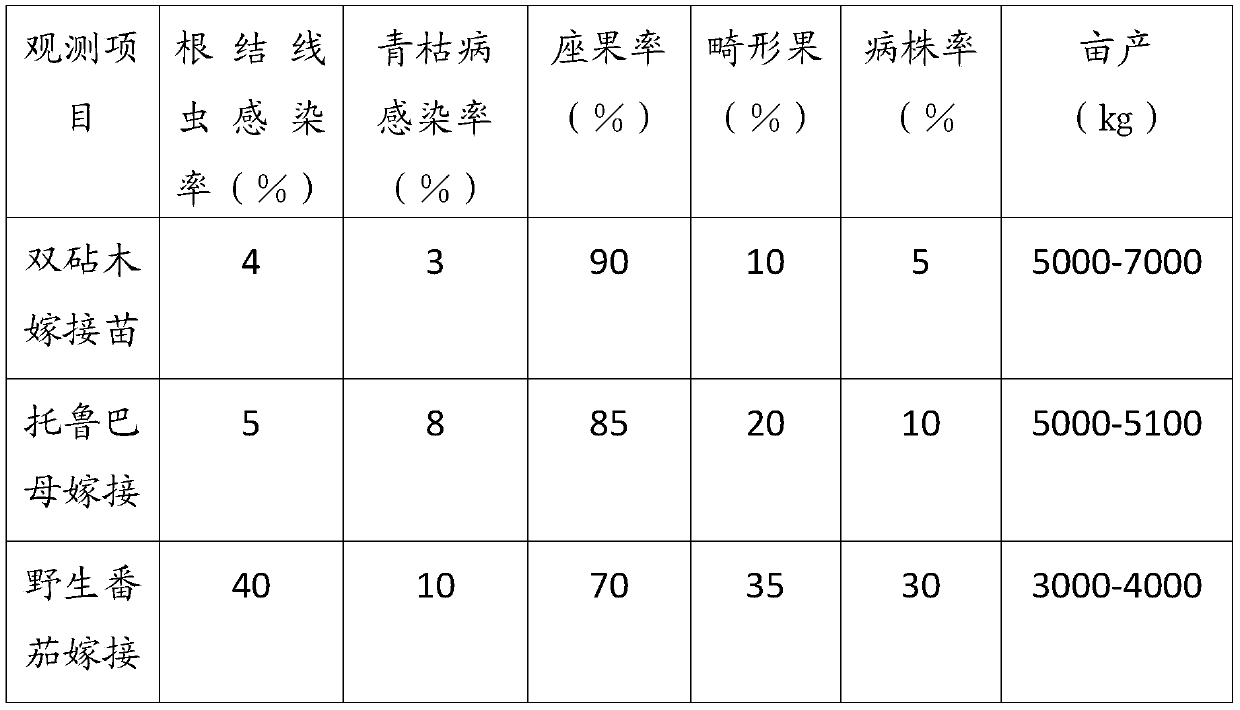
Tomato grafting method through double root stocks
A technology for tomatoes and rootstocks, applied in grafting, botanical equipment and methods, horticulture and other directions, can solve problems such as large-scale disease incidence and production loss, and achieve resistance to root-knot nematodes, prevent damage, and enhance resistance to bacterial wilt. The effect of sickness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Grafting method:
[0026] (1) Seedling cultivation: sterilized and soaked seeds of wild solanaceae and wild tomatoes and high-yield and disease-resistant tomato seeds, respectively sowed in seedling trays equipped with seedling substrates, and placed in sunny and ventilated places after sowing;
[0027] (2) When the scion grows to the sixth true leaf, it is the best time for grafting. Temperature requirement: 20°C-28°C), humidity requirement: 90%-95%.
[0028] (3) Preparation of rootstock 1: First, pull up the wild Sotoruba mother seedlings with the medium, cut obliquely from top to bottom with a knife at about 1 cm above the first true leaf, and make a tongue-shaped incision. Pick the seedlings, but keep the cotyledons;
[0029] (4) Preparation of the scion: Pull the tomato seedlings from the seedling dribbling medium, and cut obliquely from bottom to top with a knife at about 1 cm above the first true leaf to form a tongue-shaped incision;
[0030] (5) Grafting of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com