Method for regulating and controlling alite crystal form in Portland cement clinker through gas-solid reaction
A Portland cement, gas-solid reaction technology, applied in the field of building materials, can solve the problems of low early strength of cement, high clinker calcination temperature, influence on the structure of cement concrete, etc., and achieves the effect of high conversion rate and improved performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0059] (1) Portland cement clinker is crushed into particles of about 5 mm to obtain Portland cement clinker particle material;
[0060] (2) Weigh 3 parts of the Portland cement clinker particle material that step (1) obtains, every part 60g, put into respectively in the platinum crucible, be placed in the tube furnace that diameter is 80mm then, with 300ml / min flow into SO 2 Mixed gas with air, where SO 2 The volume concentration is 7%; then the temperature is raised at a rate of 5-10°C per minute, and when the temperature rises to 600°C, it is kept for 30 minutes;
[0061] (3) After the reaction is completed, the temperature is controlled by a program, and the temperature is lowered to room temperature at a rate of 5-10°C / min, and the sample A1 is taken out, ground and reserved for testing.
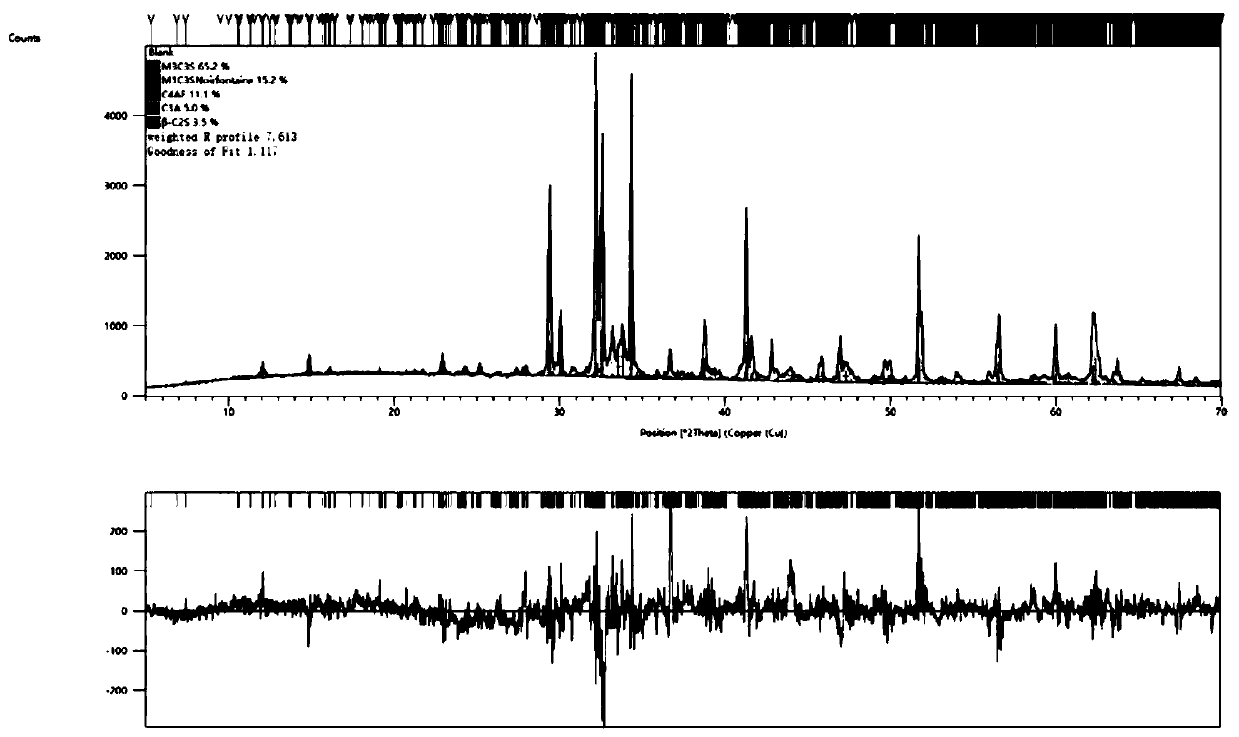
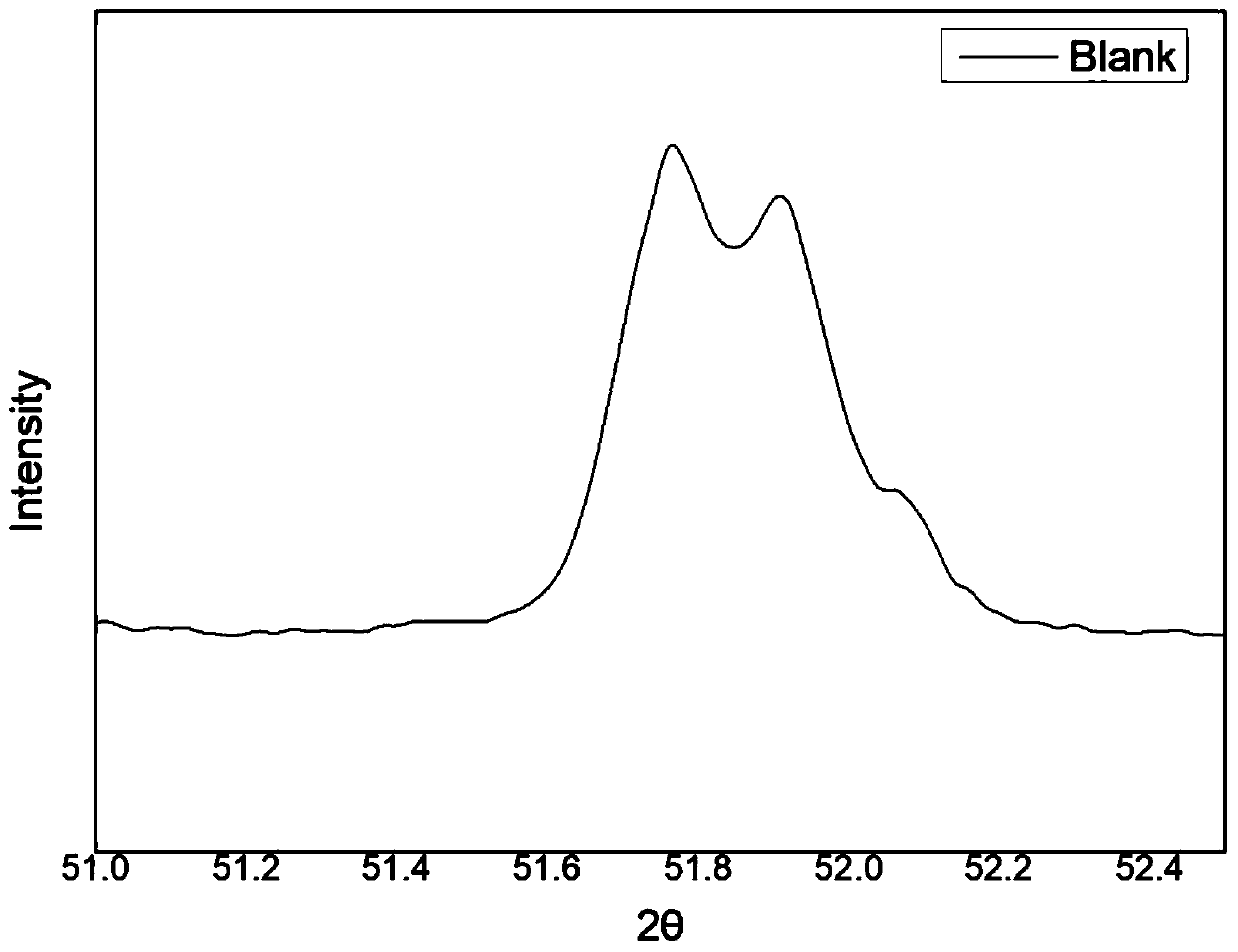
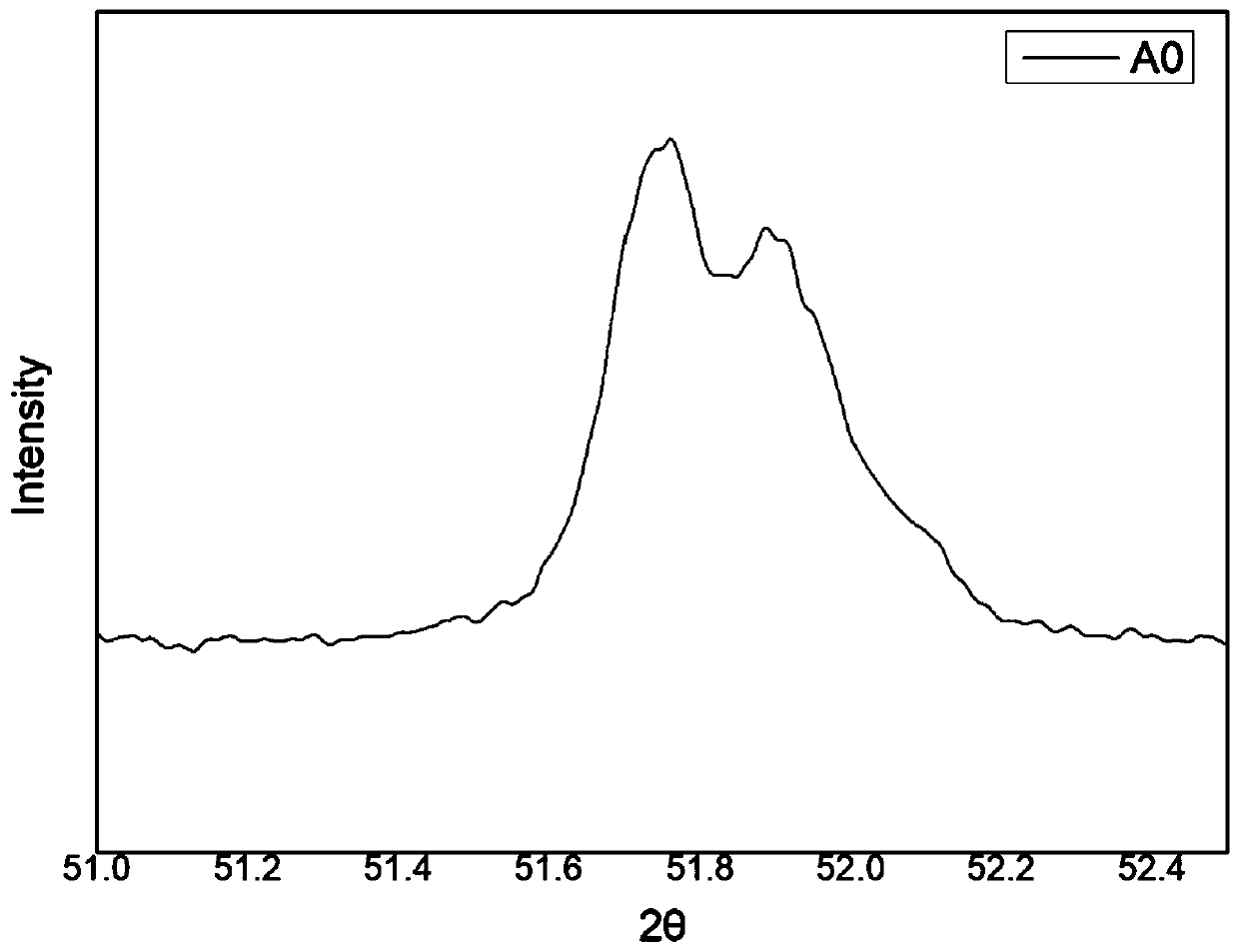
[0062] Under the same conditions, the Portland cement clinker particle material was subjected to heat treatment without atmosphere to obtain the control sample A0.
[0063] figure ...
Embodiment 2
[0072] (1) Portland cement clinker is crushed into particles of about 5 mm to obtain Portland cement clinker particle material;
[0073] (2) Weigh 3 parts of the Portland cement clinker particle material that step (1) obtains, every part 60g, put into respectively in the platinum crucible, be placed in the tube furnace that diameter is 80mm then, with 300ml / min flow into SO 2 Mixed gas with air, where SO 2 The volume concentration is 7%; then the temperature is raised at a rate of 5-10°C per minute, and when the temperature rises to 800°C, it is kept for 30 minutes;
[0074] (3) After the reaction is completed, the temperature is controlled by a program, and the temperature is lowered to room temperature at a rate of 5-10°C / min, and the sample B1 is taken out, ground and reserved for testing.
[0075] Under the same conditions, the Portland cement clinker particle material was subjected to heat treatment without an atmosphere to obtain a control sample B0.
[0076] Figure...
Embodiment 3
[0084] According to the same preparation steps as in Example 1, the cement clinker was kept at 750°C, 800°C, 850°C, 900°C, 950°C, 1000°C, 1050°C, 1100°C, 1150°C, and 1200°C for 30 minutes.
[0085] The XRD patterns of the obtained samples were obtained by X-ray powder diffraction, and the quantitative calculation was performed using Highscore Plus software. Finally plotted as Figure 7 Trend plot of mineral content versus treatment temperature is shown.
[0086] Such as Figure 7 As shown, it can be found that before 1100 °C, with the increase of temperature, the content of M3-alite decreases continuously, and at the same time, the content of M1-alite and C 2 The content of S has increased. But when the temperature exceeds 1100°C, the content of M1-alite shows an inflection point and begins to decrease, while the content of C 2 The S content has been increasing.
[0087] From this we can see that in SO 2 Under the atmosphere, treatment at a temperature below 1100 °C can ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com