Method and device for fixing and assembling DNA and markers
An assembly method and a technology of markers, which are applied in the fields of analysis and detection and material science, can solve the problems of cumbersome operation, large background signal influence, and unfavorable preparation of DNA probes, etc., and achieve the effects of less reagent consumption, simple method, and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
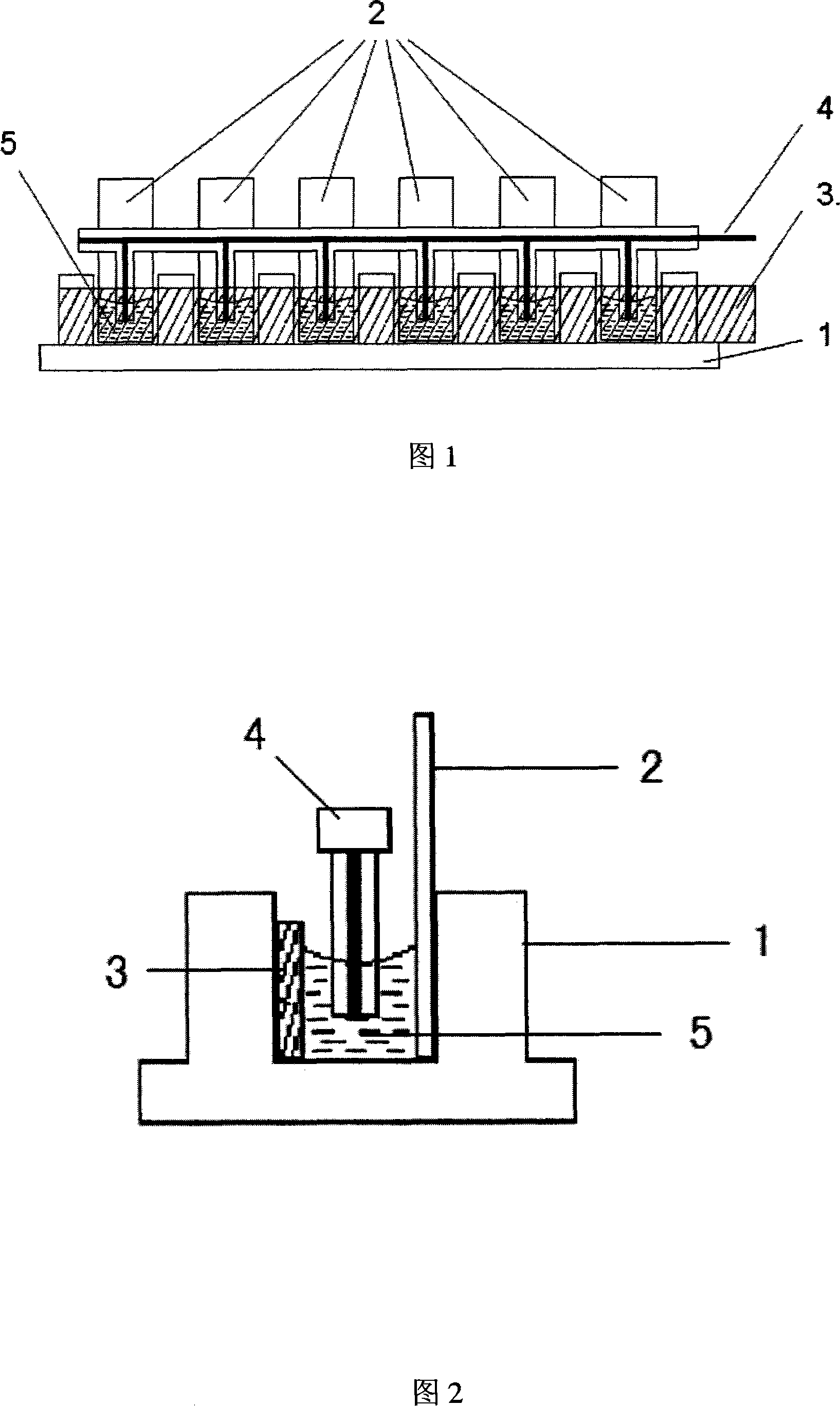
[0035] The assembly of embodiment 1 single-stranded DNA and marker on ITO conductive glass
[0036] The selected single-stranded DNA sequence structure is AACCAACACA, and the concentration is 6 μmol L -1 . The label is ruthenium complex [Ru(bpy) 2 tatp]Cl 2 , the concentration is 0.2mmolL -1 . Prepare the mixed solution of the two, take 0.4mL and add it to a chamber of the multi-channel electrolytic cell, and perform continuous differential pulse voltammetry scanning in the range of 0.2V to 1.5V. After scanning 21 times, record the differential pulse voltammetry spectrum as shown in Figure 4. It can be seen from the figure that as the number of differential pulse voltammetry scans increases, the assembly peak current gradually increases, and the assembly amount of single-stranded DNA sequences and markers on the ITO surface can be controlled by controlling the number of differential pulse voltammetry scans.
Embodiment 2
[0037] Example 2: Assembly of double-stranded DNA and markers on ITO conductive glass
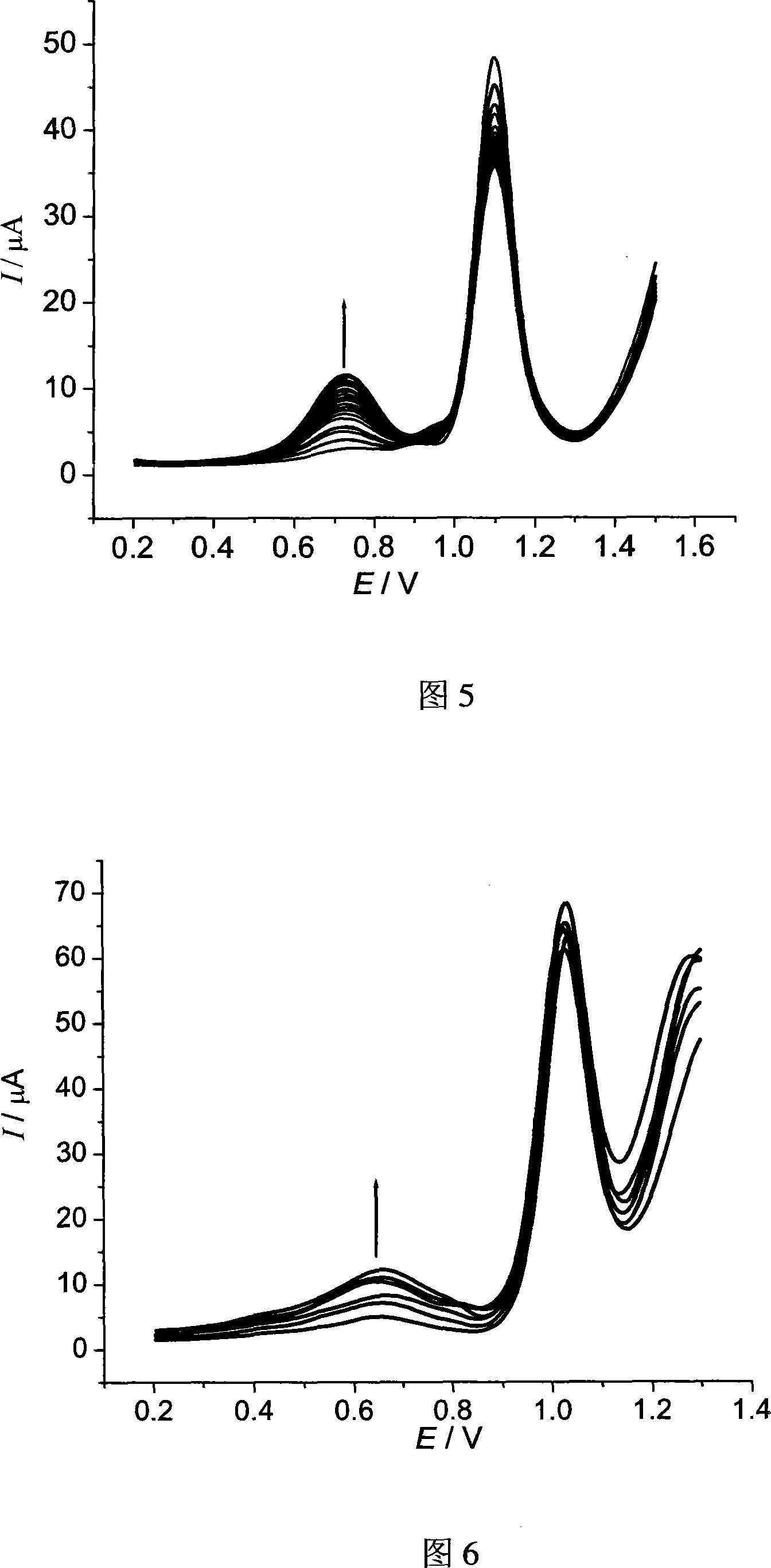
[0038] The selected double-stranded DNA is calf thymus DNA, the concentration is 0.2mmolL -1 . The label is ruthenium complex [Ru(bpy) 2 tatp]Cl 2 , the concentration is 0.2mmolL -1 . Prepare the mixed solution of the two, take 0.4mL and add it to a chamber of the multi-channel electrolytic cell, and perform continuous differential pulse voltammetry scanning in the range of 0.2V to 1.5V. After scanning 21 times, record its differential pulse voltammetry spectrum, see the attached picture 5. It can be seen from the figure that as the number of differential pulse voltammetry scans increases, the assembly peak current gradually increases, and the assembly amount of single-stranded DNA sequences and markers on the ITO surface can be controlled by controlling the number of differential pulse voltammetry scans.
Embodiment 3
[0039] Example 3: Multi-channel assembly of DNA and markers on ITO conductive glass
[0040] The selected double-stranded DNA is calf thymus DNA, and the concentrations are 0, 6, 12, 18, 24, 30 μmol L -1 . The label is ruthenium complex [Ru(bpy) 2 tatp]Cl 2 , the concentration was fixed at 0.2mmol L -1 . Prepare six kinds of mixed solutions of the two respectively, take 0.4mL each and add them to the six chambers of the multi-channel electrolytic cell, conduct continuous differential pulse voltammetry scanning in the range of 0.2V to 1.3V, and record the differential pulse voltage after scanning 21 times For the voltammogram, see Figure 6. It can be seen from the figure that the assembly peak current increases with the increase of DNA concentration, and this method can be used to quantitatively measure the concentration of DNA.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com