Carrier assembly carrying gene element combination, recipient cell library, preparation and screening methods and application
A technology of genetic elements and receptor cells, applied in the fields of biomedical engineering technology and synthetic biology, can solve problems such as unfavorable gene circuit design, low activation precision, and changes in the screening direction of CAR cell libraries
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0123] Example 1. Fully synthetic murine synNotch receptor cell library
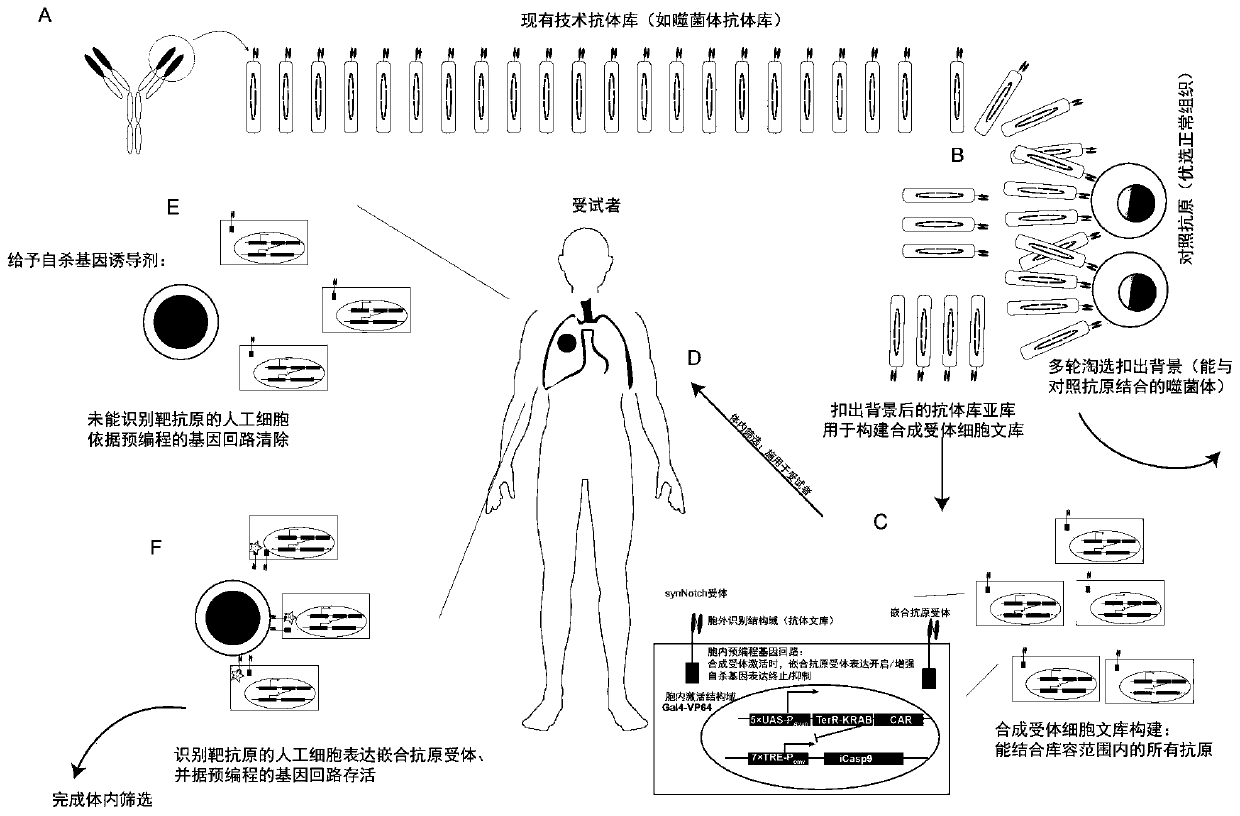
[0124] For the construction and screening process of the library, see figure 1 :
[0125] (A) Construction of phage antibody library: First, a fully synthetic mouse phage single-chain antibody library was established using a total synthesis method. The method for antibody library preparation is well known to those of ordinary skill in the art, and the method for establishing a fully synthetic mouse phage single-chain antibody library is the same as in the literature [Geuijen C et al..European Journal of Cancer, 2005,41(1):178- 187; Noronha E J, et al. Journal of Immunology, 1998, 161(6):2968-2976.]. After the evaluation of the library capacity, the library capacity of the established fully synthetic mouse phage single-chain antibody library is 1×10 9 . The method of library capacity assessment is the same as that in the literature [Ridgway J B B, et al. Cancer Research, 2013, 59(11): 2718-2723].
[...
Embodiment 2
[0134] Example 2. Fully synthetic murine synNotch receptor cell library for breast cancer
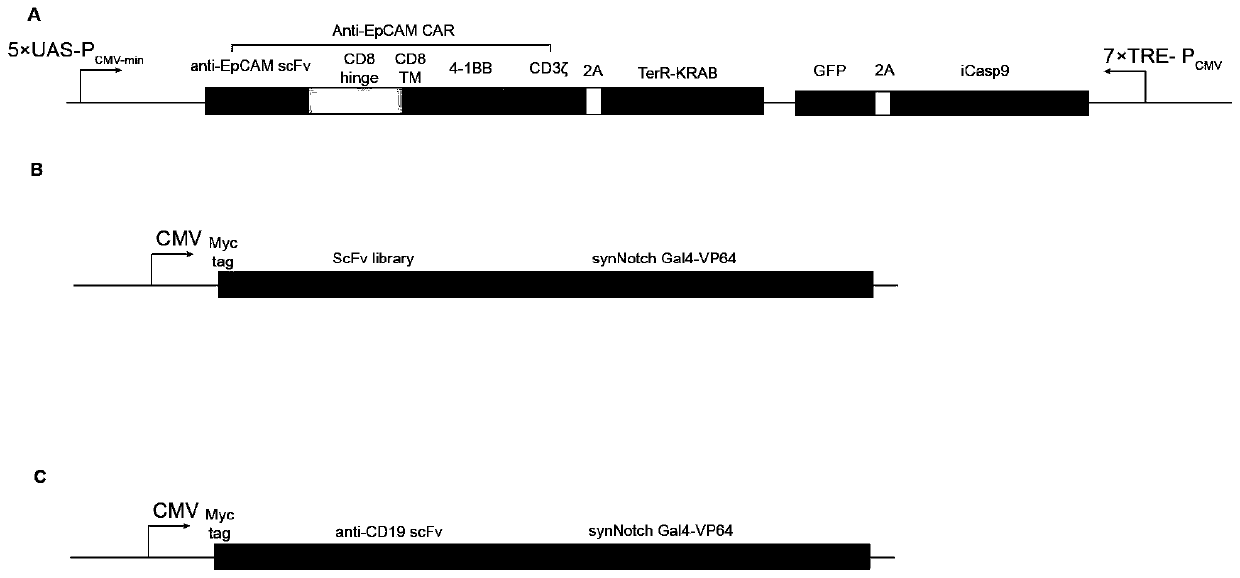
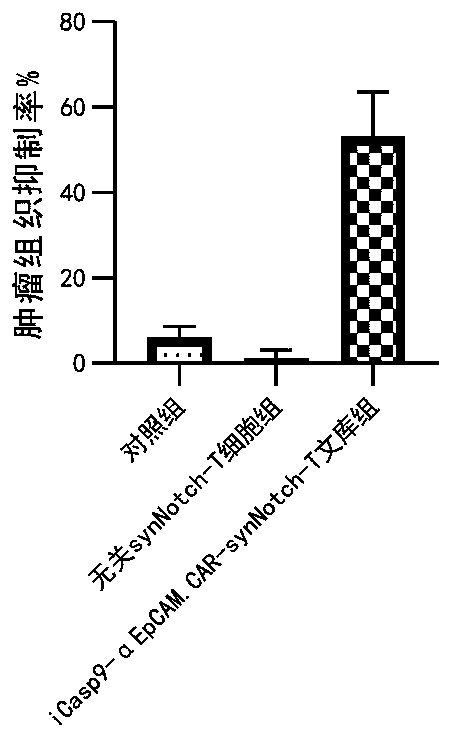
[0135] Establishment of 4T1 mouse orthotopic breast cancer model. The method of building the model is the same as the literature [Paschall A V, Liu K.JoVE2016(114):e54040.]. When the average tumor volume of the mouse reaches 100mm 3 Mice were divided into control group, irrelevant synNotch-T cell group, and KRAB-iCasp9-αEpCAM.CAR-synNotch-T library group. The receptor positivity of synNotch-T cells was normalized to 40%. The control group was treated with PBS, and the irrelevant synNotch-T cell group was treated with CD19-synNotch-T cells (gene control expression box such as figure 2 C) The dose is 5×10 6 Each cell was injected intravenously, once every 2 days, and injected 3 times. KRAB-iCasp9-αEpCAM.CAR-synNotch-T library group, the dose is 5×10 6 Cells were injected intravenously, and cells were diluted with serum-free 1640 medium for cell therapy. In the second week of treat...
Embodiment 3
[0136] Example 3. In vivo screening of a fully synthetic murine synNotch receptor cell library targeting 4T1 breast cancer
[0137] All the experimental groups in Example 2 were killed after the experiment, and the blood and tumor tissues of the mice were separated, and the CAR-positive cells of the iCasp9-αEpCAM.CAR-synNotch-T library group were isolated and cultured by flow cytometry. This completes the in vivo screening.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com