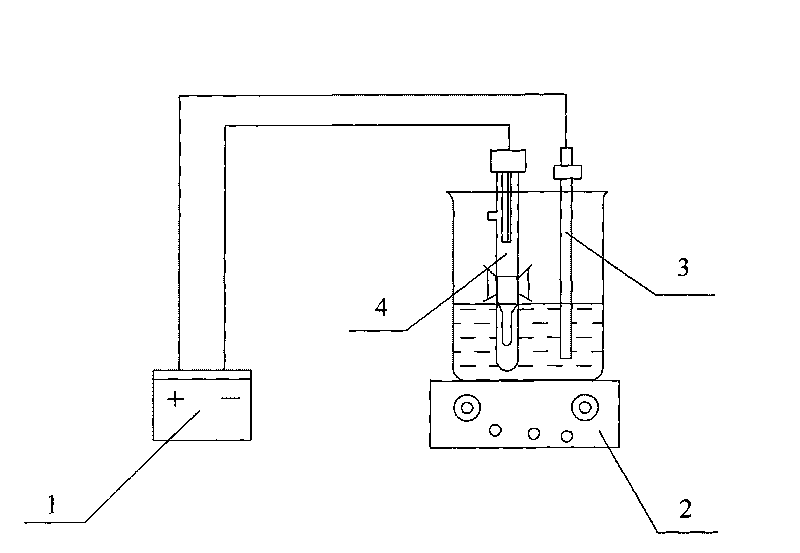
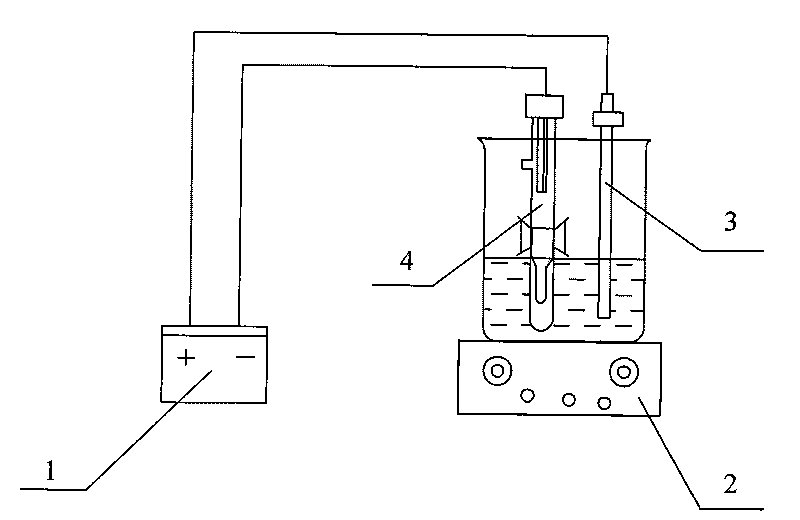
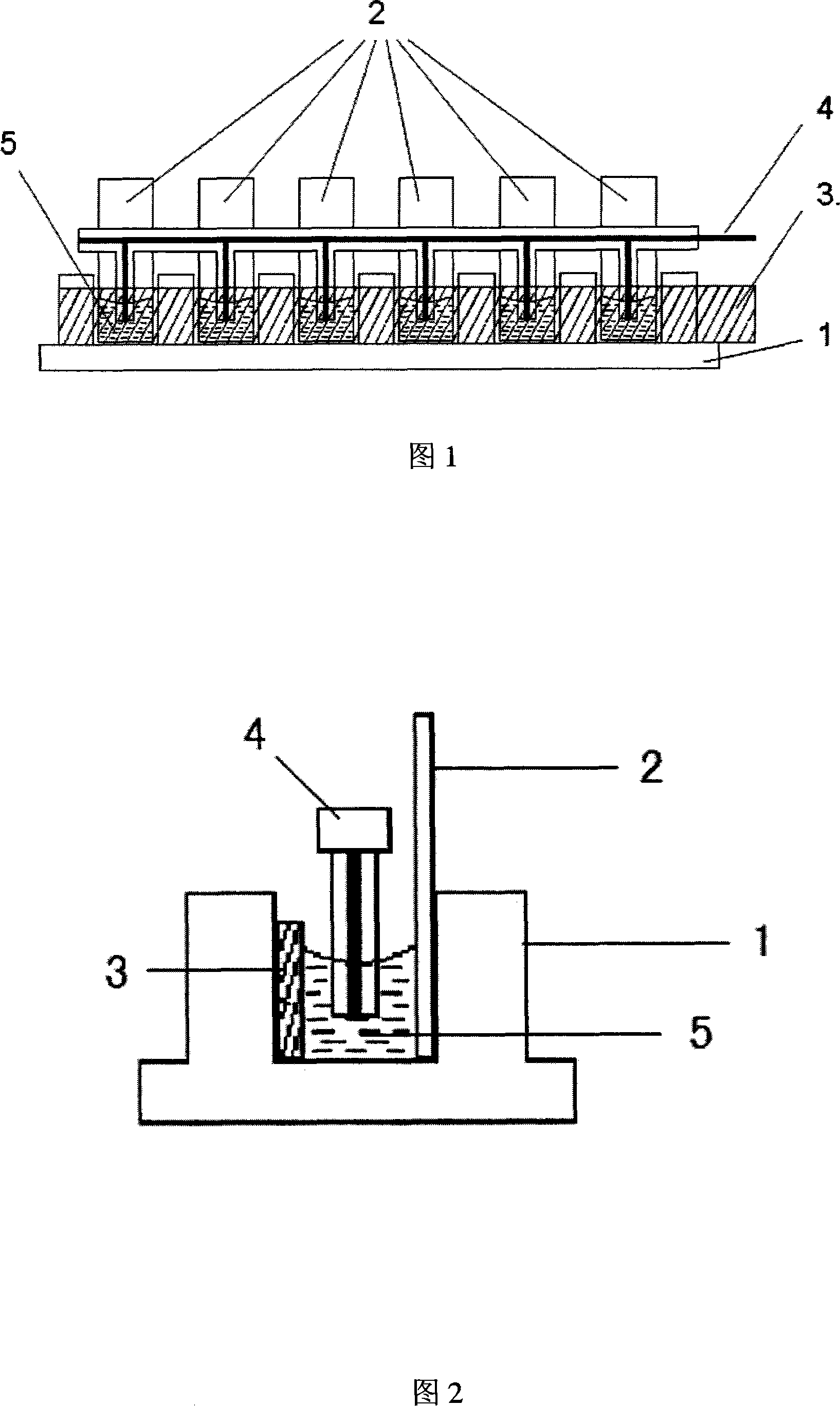
The invention discloses a method for immobilizing and assembling a DNA and a marker, which is characterized in that a testing solution comprising the DNA and the marker is prepared and filled in an electrolytic tank to do a continuous differentiating impulse volt-ampere scanning, completing the electrochemical assembly of the DNA and the marker on a conductive glass surface. The invention simultaneously discloses a multi-channel electrolytic tank to complete the process. The method for immobilizing and assembling a DNA and the marker has the advantages of convenient operation, less reagent consumption, low cost, real-time monitoring for the assembly amount of the DNA and the marker on the ITO surface, and synchronous implementation of assembly.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com