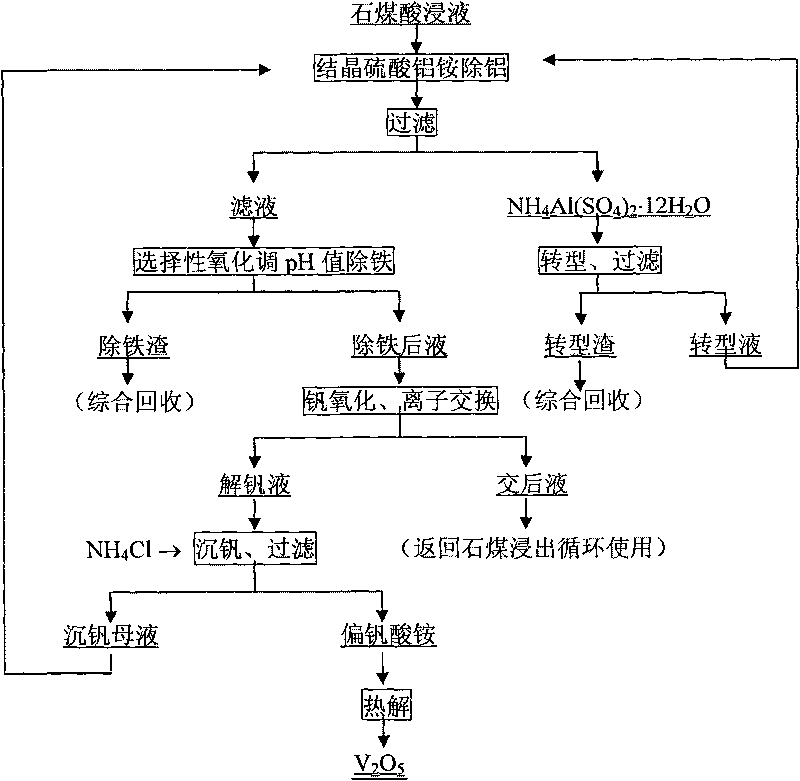
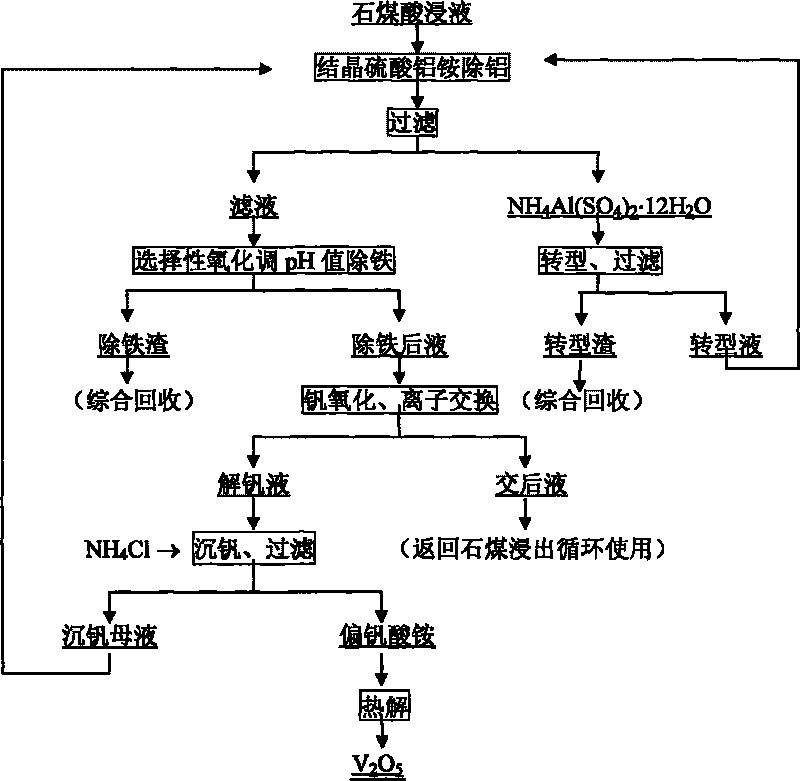
Process for extracting vanadium by acid leaching of stone coal
A stone coal acid and leaching technology, which is applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, can solve the problems of affecting vanadium recovery rate, high production cost, and large reagent consumption, so as to achieve low vanadium loss, good product quality, and low reagent consumption. little effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Vanadium (V 2 o 5 1.06%) stone coal was broken by adding 6% CaO and then roasted at 800°C for 2h. The calcined sand was leached with sulfuric acid solution at room temperature for 6 hours at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:1.2g / ml and filtered to obtain vanadium-containing (V 2 o 5 6.42g / L) of the leaching solution, add ammonia water to adjust the pH value to 0.5, crystallize and separate out aluminum ammonium sulfate NH 4 Al(SO 4 ) 2 12H 2 O crystals, add NaHCO to the solution after crystallization 3 Adjust the pH value to 2.0 to remove iron and get 0.21% V 2 o 5 The iron removal slag is oxidized to 2.0 times of the stoichiometric number of V(V) after the iron removal, and the hydrogen peroxide is oxidized at room temperature for 2 hours, and the vanadium is adsorbed with a strong alkali resin 201×7, and the contact time is 40 minutes. The negative vanadium resin is used 4.0mol / L NH 3 ammonia solution desorption, contact time 60min, with 2.0mol / L H 2 SO 4Dilute...
Embodiment 2
[0025] Vanadium (V 2 o 5 1.17%) stone coal was crushed, added concentrated sulfuric acid and mixed thoroughly, then roasted at 250°C for 2 hours, added the ion-exchanged liquid obtained in Example 1 to the calcined sand at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1: 1.2g / ml, leached at 85°C for 1.0 hour, and filtered to obtain Vanadium (V 2 o 5 7.23g / L) leachate, the leachate is NH 4 Al(SO 4 ) 2 12H 2 Adding 2.0 times the stoichiometric number of O crystal precipitation (NH 4 ) SO 4 Aluminum removal, adding CaCO to liquid after aluminum removal 3 Adjust the pH value to 1.9, according to the Fe in the solution 2+ Oxidized to Fe 3+ Add V (V) to 1.0 times the stoichiometric number, remove iron at 40°C for 1.5 hours and filter, the filter residue contains 0.05% V 2 o 5 , the filtrate is oxidized to 1.2 times the stoichiometric number of V (V) by low-valent vanadium, and then oxidized with sodium chlorate at 70°C for 1.5h. mol / L NaOH solution desorption, contact time 40min, then use...
Embodiment 3
[0027] Vanadium (V 2 o 5 0.83%) stone coal is crushed and presses solid-liquid ratio 1: 1.2g / ml adds the liquid after the exchange that embodiment 2 obtains, then adds concentrated sulfuric acid oxygen pressure leaching filtration and obtains vanadium-containing (V 2 o 5 6.62g / L) leachate, the leachate is NH 4 Al(SO 4 ) 2 12H 2 1.5 times of the stoichiometric number of O crystals are separated out, add the ammonium-containing liquid after conversion that embodiment 2 obtains, and add N 4 HCO 3 Adjust the pH value to 2.5 to crystallize NH 4 Al(SO 4 ) 2 12H 2 O crystal, according to Fe in liquid after crystallization 2+ Oxidized to Fe 3+ Add hydrogen peroxide to 1.1 times the stoichiometric number, stir at room temperature for 1.0 h to remove iron, and get 0.13% V 2 o 5 Iron removal slag, after iron removal, the liquid is oxidized to 1.5 times of V (V) stoichiometric number of ammonium persulfate at 85°C for 0.5h, and the vanadium is adsorbed with strong base anion...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com