Heat supply system thermal delay time identification method based on Pearson correlation coefficient and moving average method
A technology of moving average method and correlation coefficient, which is applied in the field of thermal delay time analysis and identification, can solve problems such as poor data quality, low efficiency, and different thermal response times, and achieve the effect of reducing influence and error
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
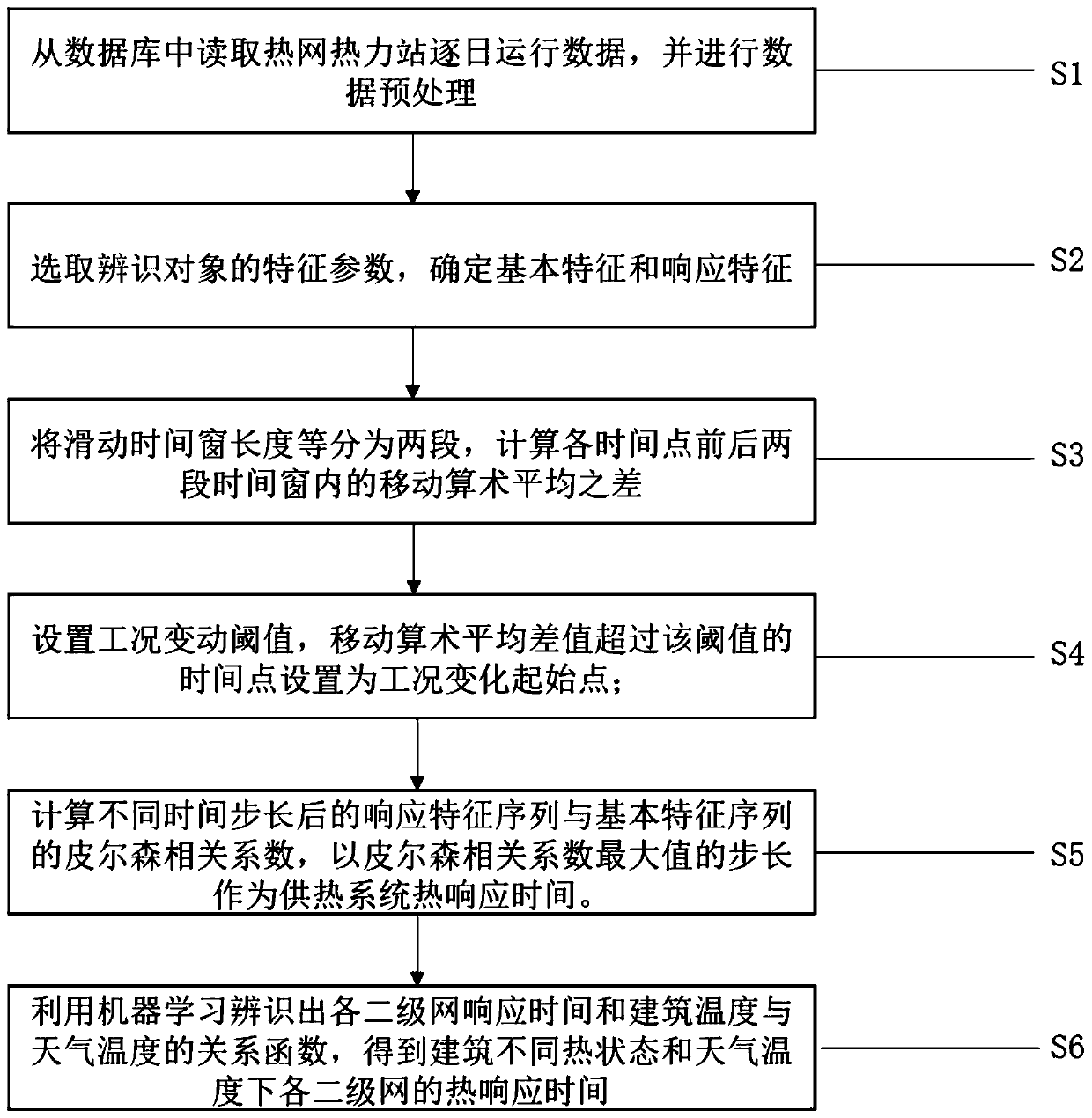
[0048] figure 1 It is a flow chart of the method for identifying the thermal delay time of the heating system based on the Pearson correlation coefficient and the moving average method involved in the present invention.
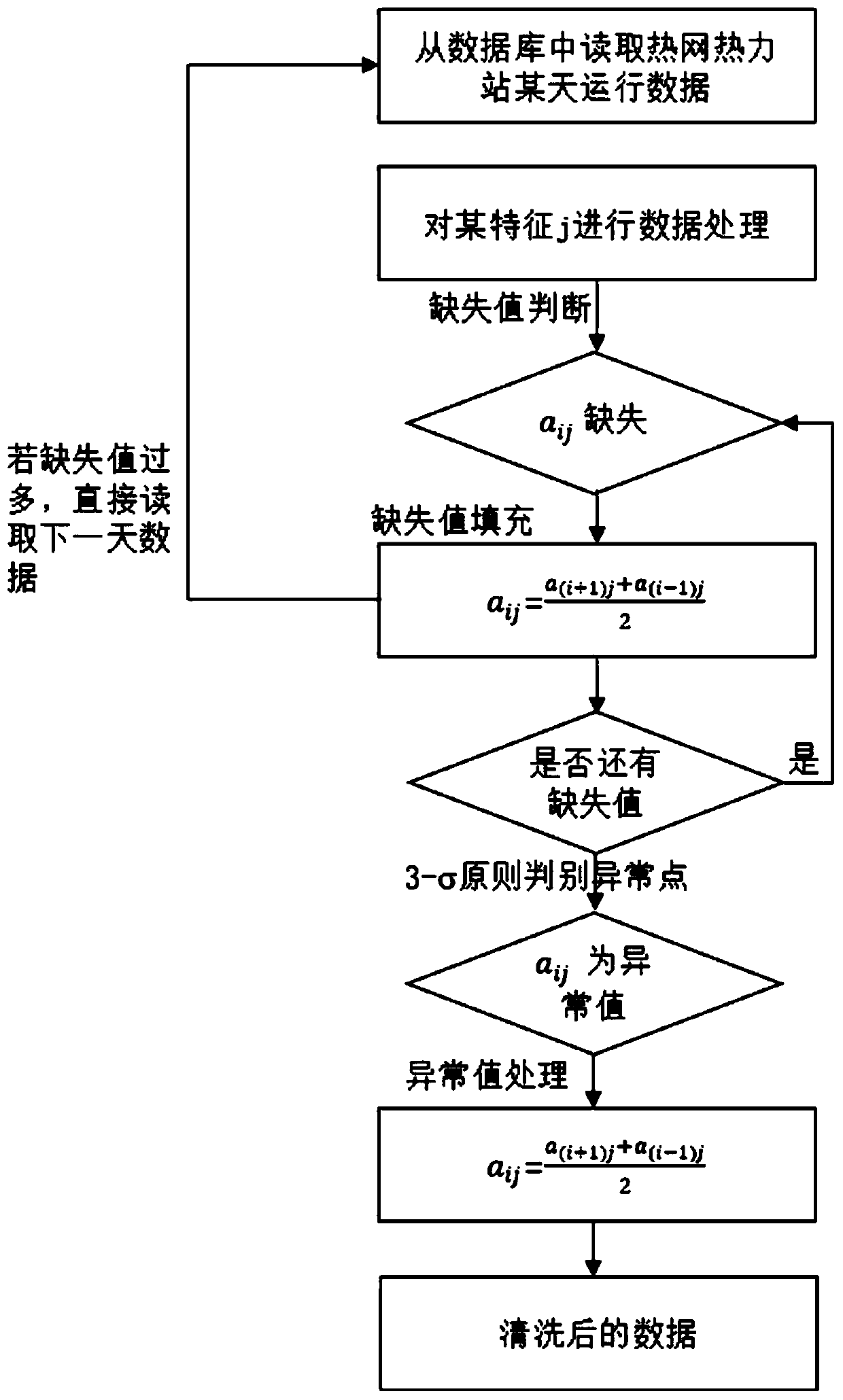
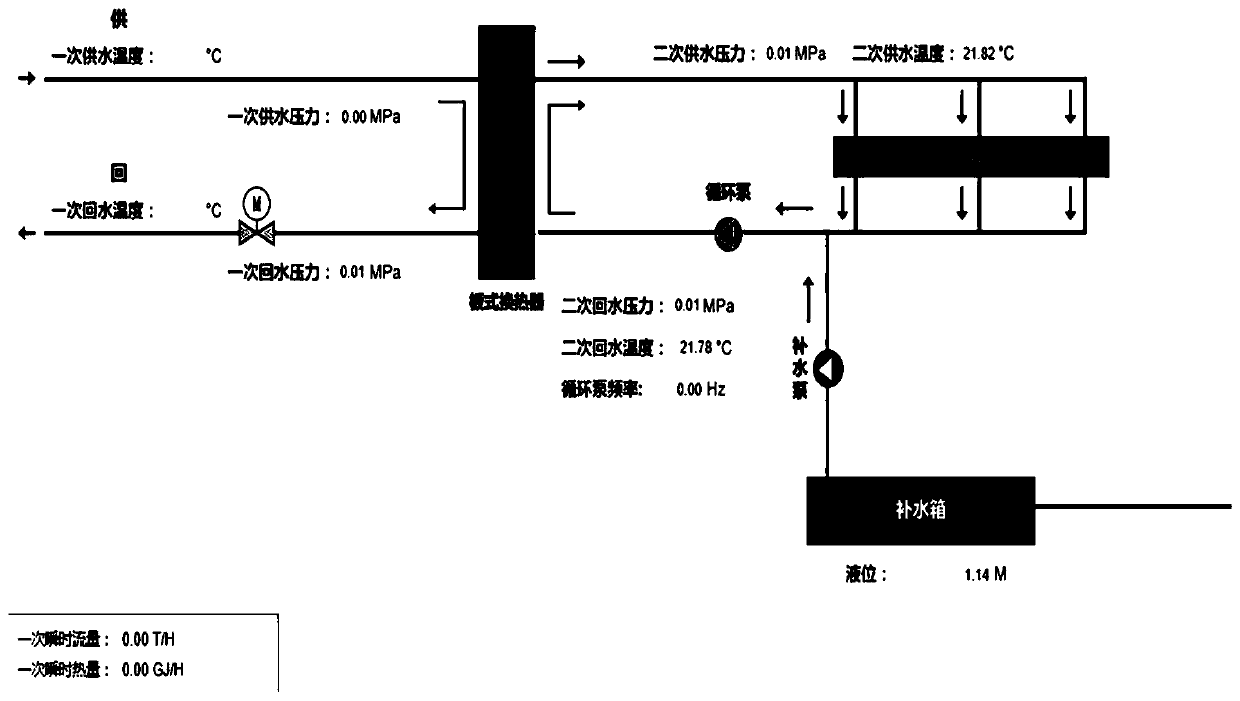
[0049] Such as figure 1 As shown, this embodiment provides a method for identifying thermal delay time of a heating system based on Pearson correlation coefficient and moving average method, including: step S1, reading the daily operation data of the thermal station of the heating network from the database, and performing Data preprocessing; Step S2: According to expert knowledge, select the characteristic parameters of the identification object to determine the basic characteristics and response characteristics; Step S3: Divide the length of the sliding time window into two equal parts, and calculate the basic feature movement in the two time windows before and after Arithmetic mean difference, to obtain the time series of moving arithmetic mean difference;...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com