Method for starting livestock and poultry manure compost secondary fermentation by utilizing oyster mushrooms
A livestock and poultry manure, secondary fermentation technology, applied in the application, fertilization device, organic fertilizer and other directions, can solve problems such as poor adaptability of high nitrogen substrates, and achieve the effect of low environmental safety risk
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Embodiment 1: start-up test of inoculating Pleurotus ostreatus mycelium plaque
[0029] Get 10g of high-temperature sterilized chicken manure primary compost product (equivalent to the fermentation product in the high-temperature stage, with a moisture content of 50%), and spread 1g of high-temperature sterilized corn stalk debris on the primary compost product to form corn stalk debris Upper and lower layers of compost; cut 0.5cm × 0.5cm Pleurotus ostreatus mycelium plaques from the solid PDB medium (the blank control does not add Pleurotus ostreatus mycelium plaques) and add them to the middle of the corn stalk debris, Then 50 μL of sterile water was added around the mycelium plaque, and the system was fermented at a constant temperature of 25° C. for 15 days. The one without Pleurotus ostreatus mycelium plaque was used as the blank control. Determination of fulvic acid content to judge the effect of secondary fermentation.
[0030] The results showed that the conte...
Embodiment 2
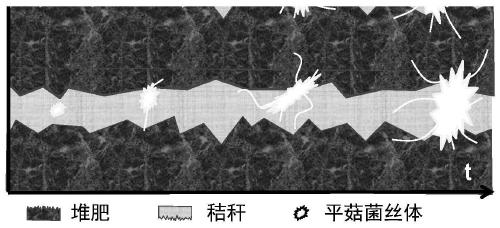
[0031] Embodiment 2: the growth form of the stalk of pre-inoculated Pleurotus ostreatus during interlayer fermentation
[0032] Get 2.5g chicken manure primary compost product (about 1cm thick, moisture content 50%), on the primary compost product, tile the corn stalk debris (about 0.5cm thick) of 0.5g pre-inoculation oyster mushroom, on the corn stalk debris Spread 2.5g of chicken manure primary compost products (about 1cm thick) on the top to form a sandwich pattern with corn stalk debris in the middle and compost on the top and bottom ( figure 1 ), fermented at a constant temperature of 25°C for 15 days. Observe the growth status of the mycelium of Pleurotus ostreatus in the straw layer. The corn stalk debris of the pre-inoculated Pleurotus ostreatus is to inoculate 1 mL of Pleurotus ostreatus spherical mycelium particles into 10 g of corn stalk crumbs under aseptic conditions, and pre-cultivate at 25°C for 10 days to obtain the pre-inoculated Pleurotus ostreatus of corn ...
Embodiment 3
[0034] Example 3: Comparison of different inoculation patterns (mixing, layering up and down, sandwiching)
[0035] (1) Hybrid mode:
[0036] Take 5g of chicken manure as a primary compost product (with a moisture content of 50%), add 0.5g of corn stalk debris, and mix evenly. Take 1.5mL of oyster mushroom spherical mycelium particles and evenly add them to the compost, and ferment at a constant temperature of 25°C for 15 days.
[0037] (2) Upper and lower layer mode:
[0038] Take 5g of chicken manure primary composting product (moisture content 50%), spread 0.5g of corn stalk debris on the primary composting product to form upper and lower layers with corn stalk debris on top and compost on the bottom, take 1.5mL oyster mushroom spherical The mycelium particles are evenly added to the corn stalk debris, and fermented at a constant temperature of 25° C. for 15 days.
[0039] (3) Mezzanine mode
[0040] Take 2.5g chicken manure primary compost product (moisture content 50%)...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com