Quenching strengthening process of thin blade cutting edge
A thin blade and cutting edge technology, applied in the field of heat treatment, can solve the problems of reduced sharpness and wear resistance, low value-added application value, and reduced edge hardness, etc., to achieve sharpness and wear resistance, and not easy to break Knives and jumpers, performance-enhancing effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
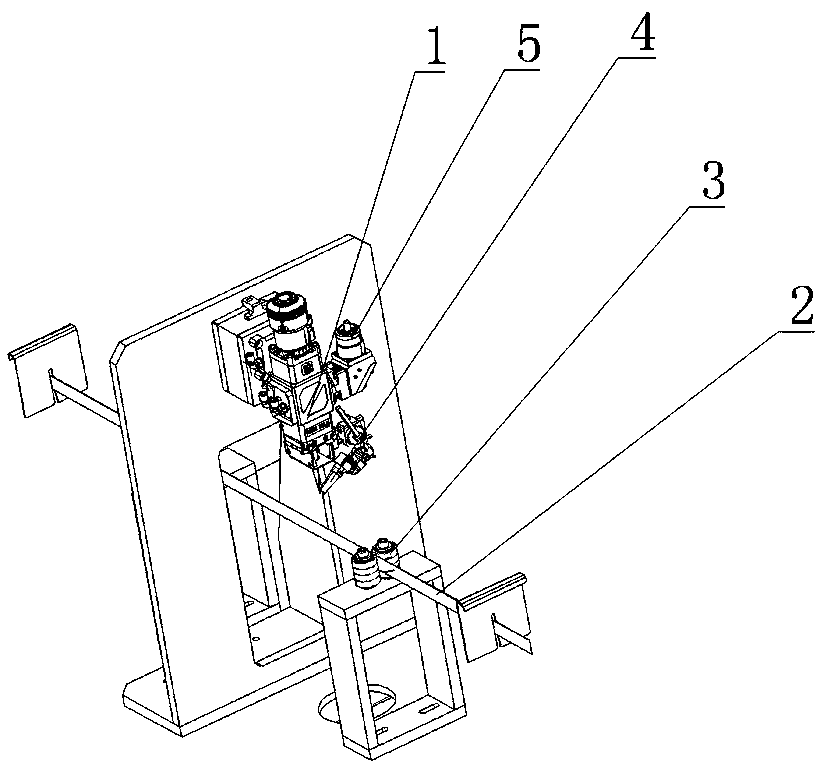
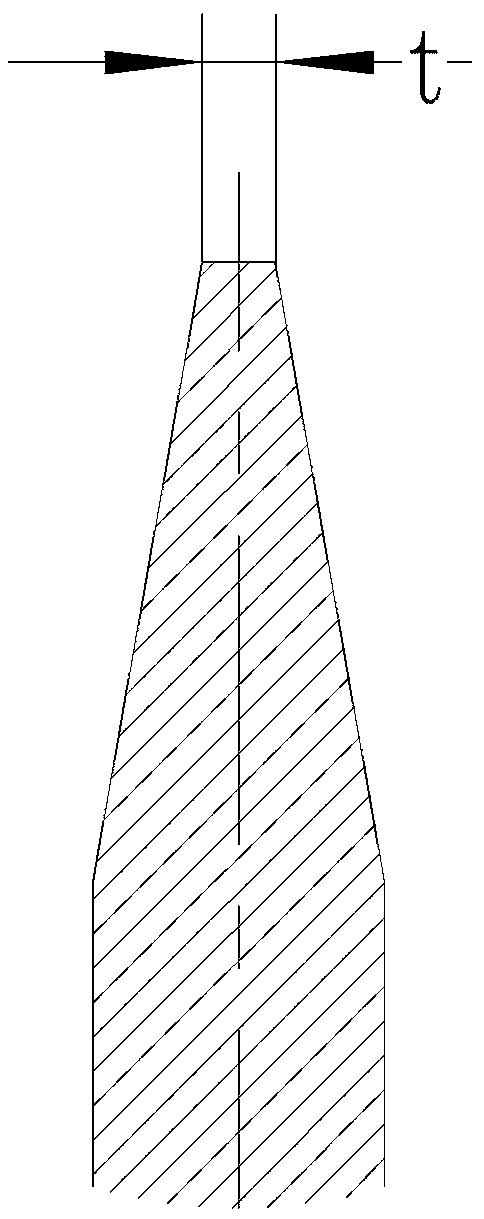
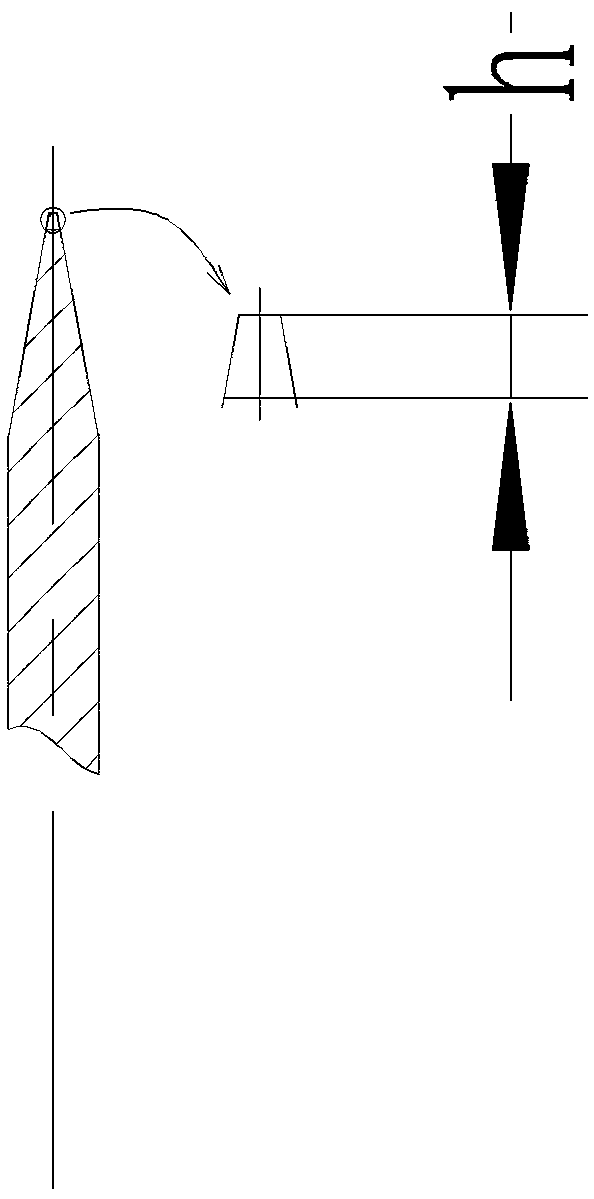
[0027] The quenching and strengthening process of the thin blade edge has the following steps: the thin blade 2 is tempered after overall quenching using the traditional quenching process; the traditional quenching process refers to the high-frequency quenching process or mesh belt furnace quenching The overall quenching process; the thin blade 2 after overall quenching is roughly ground and edged; the thin blade 2 is moved at a high speed, and its relative moving speed is 100-400mm / s; the high power density laser spot is irradiated on the cutting edge 5 , its power density ≥ 150W / mm 2, so that the cutting edge forms a laser quenching layer; among them, the power of laser 1 is a continuous fiber laser or a continuous semiconductor laser with a medium and small power of 500-2000W, which has lower quenching energy consumption and lower maintenance costs than pulse lasers, and is more conducive to application in large Workpieces processed in batches. Laser quenching is originall...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com