Method for treating aqueous feed by dissolved gas flotation
A dissolved air flotation, water-based technology, applied in the direction of fiber raw material treatment, water/sewage treatment, chemical instruments and methods, etc., to achieve the effect of improving scraping results and enhancing the size of flocs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0077] Preparation of Polymer Compositions Used in Examples
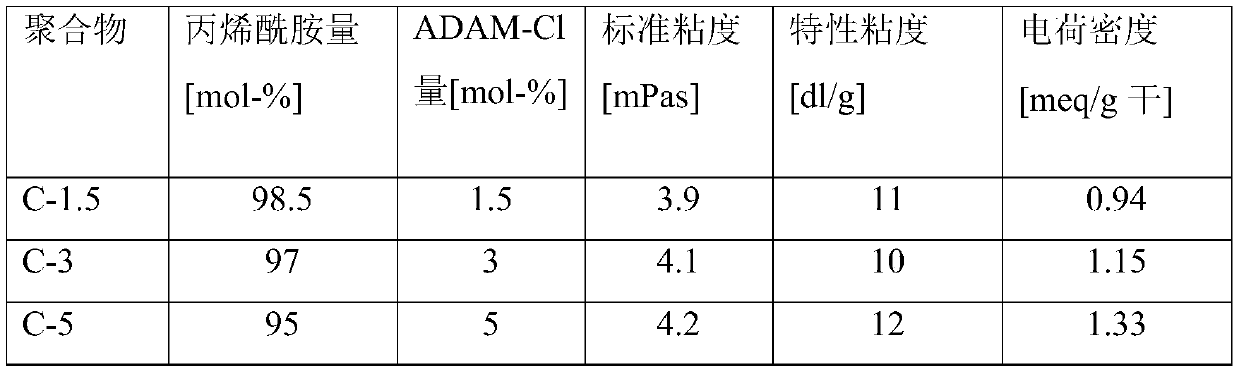
[0078] The cationic first polymer is a condensation copolymer of epichlorohydrin and dimethylamine. The amount of cationic first polymer in all final polymer compositions was 6 wt-%, based on the weight of dry polymer material of the polymer composition.
[0079] The second polymer is a copolymer of acrylamide and [2-(acryloyloxy)ethyl]trimethylammonium chloride (ADAM-Cl). Prior to polymerization of the second polymer, the monomers used, the first polymer, a pH adjuster (e.g., adipic acid, citric acid), chain transfer agent, chelating agent, redox initiator, and thermal The initiator was degassed with nitrogen. Acrylamide and ADAM-C1 monomers were added to the solution of the first polymer, the host polymer. In Table 1 the mol-% of the monomers used are given.
[0080] The resulting reaction solution was cooled at -3°C, a redox initiator was added, and radical polymerization was started. Polymerization is carri...
Embodiment 1
[0099] Treated water samples were obtained from the second loop of the old newsprint deinking process.
[0100] Deinking Facility Second Loop Disc Filter Cloudy Filtrate for Feed has the following characteristics:
[0101] 500 mg / l suspended solids, pH 7.5, ash content 55%, conductivity 2 mS / cm, cation requirement 300 μeq / l.
[0102] The dispersion water used has the following characteristics:
[0103] 150 mg / l suspended solids, pH 7.5, ash content 55%, conductivity 2 mS / cm, cation requirement 300 μeq / l.
[0104] The results in Table 4 show that using a flocculant comprising a polymer composition enables faster floc rise time in clear filtrate, reduced filtrate turbidity and reduced suspended solids, given in ppm compared to the reference composition. out (solid polymer to feed stream). Alternatively, good performance can be obtained by using lower dosages of the polymer composition. Another benefit may be increased feed capacity of the dissolved air flotation unit due to ...
Embodiment 2
[0109] Treated water samples were obtained from the first loop of a tissue washing deinking process for mixed office waste.
[0110] The scrubber filtrate used for feed has the following characteristics:
[0111] 1950 mg / l suspended solids, pH 7.7, ash content 34%, conductivity 0.64 mS / cm, cation demand 250 μeq / l.
[0112] The dispersion water used has the following characteristics:
[0113] 50 mg / l suspended solids, pH 7.5, ash content 15%, conductivity 0.62 mS / cm, cation demand 250 μeq / l.
[0114] The results in Table 5 show that using a flocculant comprising a polymer composition according to the invention enables faster rise times of flocs in clarified filtrate, reduced filtrate turbidity and reduced of suspended solids, given in ppm (solid polymer to feed stream). Alternatively, good performance can be obtained by using lower dosages of the polymer composition. Another benefit may be increased feed capacity of the dissolved air flotation unit due to faster rise times....
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Charge density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Intrinsic viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com