Production technology of fat-reducing Puer tea
A preparation process and slimming tea technology, which is applied in tea, tea extraction, food science, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing starch decomposition to sugar conversion and lowering blood lipids
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
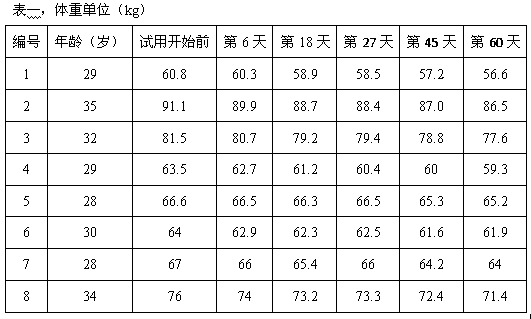
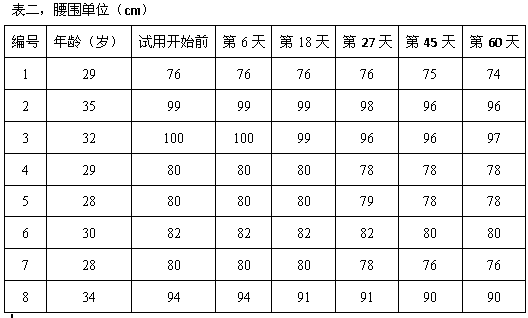
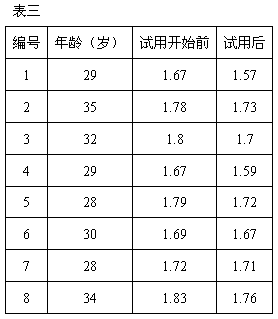
[0023] 1) Softening water extraction: Soften cooked Puer tea by steaming at 80°C for 20 minutes, add the softened tea leaves to 40°C hot water, the amount of hot water added is 12 times the weight of the tea leaves, and then the hot water circulates for a period of time for 40min.
[0024] 2) Filtration: After the liquid in step 1) is pre-filtered, it is filtered again through an ultrafiltration membrane to obtain a filtrate.
[0025] 3) Extraction and enzymatic hydrolysis: send the filtrate cooled to 10°C into a rotary distillation tower for extraction, and add immobilized tannase at 1% of the filtrate mass during extraction.
[0026] 4) Add inhibitory protein: add white kidney bean α-amylase inhibitory protein to the tea liquid in step 3) according to 10% of the weight of the filtrate, and stir to completely dissolve the added white kidney bean α-amylase inhibitory protein.
[0027] 5) Concentration: use reverse osmosis membrane to concentrate the additive liquid in step 4)...
Embodiment 2
[0030] 1) Softening water extraction: Soften raw Puer tea by steaming at 110°C for 25 minutes, add the softened tea leaves to 42°C hot water, the amount of hot water added is 13 times the weight of the tea leaves, and then the hot water circulates for a period of time for 50min.
[0031] 2) Filtration: After the liquid in step 1) is pre-filtered, it is filtered again through an ultrafiltration membrane to obtain a filtrate.
[0032] 3) Extraction and enzymatic hydrolysis: send the filtrate cooled to 20°C into a rotary distillation tower for extraction, and add immobilized tannase with a mass of 1.2% of the filtrate during extraction.
[0033] 4) Add inhibitory protein: Add white kidney bean α-amylase inhibitory protein to the tea liquid in step 3) according to 15% of the weight of the filtrate, and stir to completely dissolve the added white kidney bean α-amylase inhibitory protein.
[0034] 5) Concentration: use reverse osmosis membrane to concentrate the additive liquid in ...
Embodiment 3
[0037] 1) Softening water extraction: Soften ripe Puer tea or raw Puer tea by steaming at 120°C for 35 minutes, add the softened tea leaves to 45°C hot water, the amount of hot water added is 15 times the weight of the tea leaves, and then heat Water circulation, time is 60min.
[0038] 2) Filtration: After the liquid in step 1) is pre-filtered, it is filtered again through an ultrafiltration membrane to obtain a filtrate.
[0039] 3) Extraction and enzymatic hydrolysis: send the filtrate cooled to 25°C into a rotary distillation tower for extraction, and add immobilized tannase with a mass of 1.5% of the filtrate during extraction.
[0040] 4) Add inhibitory protein: add white kidney bean α-amylase inhibitory protein to the tea liquid in step 3) according to 20% of the weight of the filtrate, and stir to completely dissolve the added white kidney bean α-amylase inhibitory protein.
[0041] 5) Concentration: use reverse osmosis membrane to concentrate the additive liquid in s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com